Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录学习前言slim是什么slim常用函数1、slim = tf.contrib.slim2、slim.create_global_step3、slim.dataset.Datase
在SSD的框架中,除去tfrecord处理是非常重要的一环之外,slim框架的使用也是非常重要的一环,于是我开始学习slim啦
slim的英文本意是苗条的意思,其实在Tensorflow中,它相当于就是tensorflow简洁版的意思,直接使用tensorflow构建代码可能会比较复杂,使用slim可以将一些tensorflow代码合并在一起,其具体作用与keras类似。
但是相比Keras,slim更加贴近tensorflow原生,其更加轻量级。
TF-Slim是tensorflow中定义、训练和评估复杂模型的轻量级库。tf-slim中的组件可以轻易地和原生tensorflow框架以及例如tf.contrib.learn这样的框架进行整合。
slim = tf.contrib.slim用于在python中声明slim框架的对象,只有完成该声明后才可以利用slim框架构建tensorflow神经网络。
该函数用于生成全局步数,全局步数可以用于学习率的自适应衰减。
该函数用于从tfrecords类型的文件中获取数据,实际上是利用该数据生成了一个数据库,在slim之后训练时可以从中获取数据用于训练。常见的Dataset使用方式如下:
slim.dataset.Dataset(
data_sources=record_path,
reader=reader,
decoder=decoder,
num_samples=num_samples,
num_classes=num_classes,
items_to_descriptions=items_to_descriptions,
labels_to_names=labels_to_names)
其中:
其内部参数具体的设置方式如下,本段代码主要是对神经网络学习tfrecords文件的写入、读取及其内容解析中MNIST数据集进行slim数据库的构建,如果不知道如何构建tfrecord文件的可以看我的上一篇博文。
def get_record_dataset(record_path,
reader=None, image_shape=[784],
num_samples=55000, num_classes=10):
if not reader:
reader = tf.TFRecordReader
keys_to_features = {
'image/encoded': tf.FixedLenFeature([784], tf.float32, default_value=tf.zeros([784], dtype=tf.float32)),
'image/class/label':tf.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64,
default_value=tf.zeros([1], dtype=tf.int64))}
items_to_handlers = {
'image': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/encoded', shape = [784]),
'label': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/class/label', shape=[])}
decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(
keys_to_features, items_to_handlers)
labels_to_names = None
items_to_descriptions = {
'image': 'An image with shape image_shape.',
'label': 'A single integer between 0 and 9.'}
return slim.dataset.Dataset(
data_sources=record_path,
reader=reader,
decoder=decoder,
num_samples=num_samples,
num_classes=num_classes,
items_to_descriptions=items_to_descriptions,
labels_to_names=labels_to_names)
本段代码分别对image和label进行读取。
其中:
上一步的函数构成的是数据库,但是如何从数据库里面读取数据我们还不知道,实际上slim已经给了一个函数作为数据库的接口,利用该函数可以生成provider,顾名思义,provider就是数据库向外界提供数据的接口。
具体使用方式如下:
# 创建provider
provider = slim.dataset_data_provider.DatasetDataProvider(
dataset,
num_readers= FLAGS.num_readers,
common_queue_capacity=20*FLAGS.batch_size,
common_queue_min=10*FLAGS.batch_size,
shuffle=True)
# 在提供商处获取image
image, label = provider.get(['image', 'label'])
其中:
在提供商处获取image后,可以利用tf.train.batch分批次获取训练集。
inputs, labels = tf.train.batch([image, label],
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size,
allow_smaller_final_batch=True,
num_threads=FLAGS.num_readers,
capacity=FLAGS.batch_size*5)
其中:
tf.train.batch具体的使用方法可以参照我的另一篇博文神经网络之批量学习tf.train.batch
此时获得的inputs, labels可以在下一步传入网络了。
slim.conv2d用于构建卷积层,其具体的代码如下:
slim.conv2d(inputs,
num_outputs,
kernel_size,
stride=1,
padding='SAME',
data_fORMat=None,
rate=1,
activation_fn=nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=None,
normalizer_params=None,
weights_initializer=initializers.xavier_initializer(),
weights_regularizer=None,
biases_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(),
biases_regularizer=None,
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
trainable=True,
scope=None)
其中参数很多,常用的参数解析如下:
slim.max_pool2d用于最大池化,具体代码如下:
slim.fully_connected(inputs,
num_outputs,
activation_fn=nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=None,
normalizer_params=None,
weights_initializer=initializers.xavier_initializer(),
weights_regularizer=None,
biases_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(),
biases_regularizer=None,
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
trainable=True,
scope=None)
其中:
slim.fully_connected用于定义全连接层。
具体代码如下:
slim.fully_connected(inputs,
num_outputs,
