Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录一、Java注解(Annotation)1、jdk基本注解2、JDK元注解二、自定义注解开发1、含义2、演示三、完成切面日志操作四、完成前端响应反应总结一、Java注解(Anno
含义:Java注解是附加在代码中的一些元信息,用于一些工具在编译、 运行时进行解析和使用,起到说明、配置的功能。
@Override ——》重写
@Deprecated ——》已过时
@SuppressWarnings(value = "unchecked") ——》压制编辑器警告
含义:元注解用于修饰其他的注解(纪委:管干部的干部)
①、@Retention ——》定义注解的保留策略
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) //注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)//默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得,
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
②、@Target ——》指定被修饰的Annotation可以放置的位置(被修饰的目标)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) ——》接口、类
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) ——》属性
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) ——》方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) ——》方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) ——》构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE) ——》局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) ——》注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) ——》包
注:可以指定多个位置,如:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}),也就是此注解可以在方法和类上面使用
③、@Inherited:指定被修饰的Annotation将具有继承性
④、@Documented:指定被修饰的该Annotation可以被javadoc工具提取成文档.
使用@interface关键字, 其定义过程与定义接口非常类似, 需要注意的是:
Annotation的成员变量在Annotation定义中是以无参的方法形式来声明的, 其方法名和返回值类型定义了该成员变量的名字和类型, 而且我们还可以使用default关键字为这个成员变量设定默认值
①、枚举类:enum,指的是常量的集合
②、注解类
Ⅰ、演示@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)注解:MyAnnotation.java
package com.lv.annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//生成一个注释
@Documented
//表示当前注解可以打在什么东西上面,此处可以放在类上与方法上
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
//指定被修饰的Annotation将具有继承性
@Inherited
//注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "";
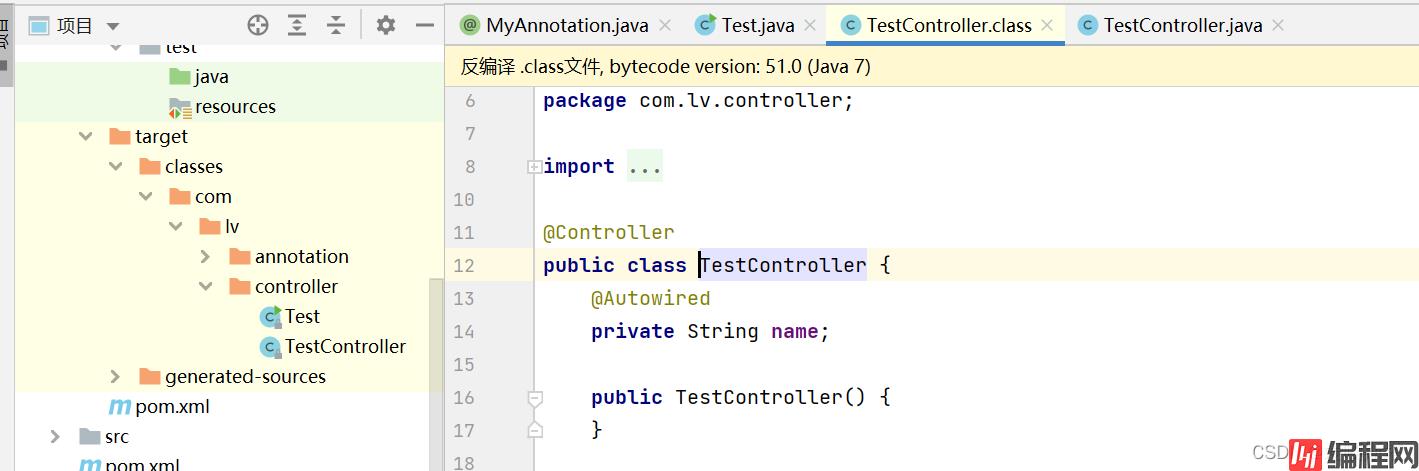
}TestController.java:注意这引用了MyAnnotation注解
package com.lv.controller;
import com.lv.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@MyAnnotation
@Controller
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private String name;
@MyAnnotation
public void aa(){
}
}运行后target层注解消失:注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
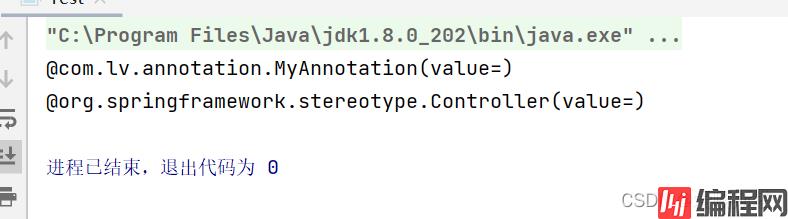
Ⅱ、MyAnnotation注解为@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)时
——注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
运行test.java:
package com.lv.controller;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 反射
for(Annotation a:TestController.class.getAnnotations()){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
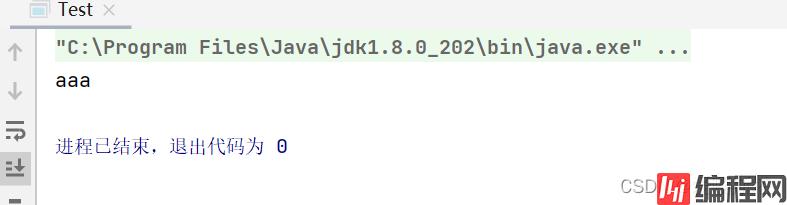
Ⅲ、取注解里的属性值
注解:MyAnnotation.java
String message() default "aaa";
拿值:
package com.lv.controller;
import com.lv.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 反射
for(Annotation a:TestController.class.getAnnotations()){
if(a instanceof MyAnnotation){
System.out.println(((MyAnnotation) a).message());
