Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录yolox的decoupled head结构对于decouple head的改进特点疑问总结yolov5的head修改为decouple head yolox的decoupled
yolov5的head修改为decouple head
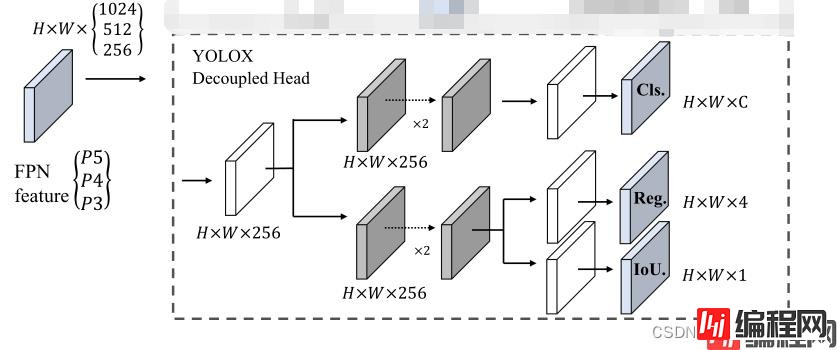
本来想将yolov5的head修改为decoupled head,与yolox的decouple head对齐,但是没注意,该成了如下结构:
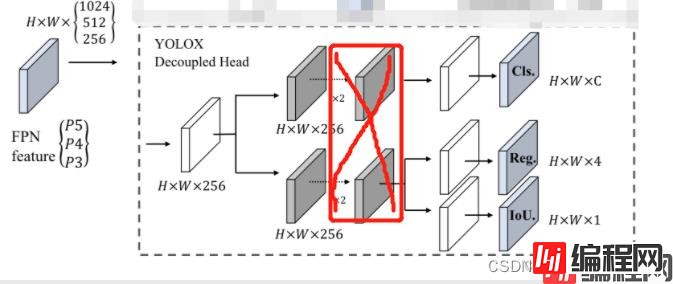
感谢少年肩上杨柳依依的指出,如还有问题欢迎指出
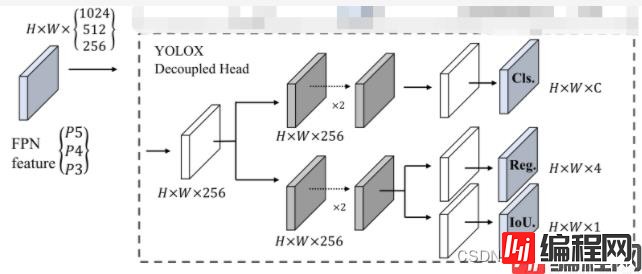
1.修改models下的yolo.py文件中的Detect
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.reGISter_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2)
# self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.m_box = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, 4 * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.m_conf = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, 1 * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.m_labels = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, self.nc * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.base_conv = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = x, out_channels = 256, ksize = 1, stride = 1) for x in ch)
self.cls_convs = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = 256, out_channels = 256, ksize = 3, stride = 1) for x in ch)
self.reg_convs = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = 256, out_channels = 256, ksize = 3, stride = 1) for x in ch)
# self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, 4 * self.na, 1) for x in ch, nn.Conv2d(x, 1 * self.na, 1) for x in ch,nn.Conv2d(x, self.nc * self.na, 1) for x in ch)
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)self.ch = ch
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
# # x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # convs
# print("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&", i)
# print(x[i].shape)
# print(self.base_conv[i])
# print("%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%")
x_feature = self.base_conv[i](x[i])
# x_feature = x[i]
cls_feature = self.cls_convs[i](x_feature)
reg_feature = self.reg_convs[i](x_feature)
# reg_feature = x_feature
m_box = self.m_box[i](reg_feature)
m_conf = self.m_conf[i](reg_feature)
m_labels = self.m_labels[i](cls_feature)
x[i] = torch.cat((m_box,m_conf, m_labels),1)
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://GitHub.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
2.在yolo.py中添加
def get_activation(name="silu", inplace=True):
if name == "silu":
module = nn.SiLU(inplace=inplace)
elif name == "relu":
module = nn.ReLU(inplace=inplace)
elif name == "lrelu":
module = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=inplace)
else:
raise AttributeError("Unsupported act type: {}".fORMat(name))
return module
class BaseConv(nn.Module):
"""A Conv2d -> Batchnorm -> silu/leaky relu block"""
def __init__(
self, in_channels, out_channels, ksize, stride, groups=1, bias=False, act="silu"
):
super().__init__()
# same padding
pad = (ksize - 1) // 2
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=ksize,
stride=stride,
padding=pad,
groups=groups,
bias=bias,
)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.act = get_activation(act, inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
# print(self.bn(self.conv(x)).shape)
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
# return self.bn(self.conv(x))
def fuseforward(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
decouple head的特点:
由于训练模型时,应该是channels = 256的地方改成了channels = x(失误),所以在decoupled head的部分参数量比yolox要大一些,以下的结果是在channels= x的情况下得出
比yolov5s参数多,计算量大,在我自己的2.5万的数据量下map提升了3%多
1.模型给出的目标cls较高,需要将conf的阈值设置较大(0.5),不然准确率较低
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.5, help='confidence threshold')
2.对于少样本的检测效果较好,召回率的提升比准确率多
3.在conf设置为0.25时,召回率比yolov5s高,但是准确率低;在conf设置为0.5时,召回率与准确率比yolov5s高
4.比yolov5s参数多,计算量大,在2.5万的数据量下map提升了3%多
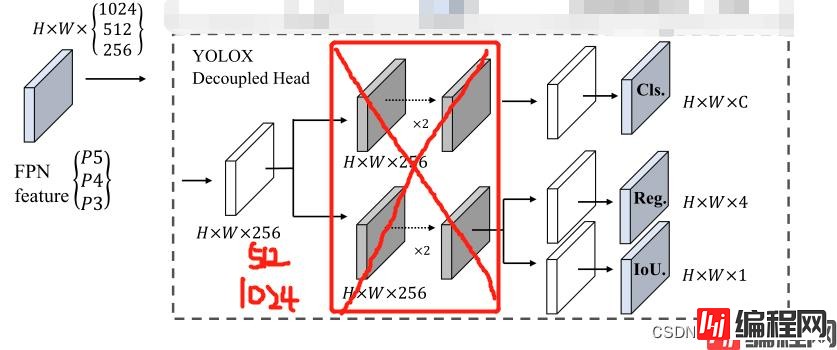
改进:
1.将红色框中的conv去掉,缩小参数量和计算量;
2.channels =256 ,512 ,1024是考虑不增加参数,不进行featuremap的信息压缩
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia Https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
1.模型给出的目标cls较高,需要将conf的阈值设置较大(0.4),不然准确率较低
2.对于少样本的检测效果较好,准确率的提升比召回率多
3. 准确率的提升比召回率多,
该改进不如上面的模型提升多,但是参数量小,计算量小少9Gflop,占用显存少
decoupled head指标提升的原因:由于yolov5s原本的head不能完全的提取featuremap中的信息,decoupled head能够较为充分的提取featuremap的信息;
为什么decoupled head目标的cls会比较高,没想明白
为什么去掉base_conv,召回率要比准确率提升少
到此这篇关于yolov5中head修改为decouple head的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关yolov5 head修改为decouple head内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: yolov5中head修改为decouple head详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/118684.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0