目录一、第一个小例子二、第二个小例子(给box1添加相对定位)三、第三个小例子(给box1,box2添加相对定位)四、解析五、扩展(在第三个例子中,假如我想获取到box3到浏览器窗口
前言:偏移量,很多动画效果的实现都是通过去改变偏移量的改变来实现的,但是你真的完全了解offsetLeft,offsetTop吗?
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; }
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
console.log('box1: '+ oBox1.offsetLeft +','+ oBox1.offsetTop);
console.log('box2: '+ oBox2.offsetLeft +','+ oBox2.offsetTop);
console.log('box3: '+ oBox3.offsetLeft +','+ oBox3.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>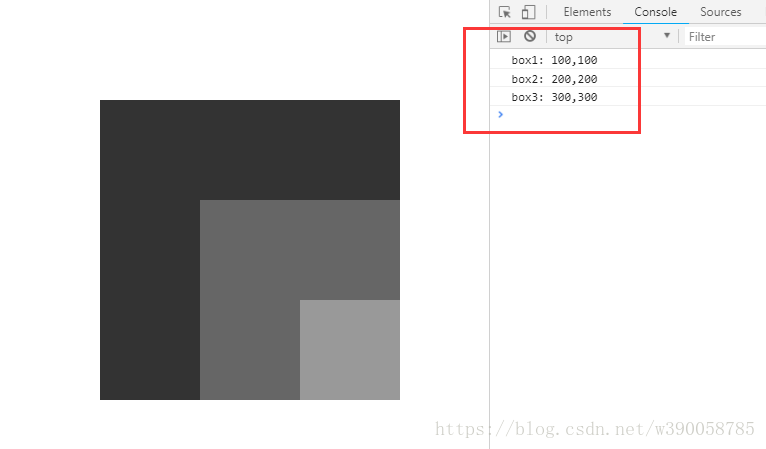
①第一个例子中,三个div的上一级的定位元素都是body,body是最外层的定位元素,三个div获取到的offsetLeft值跟offsetTop值都是相对于body的偏移量。
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; position:relative;}
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
console.log('box1: '+ oBox1.offsetLeft +','+ oBox1.offsetTop);
console.log('box2: '+ oBox2.offsetLeft +','+ oBox2.offsetTop);
console.log('box3: '+ oBox3.offsetLeft +','+ oBox3.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>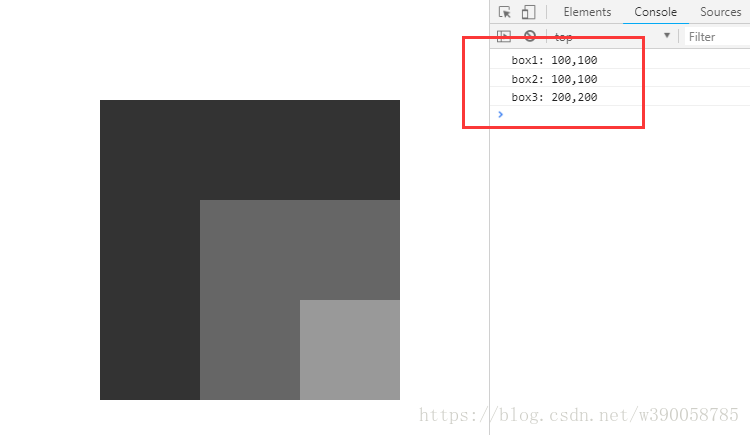
②第二个例子中,box1加上了相对定位,这时候box2,box3的上一级定位元素不再是body了,这时他们获取到的offsetLeft值跟offsetTop值都是相对于box1的偏移量。而box1的上一级定位元素还是body,所以他的偏移量还是相对于body的。
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
console.log('box1: '+ oBox1.offsetLeft +','+ oBox1.offsetTop);
console.log('box2: '+ oBox2.offsetLeft +','+ oBox2.offsetTop);
console.log('box3: '+ oBox3.offsetLeft +','+ oBox3.offsetTop);
</script>
</body>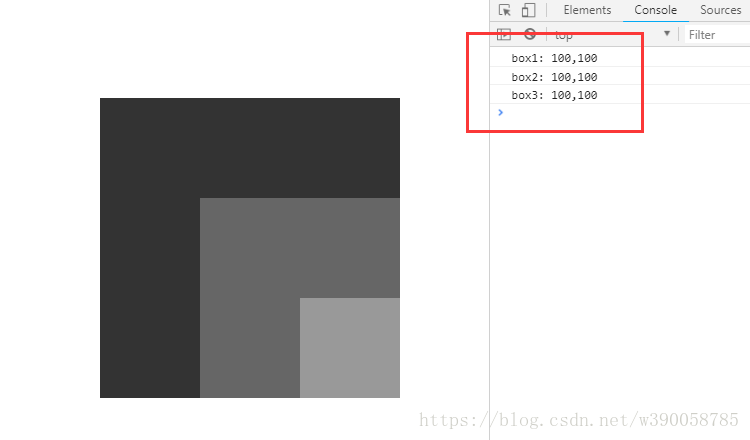
③第三个例子中,box1跟box2都加上了相对定位,这时候,box3的上一级定位元素变成是box2,box2的上一级定位元素是box1,box1的上一级定位元素还是body。所以这时候就出现了。三个div的偏移量都为100;
通过上面的三个例子不难看出,offsetLeft值跟offsetTop值的获取跟父级元素没关系,而是跟其上一级的定位元素(除position:static;外的所有定位如fixed,relative,absolute)有关系。
思路很简单,就是把元素本身的偏移量跟所有上级定位元素的偏移量都加起来就可以了,问题又来了,假如我们不知道他有几个上级定位元素呢?
