关于IPC应该不用多介绍了,Android系统中的进程之间不能共享内存,那么如果两个不同的应用程序之间需要通讯怎么办呢?比如公司的一个项目要更新,产品的需求是依附于当前项目开发
关于IPC应该不用多介绍了,Android系统中的进程之间不能共享内存,那么如果两个不同的应用程序之间需要通讯怎么办呢?比如公司的一个项目要更新,产品的需求是依附于当前项目开发一个插件,但是呢这个插件功能以及界面比较复杂,不能和当前项目在一个进程中,同时呢,还要用到当前项目中已经写好了的一些东西,那么因为新开发的依附于当前项目的插件和当前项目不是一个进程,因此不能共享内存,就出现了问题,于是,需要提供一些机制在不同进程之间进行数据通信,这个机制就是aiDL了。
一、一个android中AIDL的简单例子
假如是这样,现在有一个项目中提供了比较成熟的计算的方法,而现在我想开发一款软件其中一个模块想用到一个计算类,而我又不想重新写了,那么就可以通过AIDL实现啦。假设,已经开发完成的那个已经提供了比较成熟的计算类的程序叫AIDLCalculateDemoServer(相当于服务器),而我要写的程序叫AIDLCalculateDemoClient(相当于客户端),类似与客户端服务器模式。首先至关的看下工程结构图: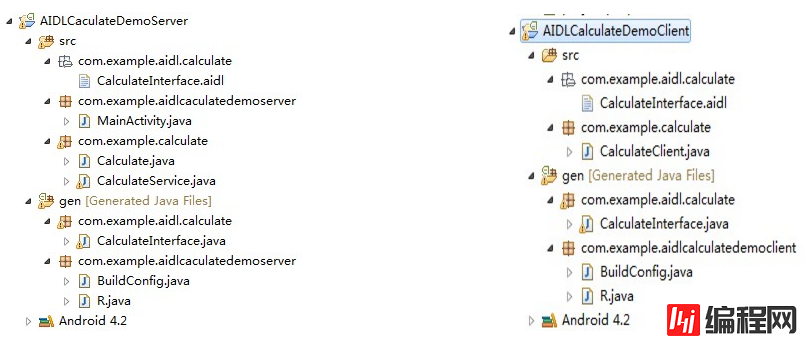
图1-1 服务器 图1-2 客户端
现在假设自己写的程序要调用服务端的运算界面,输入num1和num2,进行远程运算,调用服务端的接口,服务端运算好之后,返回结果给客户端,效果图如下:
然后来看看实现,首先需要定义AIDL接口,客户端和服务器端都要定义,并且要在同一包中,也就是图1-1和图1-2 com.example.aidl.calculate中的CalculateInterface,其中的代码如下:
package com.example.aidl.calculate;
interface CalculateInterface {
double doCalculate(double a, double b);
}
编译发现,目录结构如图1-1和图1-2中gen/com.example.aidl.calculate中多了CalculateInterface.java文件,内容如下:
package com.example.aidl.calculate;
interface CalculateInterface {
double doCalculate(double a, double b);
}定义好接口就是要看服务端和客户端的代码啦,其中服务端主要看CalculateService代码,这个一个继承Service的类,在其中对AIDL中的接口进行赋予实际意义,如下:
package com.example.calculate;
import com.example.aidl.calculate.CalculateInterface;
import com.example.aidl.calculate.CalculateInterface.Stub;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
public class CalculateService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "CalculateService";
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("onBind()");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("onCreate()");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("onStart()");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("onUnbind()");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("onDestroy()");
super.onDestroy();
}
private static void logE(String str) {
Log.e(TAG, "--------" + str + "--------");
}
private final CalculateInterface.Stub mBinder = new CalculateInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public double doCalculate(double a, double b) throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.e("Calculate", "远程计算中");
Calculate calculate = new Calculate();
double answer = calculate.calculateSum(a, b);
return answer;
}
};
}
然后可以看看,关键的服务都提供完毕,那么在客户端是怎么访问的呢,要进行绑定服务和一个ServiceConnection类完成,如下:
package com.example.calculate;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.example.aidl.calculate.CalculateInterface;
import com.example.aidlcalculatedemoclient.R;
public class CalculateClient extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "CalculateClient";
private Button btnCalculate;
private EditText etNum1;
private EditText etNum2;
private TextView tvResult;
private CalculateInterface mService;
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("disconnect service");
mService = null;
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("connect service");
mService = CalculateInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Bundle args = new Bundle();
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.calculate.CalculateService");
intent.putExtras(args);
bindService(intent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
etNum1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_num_one);
etNum2 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_num_two);
tvResult = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_result);
btnCalculate = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_cal);
btnCalculate.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logE("开始远程运算");
try {
double num1 = Double.parseDouble(etNum1.getText().toString());
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(etNum2.getText().toString());
String answer = "计算结果:" + mService.doCalculate(num1, num2);
tvResult.setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
tvResult.setText(answer);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
});
}
private void logE(String str) {
Log.e(TAG, "--------" + str + "--------");
}
}
如此一来,大功已经基本告成,最后,我们在来看看服务端的配置文件吧:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="Http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.aidlcaculatedemoserver"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.aidlcaculatedemoserver.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<cateGory android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="com.example.calculate.CalculateService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.calculate.CalculateService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
二、写AIDL注意事项
1. 客户端和服务端的AIDL接口文件所在的包必须相同
2. 需要一个Service类的配合
--结束END--
本文标题: android中的AIDL进程间通信示例
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/23425.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-21
2023-10-28
2023-10-28
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0