}
}
}
}
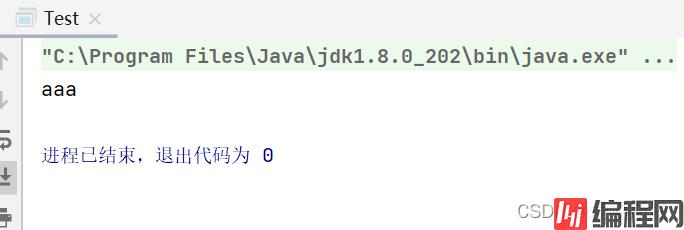
Ⅳ、判断在该类有无该注解
测试:
package com.lv.controller;
import com.lv.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 直接将MyAnnotation这注解取出
MyAnnotation myAnnotation=TestController.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
if(myAnnotation !=null){
System.out.println(myAnnotation.message());
}
}
}
当我们在写增删改的时候,会有很多冗余的代码,后期修改很麻烦,如:
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(){
System.out.println("xxx在增加");
System.out.println("增加成功");
return "yes";
}我们就可以定义aop面向切面,将前面那部分放入前置通知,后面一部分后置通知
新建切面:LogAop.java
package com.lv.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
//类不被识别,将类变成一个组件
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LogAop {
// 指定切入的规则,".."代表可有参可无参
@Pointcut("execution(* com.lv.controller.*Controller.*(..))")
public void logger(){}
// 环绕通知
@Around("logger()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point){
// 获得方法名称
Signature methodName=point.getSignature();
// 日志输出
log.info(methodName+"进来了");
Long l1=System.currentTimeMillis();
// 让方法执行
Object obj=null;
try {
obj=point.proceed(point.getArgs());
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
log.info(methodName+"走了"+"\t耗时"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-l1));
return obj;
}
}使用jrebel运行:
package com.lv.controller;
import com.lv.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.WEB.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@MyAnnotation
//直接返回JSON数据
@RestController
//返回页面跳转数据
//@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/add")
public String add(){
return "yes";
}
@RequestMapping("/del")
public String del(){
return "yes";
}
@RequestMapping("/upd")
public String upd(){
return "yes";
}
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String list(){
return "yes";
}
}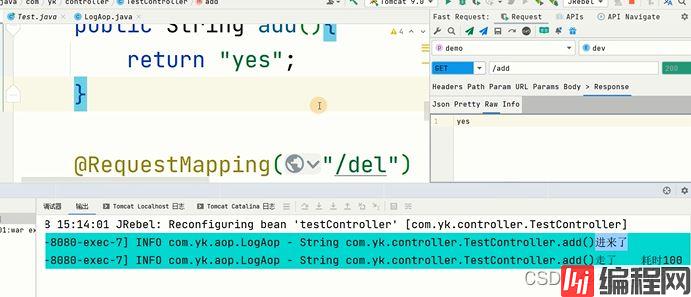
使用注解来开发aop日志:
新建注解类:MyLog.java
package com.lv.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Inherited
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyLog {
}同样在切面类中,记得改变切入的规则
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.lv.annotation.MyLog)")
需要输出日志的方法就将新建的注解加上
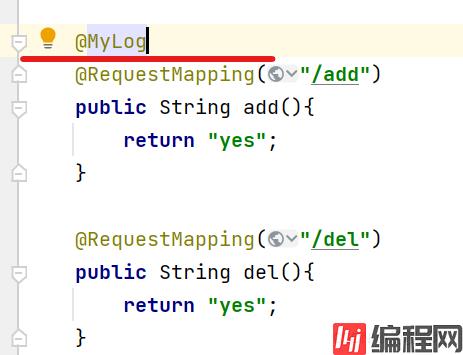
传入四个文件:
ResponseParse.java:
package com.lv.response;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.Http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseBodyAdvice;
//响应增强类
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ResponseParse implements ResponseBodyAdvice {
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Class aClass) {
//返回值决定他是否需要进入beforeBodyWrite
return methodParameter.getMethod().isAnnotationPresent(ResponseResult.class);
}
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object o, MethodParameter methodParameter, MediaType mediaType, Class aClass, ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, ServerHttpResponse serverHttpResponse) {
