目录前言效果预览代码片段styleScript核心科技获取旋转角度监听 touch 事件,通过开始、结束坐标计算移动方向根据坐标计算移动方向PC端支持 touch 事件前言 前几年实
前几年实现的一个 demo 效果,今天翻出来整理下,给大家提供类似场景参考思路。
当时的需求场景是需要 3D 展示手办模型,但是因为甲方预算有限,问有没有其他青春版(性价比)方案。
刚好那段时间在处理 lottie 动画跳帧的问题,就提出了给模型拍个全身照,旋转的时候逐帧播放达到模拟手办模型旋转的动画效果。
众所周知,帧率越高,单位时间内图像帧的个数就会越多,对应动画效果就会越流畅,当然了,对应需要准备的模型素材也就越多。

为了省流,这里没有预渲染图片资源,?可能出现转动太快,图片未加载的情况,请?等待片刻
body {
padding: 24px;
}
.model-box {
box-shadow: 0 10px 40px #00000029;
padding: 24px;
margin: 12px 0;
border-radius: 12px;
h4 {
margin: 12px 0;
}
span {
font-size: 12px;
}
}
.content-box {
position: relative;
width: 318px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid #2196f3;
border-radius: 20px;
margin: 0 auto;
img {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
pointer-events: none;
width: 100%;
transfORM: translateY(-50%);
}
}<template>
<div class="model-box">
<button @click="auto">切换为自动旋转</button>
<h4>模型展台 旋转状态:{{ autoPlay ? '自动' : '手动'}} <span>(左右滑动旋转模型)</span></h4>
<div class="content-box" ref="content">
<img
v-for="(item, i) in modelImgs"
v-show="i === activeIndex"
:key="i"
:src="item"
/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
class ModelBooth {
constructor ({ el, event, total }) {
this.$el = el
this.$event = event
this.data = {
total: total,
index: 0,
x: 0,
y: 0
}
this.change = this.throttle(this.emitChange.bind(this), 50)
}
init () {
this.addListener()
}
addListener () {
this.$el.addEventListener('touchstart', (e) => {
this.$event?.onStop()
this.data.x = e.touches[0].pageX
this.data.y = e.touches[0].pageY
}, false)
this.$el.addEventListener('touchmove', (e) => {
this.$event?.onStop()
const endx = e.changedTouches[0].pageX
const endy = e.changedTouches[0].pageY
const direction = this.calcDirection(this.data.x, this.data.y, endx, endy)
switch (direction) {
case 'left':
e.preventDefault()
this.change(false)
break
case 'right':
e.preventDefault()
this.change(true)
break
}
}, false)
}
auto ({ index }) {
this.data.index = index
this.change(true)
}
throttle (fn, time){
let t1 = 0
return function () {
let t2 = Date.now()
if (t2 - t1 > time) {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
t1 = t2
}
}
}
emitChange (type) {
let nowIndex = this.data.index
if (!type) {
++nowIndex
} else {
--nowIndex
}
const result = ((nowIndex % this.data.total) + this.data.total) % this.data.total
this.data.index = nowIndex
this.$event?.onChange(result)
}
calcDirection (startX, startY, endX, endY) {
const angX = endX - startX
const angY = endY - startY
let result = ''
// 消除噪音
if (Math.abs(angX) < 2 && Math.abs(angY) < 2) {
return result
}
const baseAngle = 45
const angle = this.calcAngle(angX, angY)
if (angle >= -(baseAngle * 3) && angle <= -baseAngle) {