其实也不难。js不但提供了offsetLeft、offsetTop方法,还提供了offsetParent(获取上一级定位元素对象)的方法。所以现在我们只需封装一个函数就可以了。
function offset(obj,direction){
//将top,left首字母大写,并拼接成offsetTop,offsetLeft
var offsetDir = 'offset'+ direction[0].toUpperCase()+direction.substring(1);
var realNum = obj[offsetDir];
var positionParent = obj.offsetParent; //获取上一级定位元素对象
while(positionParent != null){
realNum += positionParent[offsetDir];
positionParent = positionParent.offsetParent;
}
return realNum;
}运用程序中
<body>
<style>
body { margin:0; }
.box1 { width:300px; height:300px; margin:100px; background:#333; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box2 { width:200px; height:200px; margin:100px; background:#666; overflow:hidden; position:relative; }
.box3 { width:100px; height:100px; margin:100px; background:#999;}
</style>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var oBox1 = document.querySelector('.box1');
var oBox2 = document.querySelector('.box2');
var oBox3 = document.querySelector('.box3');
function offset(obj,direction){
//将top,left首字母大写,并拼接成offsetTop,offsetLeft
var offsetDir = 'offset'+ direction[0].toUpperCase()+direction.substring(1);
var realNum = obj[offsetDir];
var positionParent = obj.offsetParent; //获取上一级定位元素对象
while(positionParent != null){
realNum += positionParent[offsetDir];
positionParent = positionParent.offsetParent;
}
return realNum;
}
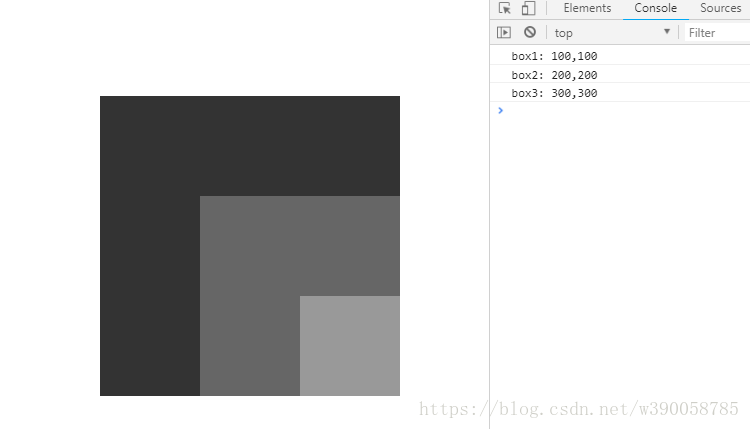
console.log('box1: '+ offset(oBox1,'left') +','+ offset(oBox1,'top'));
console.log('box2: '+ offset(oBox2,'left') +','+ offset(oBox2,'top'));
console.log('box3: '+ offset(oBox3,'left') +','+ offset(oBox3,'top'));
</script>
</body>运行结果为:
到此这篇关于全面解析javascript中offsetLeft、offsetTop的用法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关JavaScript offsetLeft offsetTop内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: 全面解析JavaScript中offsetLeft、offsetTop的用法
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/210996.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-12
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0