activation_fn=nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=None,
normalizer_params=None,
weights_initializer=initializers.xavier_initializer(),
weights_regularizer=None,
biases_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(),
biases_regularizer=None,
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
trainable=True,
scope=None)
其中:
该函数用于将训练托管给slim框架进行,非常好用,具体使用代码如下。
slim.learning.train(
train_op,
logdir=FLAGS.train_dir,
master='',
is_chief=True,
number_of_steps = FLAGS.max_number_of_steps,
log_every_n_steps = FLAGS.log_every_n_steps,
save_summaries_secs= FLAGS.save_summaries_secs,
saver=saver,
save_interval_secs = FLAGS.save_interval_secs,
session_config=config,
sync_optimizer=None)
其中:
其使用的参数较多,具体配置方式如下,并不复杂:
# 获得损失值
loss = Conv_Net.get_loss(labels=labels,logits = logits)
# 学习率多久衰减一次
decay_steps = int(dataset.num_samples / FLAGS.batch_size *
FLAGS.num_epochs_per_decay)
# 学习率指数下降
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(FLAGS.learning_rate,
global_step,
decay_steps,
FLAGS.learning_rate_decay_factor,
staircase=False,
name='exponential_decay_learning_rate')
# 优化器
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)
# 构建训练对象
train_op = slim.learning.create_train_op(loss, optimizer,
summarize_gradients=False)
# gpu使用比率
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=FLAGS.gpu_memory_fraction,
allow_growth = True)
# 参数配置
config = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=False,
gpu_options=gpu_options)
# 保存方式
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5,
keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=1.0,
write_version=2,
pad_step_number=False)
本次博文主要是利用slim构建了一个卷积神经网络,用于手写体的识别,经过20000次训练后,精度达到99.2%。
具体的代码可以点击下载
已经存储好的tfrecords也可以点击下载
整个思路的构建如下图所示:

其中:
网络构建部分的函数比较简单,主要是设计了一个对象用于读取网络结构,网络结构比较简单,其shape变化如下:
(28,28,1)=>(28,28,32)=>(14,14,32)=>(14,14,64)=>(7,7,64)=>(3136)=>(1024)=>(10)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 创建slim对象
slim = tf.contrib.slim
class Conv_Net(object):
def net(self,inputs):
with tf.variable_scope("Net"):
# 第一个卷积层
net = slim.conv2d(inputs,32,[5,5],padding = "SAME",scope = 'conv1_1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net,[2,2],stride = 2,padding = "SAME",scope = 'pool1')
# 第二个卷积层
net = slim.conv2d(net,64,[3,3],padding = "SAME",scope = 'conv2_1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net,[2,2],stride = 2,padding = "SAME",scope = 'pool2')
net = tf.reshape(net,[-1,7*7*64])
# 全连接层
layer1 = slim.fully_connected(net,512,scope = 'fully1')
layer1 = slim.dropout(layer1, 0.5, scope='dropout1')
# 这里的layer3忘了改成layer2了,试了很多结构,这个比较好
layer3 = slim.fully_connected(layer1,10,activation_fn=tf.nn.softmax,scope = 'fully3')
return layer3
def get_loss(self,labels,logits):
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels,logits = logits),name = 'loss')
tf.summary.Scalar("loss",loss)
return loss
进行模型训练CNN.py中的训练过程主要是模仿SSD的训练过程的框架构成的,如果大家对SSD有疑问,欢迎大家看我的博文SSD算法训练部分详解。
其具体的训练如下:
1、设定训练参数。
2、读取MNIST数据集。
3、建立卷积神经网络。
4、将数据集的image通过神经网络,获得prediction。
5、利用prediction和实际label获得loss。
6、利用优化器完成梯度下降并保存模型。
具体代码如下,其中所有执行步骤已经利用如下格式隔开:
#############################################################
# XXXXXXXXXXXXX
#############################################################
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from nets import Net
flags = tf.app.flags
#############################################################
# 设置训练参数
#############################################################
# =========================================================================== #
# General Flags.
# =========================================================================== #
# train_dir用于保存训练后的模型和日志
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string(
'train_dir', './logs',
'Directory where checkpoints and event logs are written to.')
