目录基本概念1、什么是 Module Federation?2、Module Federation核心概念3、使用案例4、插件配置工作原理1、使用MF后在构建上有什么不同?2、如何加
首先看一下官方给出的解释:
Multiple separate builds should fORM a single application. These separate builds should not have dependencies between each other, so they can be developed and deployed individually. This is often known as Micro-Frontends, but is not limited to that.
简单理解就是说 “一个应用可以由多个独立的构建组成,这些构建彼此独立没有依赖关系,他们可以独立开发、部署。这就是常被认为的微前端,但不局限于此”

MF 解决的问题其实和微前端有些类似,都是将一个应用拆分成多个子应用,每个应用都可以独立开发、部署,但是他们也有一些区别,比如微前端需要一个中心应用(简称基座)去承载子应用,而 MF 不需要,因为任何一个应用都可以作为中心应用,其次就是 MF 可以实现应用之间的依赖共享。
一个使用 ModuleFederationPlugin 构建的应用就是一个 Container,它可以加载其他的 Container,也可以被其他的 Container 加载。
从消费者和生产者的角度看 Container,Container 可以分为 Host 和 Remote,Host 作为消费者,他可以动态加载并运行其他 Remote 的代码,Remote 作为提供方,他可以暴露出一些属性、方法或组件供 Host 使用,这里要注意的一点是一个 Container 既可以作为 Host 也可以作为 Remote。
shared 表示共享依赖,一个应用可以将自己的依赖共享出去,比如 React、react-dom、mobx等,其他的应用可以直接使用共享作用域中的依赖从而减少应用的体积。
下面通过一个实例来演示一下 MF 的功能,该项目由 main 和 component 两个应用组成,component 应用会将自己的组件 exposes 出去,并将 react 和 react-dom 共享出来给 main 应用使用。
完成代码可查看这里 GitHub.com/projectCSS/…
大家最好将源代码下载下来自己跑一遍便于理解,下面展示的是 main 应用的代码,在 App 组件中我们引入了 component 应用的 Button、Dialog和 ToolTip 组件。
main/src/App.js
import React, {useState} from 'react';
import Button from 'component-app/Button';
import Dialog from 'component-app/Dialog';
import ToolTip from 'component-app/ToolTip';
const App = () => {
const [dialogVisible, setDialogVisible] = useState(false);
const handleClick = (ev) => {
setDialogVisible(true);
}
const handleSwitchVisible = (visible) => {
setDialogVisible(visible);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>Open Dev Tool And Focus On Network,checkout resources details</h1>
<p>
components hosted on <strong>component-app</strong>
</p>
<h4>Buttons:</h4>
<Button type="primary" />
<Button type="warning" />
<h4>Dialog:</h4>
<button onClick={handleClick}>click me to open Dialog</button>
<Dialog switchVisible={handleSwitchVisible} visible={dialogVisible} />
<h4>hover me please!</h4>
<ToolTip content="hover me please" message="Hello,world!" />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
效果如下:

我们看到,因为 main 应用 引用了 component 应用的组件,所以在渲染的时候需要异步去下载 component 应用的入口代码(remoteEntry)以及组件,同时只下载了 main 应用共享出去的 react 和 react-dom 这两个依赖,也就是说 component 中的组件使用的就是 main 应用 提供的依赖,这样就实现了代码动态加载以及依赖共享的功能。
为了实现联邦模块的功能,webpack 接住了一个插件 ModuleFederationPlugin,下面我们就拿上面的例子来介绍插件的配置。
component/WEBpack.config.js
const {ModuleFederationPlugin} = require('webpack').container;
const htmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './index.js',
// ...
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'component_app',
filename: 'remoteEntry.js',
exposes: {
'./Button': './src/Button.jsx',
'./Dialog': './src/Dialog.jsx',
'./LoGo': './src/Logo.jsx',
'./ToolTip': './src/ToolTip.jsx',
},
shared: { react: { singleton: true }, 'react-dom': { singleton: true } },
})
],
};
作为提供方,component 将自己的 Button、Dialog等组件暴露出去,同时将 react 和 react-dom 这两个依赖共享出去。
main/webpack.config.js
const { ModuleFederationPlugin } = require('webpack').container;
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './index.js',
// ...
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'main_app',
remotes: {
'component-app': 'component_app@Http://localhost:3001/remoteEntry.js',
},
shared: { react: { singleton: true }, 'react-dom': { singleton: true } },
})
],
};
作为消费者的 main 应用需要定义需要消费的应用的名称以及地址,同时 main 应用也将自己的 react 和 react-dom 这两个依赖共享出去。
下面来介绍几个核心的配置字段:
name 表示当前应用的别名,当作为 remote 时被 host引用时需要在路径前加上这个前缀,比如 main 中的 remote 配置:
remotes: {
'component-app': 'component_app@http://localhost:3001/remoteEntry.js',
},
路径的前缀 component_app 就是 component 应用的 name 值。
exposes 表示 remote 应用有哪些属性、方法和组件需要暴露给 host 应用使用,他是一个对象,其中 key 表示在被 host 使用的时候的相对路径,value 则是当前应用暴露出的属性的相对路径,比如在引入 Button 组件时可以这么写:
import Button from 'component-app/Button';
remote 表示当前 host 应用需要消费的 remote 应用的以及他的地址,他是一个对象,key 为对应 remote 应用的 name 值,这里要注意这个 name 不是 remote 应用中配置的 name,而是自己为该 remote 应用自定义的值,value 则是 remote 应用的资源地址。
当前应用无论是作为 host 还是 remote 都可以共享依赖,而共享的这些依赖需要通过 shared 去指定。
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'main_app',
shared: { react: { singleton: true }, 'react-dom': { singleton: true } },
})
他的配置方式有三种,具体可以查看官网,这里只介绍常用的对象配置形式,在对象中 key 表示第三方依赖的名称,value 则是配置项,常用的配置项有 singleton 和 requiredVersion。
比如 singleton 为 true 时,main 的 react 版本为 16.14.0,component 的 react 版本为 16.13.0,那么 main 和 component 将会共同使用 16.14.0 的 react 版本,也就是 main 提供的 react。
如果这时 component 的配置中将 react 的 requiredVersion 设置为 16.13.0,那么 component 将会使用 16.13.0,main 将会使用 16.14.0,相当于它们都没有共享依赖,各自下载自己的 react 版本。
在没有使用 MF 之前,component,lib 和 main 的构建如下:

使用 MF 之后构建结果如下:

对比上面两张图我们可以看出使用 MF 构建出的产物发生了变化,里面新增了 remoteEntry-chunk、shared-chunk、expose-chunk 以及 async-chunk。
其中 remoteEntry-chunk、shared-chunk 和 expose-chunk 是因为使用了 ModuleFederationPlugin 而生成的,async-chunk 是因为我们使用了异步导入 import() 而产生的。
下面我们对照着 component 的插件配置介绍一下每个 chunk 的生成。
component/wenpack.config.js
const { ModuleFederationPlugin } = require('webpack').container;
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './index.js',
// ....
plugins: [
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'component_app',
filename: 'remoteEntry.js',
exposes: {
'./Button': './src/Button.jsx',
'./Dialog': './src/Dialog.jsx',
'./Logo': './src/Logo.jsx',
'./ToolTip': './src/ToolTip.jsx',
},
shared: { react: { singleton: true }, 'react-dom': { singleton: true } },
})
]
};

main/src/bootstrap.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './app';
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'));
main/src/index.js
import('./bootstrap')
一般在我们的项目中 index.js 作为我们的入口文件里面应该存放的是 bootstrap.js 中的代码,这里却将代码单独抽离出来放到 bootstrap.js 中,同时在 index.js 中使用 import('./bootstrap') 来异步加载 bootstrap.js,这是为什么呢?
我们来看下这段代码:
main/src/App.js
import React, {useState} from 'react';
import Button from 'component-app/Button';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<Button type="primary" />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
如果 bootstrap.js 不是异步加载的话而是直接打包在 main.js 里面,那么 import Button from 'component-app/Button 就会被立即执行了,但是此时 component 的资源根本没有被下载下来,所以就会报错。

如果我们开启了 shared 功能的话,那么 import React from 'react' 这句被同步执行也会报错,因为这时候还没有初始化好共享的依赖。

所以必须把原来的入口代码放到 bootstrap.js 里面,在 index.js 中使用 import 来异步加载 bootstrap.js ,这样可以实现先加载 main.js,然后在异步加载 bootstrap_js.js(async-chunk) 的时候先加载好远程应用的资源并初始化好共享的依赖,最后再执行 bootstrap.js 模块。
我们先看一下 webpack 是怎么转换 main 应用中的导入语句: main/src/App.js
import React, {useState} from 'react';
import Button from 'component-app/Button';
import Dialog from 'component-app/Dialog';
import ToolTip from 'component-app/ToolTip';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<Button type="primary" />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
在 bootstrap_js.js 中找到编译后的结果:

我们可以看到 component-app/Button 最终会被编译成 webpack/container/remote/component-app/Button,但是 webpack/container/remote/component-app/Button 又在哪呢,我们从 main 应用的 入口文件 main.js 中可以查找到:
(() => {
var chunkMapping = {
"bootstrap_js": [
"webpack/container/remote/component-app/Button",
"webpack/container/remote/component-app/Dialog",
"webpack/container/remote/component-app/ToolTip"
]
};
var idToExternalAndNameMapping = {
"webpack/container/remote/component-app/Button": [
"default",
"./Button",
"webpack/container/reference/component-app"
],
"webpack/container/remote/component-app/Dialog": [
"default",
"./Dialog",
"webpack/container/reference/component-app"
],
"webpack/container/remote/component-app/ToolTip": [
"default",
"./ToolTip",
"webpack/container/reference/component-app"
]
};
__webpack_require__.f.remotes = (chunkId, promises) => {
if(__webpack_require__.o(chunkMapping, chunkId)) {
chunkMapping[chunkId].forEach((id) => {
var getScope = __webpack_require__.R;
if(!getScope) getScope = [];
var data = idToExternalAndNameMapping[id];
if(getScope.indexOf(data) >= 0) return;
getScope.push(data);
if(data.p) return promises.push(data.p);
var onError = (error) => {
if(!error) error = new Error("Container missing");
if(typeof error.message === "string")
error.message += '\nwhile loading "' + data[1] + '" from ' + data[2];
__webpack_require__.m[id] = () => {
throw error;
}
data.p = 0;
};
var handleFunction = (fn, arg1, arg2, d, next, first) => {
try {
var promise = fn(arg1, arg2);
if(promise && promise.then) {
var p = promise.then((result) => (next(result, d)), onError);
if(first) promises.push(data.p = p); else return p;
} else {
return next(promise, d, first);
}
} catch(error) {
onError(error);
}
}
var onExternal = (external, _, first) => (external ? handleFunction(__webpack_require__.I, data[0], 0, external, onInitialized, first) : onError());
var onInitialized = (_, external, first) => (handleFunction(external.get, data[1], getScope, 0, onFactory, first));
var onFactory = (factory) => {
data.p = 1;
__webpack_require__.m[id] = (module) => {
module.exports = factory();
}哪及了
};
handleFunction(__webpack_require__, data[2], 0, 0, onExternal, 1);
});
}
}
})();
这里的 __webpack_require__.f.remotes 就是加载远程模块的核心代码,代码中有个 chunkMapping 对象,这个对象保存的是当前应用的那些模块依赖了远程应用,idToExternalAndNameMapping 对象保存的是被依赖的远程模块的基本信息,便于后面远程请求该模块。
在加载 bootstrap_js.js 的时候必须先加载完远程应用的资源,对于我们的例子来说如果我们想要使用远程应用中的 Button、Tooltip 组件就必须先加载这个应用的资源,即 webpack/container/reference/component-app,这个从 handleFunction 方法中就可以看出来,data[2] 也就代表着 idToExternalAndNameMapping 中每一项对应的数组的第二项数据,下面我们在 main.js 中找到 webpack/container/reference/component-app:

这里会异步去加载 component 的 remoteEntry.js,也就是我们在 main 应用中配置 ModuleFederationPlugin 的时候制定的 component 远程模块的入口文件的资源地址,加载完后返回 componnet_app 这个全局变量作为 webpack/container/reference/component-app 模块的输出值,这里有两个点要注意:

但是这里我们只是获得了 componnet_app 这个远程模块的输出值,但是怎么获取到 Button、Tooltip 组件呢?
我们先来看一下 component 的 remoteEntry.js 文件:
// 组件和地址的映射表
var moduleMap = {
"./Button": () => {
return Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react-_185b"), __webpack_require__.e("src_Button_jsx")]).then(() => (() => ((__webpack_require__( "./src/Button.jsx")))));
},
"./Dialog": () => {
return Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react-_185b"), __webpack_require__.e("src_Dialog_jsx")]).then(() => (() => ((__webpack_require__( "./src/Dialog.jsx")))));
},
"./Logo": () => {
return Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react-_185b"), __webpack_require__.e("src_Logo_jsx")]).then(() => (() => ((__webpack_require__( "./src/Logo.jsx")))));
},
"./ToolTip": () => {
return Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react-_185b"), __webpack_require__.e("src_ToolTip_jsx")]).then(() => (() => ((__webpack_require__( "./src/ToolTip.jsx")))));
}
};
// 获取指定模块
var get = (module, getScope) => {
__webpack_require__.R = getScope;
getScope = (
__webpack_require__.o(moduleMap, module)
? moduleMap[module]()
: Promise.resolve().then(() => {
throw new Error('Module "' + module + '" does not exist in container.');
})
);
__webpack_require__.R = undefined;
return getScope;
};
var init = (shareScope, initScope) => {
// ...
};
// 往全局变量 component_app 上挂载get和init方法
__webpack_require__.d(exports, {
get: () => (get),
init: () => (init)
});
在 remoteEntry.js 中暴露了 get 和 init 方法,我们回到 main 应用的入口文件 main.js ,在 __webpack_require__.f.remotes 里有一个方法:
var onInitialized = (_, external, first) => (handleFunction(external.get, data[1], getScope, 0, onFactory, first));
这里 external.get 其实就是 componnet_app.get 方法,data[1] 就是我们的要加载的组件,比如执行 componnet_app.get('./Button')就可以异步获取 Button 组件。
下面总结一下整个流程,main 应用首先会去执行入口文件 main.js,然后加载 bootstrap_js 模块,判断他依赖了远程模块 webpack/container/remote/component-app/Button,...,那么先会去下载远程模块 webpack/container/remote/component-app,即 remoteEntry.js ,然后返回 component_app 这个全局变量,然后执行 component-app.get('./xxx') 去获取对应的组件,等远程应用的资源以及 bootstrap_js资源全部下载完成后再执行 bootstrap.js模块。
在 webpack 的构建中每个构建产物之间都是隔离的,而要实现依赖共享就需要打破这个隔离,这里的关键在于 sharedScope(共享作用域),我们需要在 Host 和 Remote 应用之间建立一个可共享的 sharedScope,里面包含了所有可共享的依赖,之后都按照一定的规则从这个共享作用域中获取相应的依赖。