//更改返回值
if (o == null) {
return Result.success();
}
if (o instanceof Integer) {
return Result.failure(ResultCode.queryCode((Integer) o));
}
if (o instanceof ResultCode) {
return Result.failure((ResultCode) o);
}
if (o instanceof Result) {
return o;
}
return null;
}
}ResponseResult.java:
package com.lv.response;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface ResponseResult {
}Result.java:
package com.lv.response;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class Result<T> implements Serializable {
private final int code;
private final String message;
private final T data;
private Result(ResultCode resultCode, T data) {
this.code = resultCode.getCode();
this.message = resultCode.getMessage();
this.data = data;
}
public static Result success() {
return success(null);
}
public static <T> Result success(T data) {
return new Result(ResultCode.SUCCESS, data);
}
public static <T> Result failure(ResultCode resultCode, T data) {
return new Result(resultCode, data);
}
public static Result failure(ResultCode resultCode) {
return failure(resultCode, null);
}
}ResultCode.java:
package com.lv.response;
import java.io.Serializable;
public enum ResultCode implements Serializable {
SUCCESS(100, "成功"),
FAILURE(101, "失败"),
UNKNOWN(102, "未知响应"),
USER_ACCOUNT_NOT_FIND(201, "用户名不存在"),
USER_ACCOUNT_DISABLED(202, "该用户已被禁用"),
USER_PASSWord_NOT_MATCH(203, "该用户密码不一致"),
USER_PERMISSION_ERROR(204, "该用户不具备访问权限"),
USER_STATE_OFF_LINE(205, "该用户未登录");
private final Integer code;
private final String message;
ResultCode(Integer code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public static ResultCode queryCode(Integer code) {
for (ResultCode value : values()) {
if (code.equals(value.code)) {
return value;
}
}
return UNKNOWN;
}
}测试:
package com.lv.controller;
import com.lv.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import com.lv.annotation.MyLog;
import com.lv.response.ResponseResult;
import com.lv.response.Result;
import com.lv.response.ResultCode;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@MyAnnotation
//直接返回json数据
@RestController
//返回页面跳转数据
//@Controller
public class TestController {
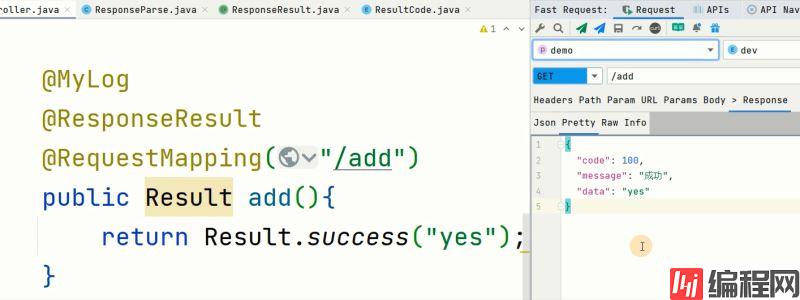
@MyLog
@ResponseResult
@RequestMapping("/add")
public Result add(){
return Result.success("yes");
}
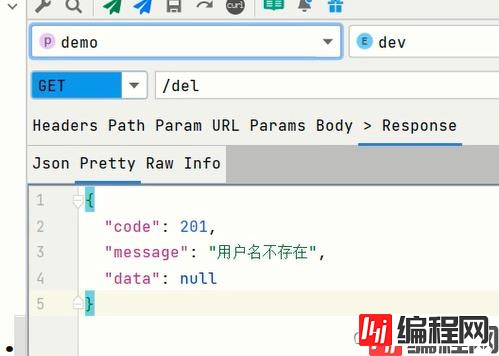
@RequestMapping("/del")
@ResponseResult
public Object del(){
return 201;
}
@RequestMapping("/upd")
@ResponseResult
public Object upd(){
return ResultCode.USER_ACCOUNT_NOT_FIND;
}
@RequestMapping("/list")
@ResponseResult
public Object list(){
return Result.success("yes");
}
}增加:
删除:
到此这篇关于SpringBoot自定义注解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot自定义注解内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: SpringBoot自定义注解开发指南
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/150498.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0