result = 'left'
} else if (angle > baseAngle && angle < (baseAngle * 3)) {
result = 'right'
} else if ((angle >= (baseAngle * 3) && angle <= (baseAngle * 4)) || (angle >= -(baseAngle * 4) && angle < -(baseAngle * 3))) {
result = 'up'
} else if (angle >= -baseAngle && angle <= baseAngle) {
result = 'down'
}
return result
}
calcAngle (x, y) {
return Math.atan2(x, y) * 180 / Math.PI
}
}
export default {
data() {
return {
modelImgs: Array.from({ length: 30 }).map((v, i) => `https://hi-zhang.com/assets/zip/${i}.png`),
activeIndex: 0,
autoPlay: false,
playTn: null
}
},
mounted () {
this._modelBooth = new ModelBooth({
el: this.$refs.content,
total: this.modelImgs.length,
event: {
onChange: (index) => {
this.activeIndex = index
},
onStop: () => {
this.stop()
}
}
})
this._modelBooth.init()
},
methods: {
stop () {
this.autoPlay = false
clearInterval(this.playTn)
},
auto () {
this.stop()
this.autoPlay = true
this.playTn = setInterval(() => {
this._modelBooth.auto({
index: this.activeIndex
})
}, 50)
}
}
}
</script>相信大家已经知道如何去实现这个需求了,那么就再简单贴一下相关的核心问题处理
this.$el.addEventListener('touchstart', (e) => {
this.data.x = e.touches[0].pageX
this.data.y = e.touches[0].pageY
}, false)
this.$el.addEventListener('touchmove', (e) => {
const endx = e.changedTouches[0].pageX
const endy = e.changedTouches[0].pageY
const direction = this.calcDirection(this.data.x, this.data.y, endx, endy)
switch (direction) {
case 'left':
e.preventDefault()
this.change(false)
break
case 'right':
e.preventDefault()
this.change(true)
break
}
}, false)
calcDirection (startX, startY, endX, endY) {
const angX = endX - startX
const angY = endY - startY
let result = ''
// 消除噪音
if (Math.abs(angX) < 2 && Math.abs(angY) < 2) {
return result
}
const baseAngle = 45
const angle = this.calcAngle(angX, angY)
if (angle >= -(baseAngle * 3) && angle <= -baseAngle) {
result = 'left'
} else if (angle > baseAngle && angle < (baseAngle * 3)) {
result = 'right'
} else if ((angle >= (baseAngle * 3) && angle <= (baseAngle * 4)) || (angle >= -(baseAngle * 4) && angle < -(baseAngle * 3))) {
result = 'up'
} else if (angle >= -baseAngle && angle <= baseAngle) {
result = 'down'
}
return result
}
calcAngle (x, y) {
return Math.atan2(x, y) * 180 / Math.PI
}
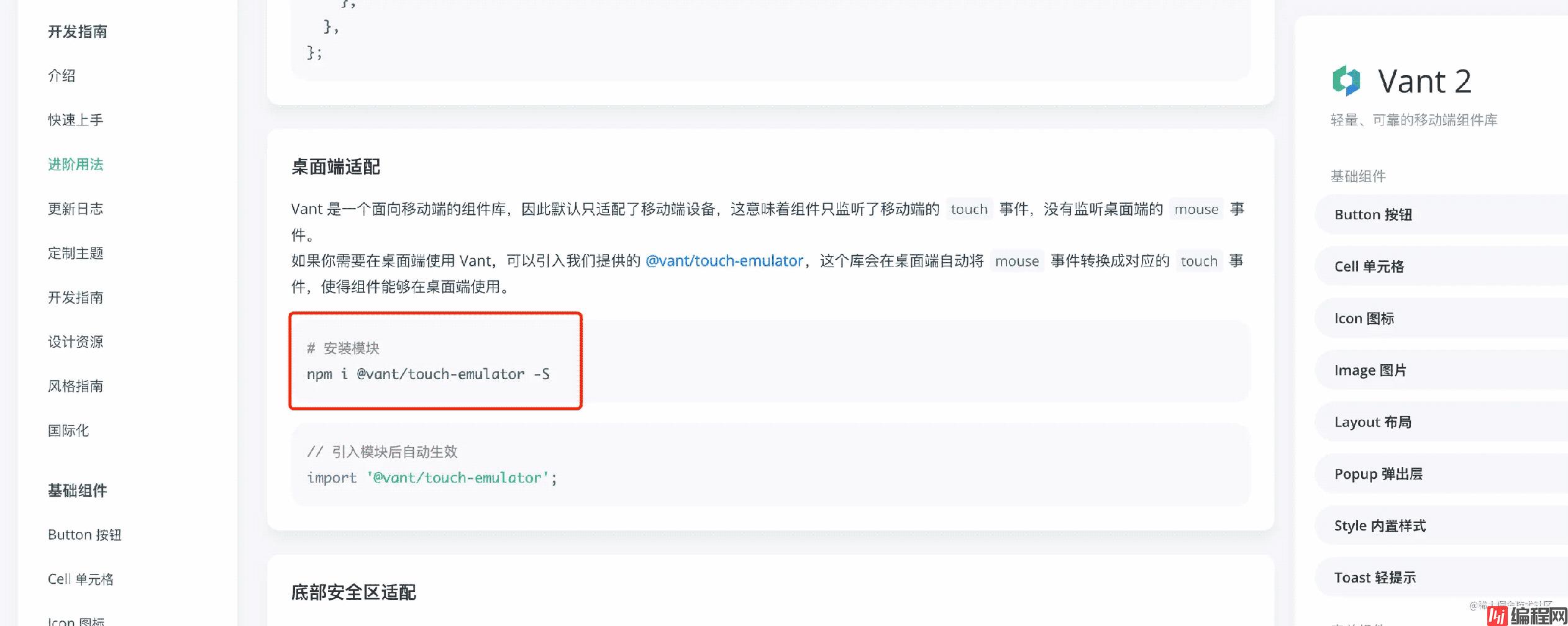
到这里你会发现PC端是不支持 touch 事件的,还好这件事不是你第一个发现的,在 VantUI 的官方示例中,有成熟的方案,相信细心的你一定注意到了。
感慨一下,输出技术文章还挺难的,组织措辞的时间比编码时间还长,这还是在原有的基础上整理,从头构建一个技术点的难度又是 up++++ ,以上就是js 实现伪3D手办模型展台示例详解的详细内容,更多关于JS 伪3D手办模型展台的资料请关注编程网其它相关文章!
--结束END--
本文标题: JS仿照3D手办模型展台实现示例详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/168212.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-12
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0