为了探究 webpack 到底是怎么实现依赖共享的,我们首先看 main 应用的入口文件 main.js:
// 共享模块与对应加载地址映射
var moduleToHandlerMapping = {
"webpack/sharing/consume/default/react/react?ad16": () => (loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback("default", "react", [4,16,14,0], () => (Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("vendors-node_modules_react_index_js"), __webpack_require__.e("node_modules_object-assign_index_js-node_modules_prop-types_checkPropTypes_js")]).then(() => (() => (__webpack_require__( "./node_modules/react/index.js"))))))),
"webpack/sharing/consume/default/react-dom/react-dom": () => (loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback("default", "react-dom", [4,16,14,0], () => (Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("vendors-node_modules_react-dom_index_js"), __webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react")]).then(() => (() => (__webpack_require__( "./node_modules/react-dom/index.js"))))))),
"webpack/sharing/consume/default/react/react?76b1": () => (loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback("default", "react", [1,16,14,0], () => (__webpack_require__.e("vendors-node_modules_react_index_js").then(() => (() => (__webpack_require__( "./node_modules/react/index.js")))))))
};
// 当前应用依赖的共享模块
var chunkMapping = {
"bootstrap_js": [
"webpack/sharing/consume/default/react/react?ad16",
"webpack/sharing/consume/default/react-dom/react-dom"
],
"webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react": [
"webpack/sharing/consume/default/react/react?76b1"
]
};
__webpack_require__.f.consumes = (chunkId, promises) => {
if(__webpack_require__.o(chunkMapping, chunkId)) {
chunkMapping[chunkId].forEach((id) => {
// ...
try {
// 调用loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback加载共享模块,
// 并将模块信息存入共享作用域
var promise = moduleToHandlerMapping[id]();
if(promise.then) {
promises.push(installedModules[id] = promise.then(onFactory)['catch'](onError));
} else onFactory(promise);
} catch(e) { onError(e); }
});
}
}
开启 shared 功能后会多了上面这部分逻辑,其中 chunkMapping 这个对象保存的是当前应用有哪些模块依赖了共享依赖,比如 bootstrap_js 依赖了 react 和 react-dom 这两个共享依赖。
那么在加载 bootstrap_js 的时候就必须先加载完这些共享依赖,这些以来都是通过 loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback 这个方法进行加载的,下面我们来看看这个方法:
var init = (fn) => (function(scopeName, a, b, c) {
var promise = __webpack_require__.I(scopeName);
if (promise && promise.then) return promise.then(fn.bind(fn, scopeName, __webpack_require__.S[scopeName], a, b, c));
return fn(scopeName, __webpack_require__.S[scopeName], a, b, c);
});
var loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback = init((scopeName, scope, key, version, fallback) => {
if(!scope || !__webpack_require__.o(scope, key)) return fallback();
return getSingletonVersion(scope, scopeName, key, version);
});
在执行 loadSingletonVersionCheckFallback之前,首先要执行了 init方法,init 方法中又会调用 webpack_require.I ,现在就来到了共享依赖的重点:
(() => {
__webpack_require__.S = {};
var initPromises = {};
var initTokens = {};
__webpack_require__.I = (name, initScope) => {
// ...
var initExternal = (id) => {
var handleError = (err) => (warn("Initialization of sharing external failed: " + err));
try {
// 请求远程应用
var module = __webpack_require__(id);
if(!module) return;
// 调用远程应用的init方法,将当前应用的sharedScope赋值给
// 远程应用的sharedScope
var initFn = (module) => (module && module.init && module.init(__webpack_require__.S[name], initScope))
// ...
} catch(err) { handleError(err); }
}
var promises = [];
switch(name) {
case "default": {
reGISter("react-dom", "16.14.0", () => (Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("vendors-node_modules_react-dom_index_js"), __webpack_require__.e("webpack_sharing_consume_default_react_react")]).then(() => (() => (__webpack_require__( "./node_modules/react-dom/index.js"))))));
register("react", "16.14.0", () => (Promise.all([__webpack_require__.e("vendors-node_modules_react_index_js"), __webpack_require__.e("node_modules_object-assign_index_js-node_modules_prop-types_checkPropTypes_js")]).then(() => (() => (__webpack_require__( "./node_modules/react/index.js"))))));
initExternal("webpack/container/reference/component-app");
}
break;
}
};
})();
这里的 __webpack_require__.S 就是保存共享依赖的信息,它是应用间共享依赖的桥梁。在经过 register 方法后,可以看到 webpack_require.S 保存的信息:

从上面我们看到 sharedScope 中保存了 react 和 react-dom 两个共享依赖,每个共享依赖都有其对应的版本号、来源以及获取依赖的方法(get)。
接着就会调用 initExternal 方法去加载远程应用 webpack/container/reference/component-ap,即 remoteEntry.js 文件,加载完之后就会调用他的 init 方法,下面我们看看 component 的 remoteEntry.js 中的 init 方法:
// shareScope表示Host应用中的共享作用域
var init = (shareScope, initScope) => {
if (!__webpack_require__.S) return;
var name = "default"
var oldScope = __webpack_require__.S[name];
if(oldScope && oldScope !== shareScope) throw new Error("Container initialization failed as it has already been initialized with a different share scope");
// 将Host的sharedScope赋值给当前应用
__webpack_require__.S[name] = shareScope;
// 又调用当前应用的__webpack_require__.I方法去处理它的remote应用
return __webpack_require__.I(name, initScope);
};
我们看到,init 方法会使用 main 应用的 webpack_require.S 初始化 component 应用的webpack_require.S,由于是引用数据类型,所以 main 和 component 共用了一个的 sharedScope。
之后 main 应用也调用了自己的 webpack_require.I,也会 register 自己的共享依赖,最终的 webpack_require.S 如下:

因为 main 和 component 使用的是不同版本的依赖,所以最终的 sharedScope 中也会保存不同版本的依赖。
现在我们的共享作用域已经初始化好了,接下来就是每个应用根据自己的配置规则去共享作用域中获取符合规则的依赖。
总结下流程:
当应用配置了 shared 后,那么依赖了这些共享依赖的模块在加载前都会先调用 __webpack_require__.I 去初始化共享依赖,使用 __webpack_require__.S 对象来保存着每个应用的共享依赖版本信息,每个应用引用共享依赖时,会根据不同的自己配制的规则从__webpack_require__.S 获取到适合的依赖版本,__webpack_require__.S是应用间共享依赖的桥梁。
在 MF 中如果想暴露一些属性、方法或者组件,只需要在 ModuleFederationPlugin 中配置一下 exposes,host 使用的时候则需要配置一下 remotes 就可以引用远程应用暴露的值。
同时在使用的时候即可以通过 同步 的方式引用也可以通过 异步 的方式,比如在 main 应用中想引入 component 应用的 Button 组件:
同步引用:
import Button from 'component-app/Button';
页面的 chunk 会等待 component 应用的 remoteEntry.js 下载完成再执行。
异步引用
const Button = React.lazy(() => import('component-app/Button'));
页面的 chunk 下载完成之后会立即执行,然后再异步下载 component 应用的 remoteEntry.js。
虽然 MF 能够帮我们很好的解决代码共享的问题,但是新的开发模式也带来了几个问题。
由上面的例子我们知道,在 MF 中所有的公共依赖最终都会存放在一个公共作用域中,所有的应用根据自己的配置规则找到相应的依赖,这只需要我们在 ModuleFederationPlugin 中配置好 shared 字段就行了:
new ModuleFederationPlugin({
name: 'main_app',
remotes: {
'component-app': 'component_app@http://localhost:3001/remoteEntry.js',
},
shared: { react: { singleton: true }, 'react-dom': { singleton: true } },
}),
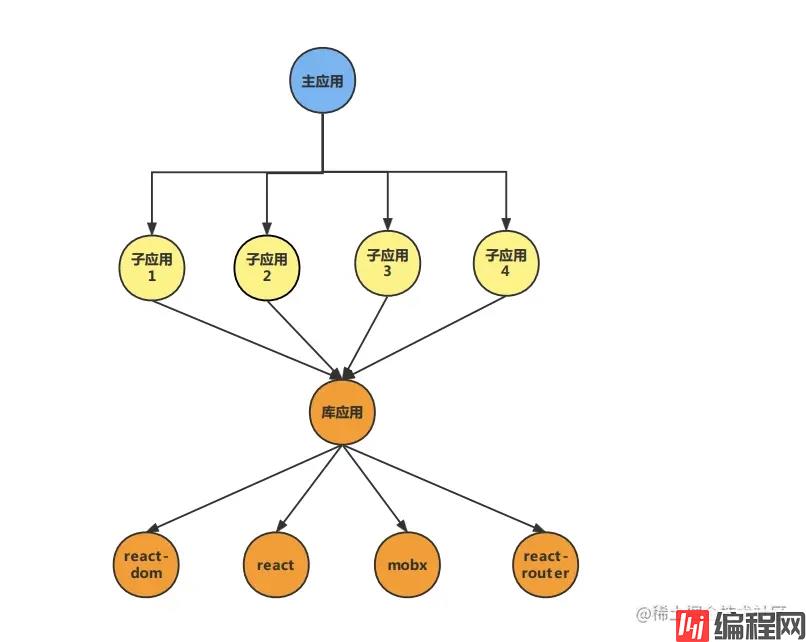
但是不仅仅是应用依赖公共依赖,公共依赖之间也会相互依赖,比如 React-Dom 依赖 React,Mobx 依赖 React 和 React-Dom,最终的结构如下所示:

这样的话也会带了一个性能问题,因为每个应用可能依赖的是不同依赖或者是相同依赖的不同版本,这样的话项目在启动的时候需要异步下载非常多的资源,这个问题其实和 vite 遇到的问题是相似的,在 vite 中每一个 import 其实就是一个请求,他们采用的方法是在预构建的时候将分散的第三方库打包在一起从而减少请求的数量。
在 MF 中我们可以新建一个库应用用于存放所有的公共依赖,这样也存在一个缺陷,就是解决不了多版本的问题,因为在库应用里装不了两个版本的依赖,如果不需要解决多版本的问题,这种方式比较好一点。
上面我们讲了 MF 的基本概念到实现原理再到应用场景,也介绍了在不同场景中存在的一些问题,下面总结下他的优缺点:
优点:
缺点:
以上就是javascript面试Module Federation实现原理详解的详细内容,更多关于JS面试Module Federation原理的资料请关注编程网其它相关文章!
--结束END--
本文标题: JavaScript面试Module Federation实现原理详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/168874.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-12
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0