# num_readers是在对数据集进行读取时所用的平行读取器个数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer(
'num_readers', 4,
'The number of parallel readers that read data from the dataset.')
# 在进行训练batch的构建时,所用的线程数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer(
'num_preprocessing_threads', 4,
'The number of threads used to create the batches.')
# 每十步进行一次log输出,在窗口上
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer(
'log_every_n_steps', 100,
'The frequency with which logs are print.')
# 每150秒存储一次记录
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer(
'save_summaries_secs', 150,
'The frequency with which summaries are saved, in seconds.')
# 每150秒存储一次模型
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer(
'save_interval_secs', 150,
'The frequency with which the model is saved, in seconds.')
# 可以使用的gpu内存数量
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'gpu_memory_fraction', 0.6, 'GPU memory fraction to use.')
# =========================================================================== #
# Learning Rate Flags.
# =========================================================================== #
# 学习率衰减的方式,有固定、指数衰减等
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string(
'learning_rate_decay_type',
'exponential',
'Specifies how the learning rate is decayed. One of "fixed", "exponential",'
' or "polynomial"')
# 初始学习率
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float('learning_rate', 0.001, 'Initial learning rate.')
# 结束时的学习率
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'end_learning_rate', 0.0001,
'The minimal end learning rate used by a polynomial decay learning rate.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'label_smoothing', 0.0, 'The amount of label smoothing.')
# 学习率衰减因素
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'learning_rate_decay_factor', 0.94, 'Learning rate decay factor.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'num_epochs_per_decay', 2.0,
'Number of epochs after which learning rate decays.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'moving_average_decay', None,
'The decay to use for the moving average.'
'If left as None, then moving averages are not used.')
# adam参数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'adam_beta1', 0.9,
'The exponential decay rate for the 1st moment estimates.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float(
'adam_beta2', 0.999,
'The exponential decay rate for the 2nd moment estimates.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float('opt_epsilon', 1.0, 'Epsilon term for the optimizer.')
# =========================================================================== #
# Dataset Flags.
# =========================================================================== #
# 数据集目录
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string(
'dataset_dir', './record/output.tfrecords', 'The directory where the dataset files are stored.')
# 每一次训练batch的大小
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer(
'batch_size', 100, 'The number of samples in each batch.')
# 最大训练次数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('max_number_of_steps', 20000,
'The maximum number of training steps.')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
def get_record_dataset(record_path,
reader=None, image_shape=[784],
num_samples=55000, num_classes=10):
if not reader:
reader = tf.TFRecordReader
keys_to_features = {
'image/encoded': tf.FixedLenFeature([784], tf.float32, default_value=tf.zeros([784], dtype=tf.float32)),
'image/class/label':tf.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64,
default_value=tf.zeros([1], dtype=tf.int64))}
items_to_handlers = {
'image': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/encoded', shape = [784]),
'label': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/class/label', shape=[])}
decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(
keys_to_features, items_to_handlers)
labels_to_names = None
items_to_descriptions = {
'image': 'An image with shape image_shape.',
'label': 'A single integer between 0 and 9.'}
return slim.dataset.Dataset(
data_sources=record_path,
reader=reader,
decoder=decoder,
num_samples=num_samples,
num_classes=num_classes,
items_to_descriptions=items_to_descriptions,
labels_to_names=labels_to_names)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 打印日志
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.DEBUG)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# 最大世代
MAX_EPOCH = 50000
# 创建slim对象
slim = tf.contrib.slim
# 步数
global_step = slim.create_global_step()
#############################################################
# 读取MNIST数据集
#############################################################
# 读取数据集
dataset = get_record_dataset(FLAGS.dataset_dir,num_samples = 55000)
# 创建provider
provider = slim.dataset_data_provider.DatasetDataProvider(
dataset,
num_readers= FLAGS.num_readers,
common_queue_capacity=20*FLAGS.batch_size,
common_queue_min=10*FLAGS.batch_size,
shuffle=True)
# 在提供商处获取image
image, label = provider.get(['image', 'label'])
# 每次提取100个手写体
inputs, labels = tf.train.batch([image, label],
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size,
allow_smaller_final_batch=True,
num_threads=FLAGS.num_readers,
capacity=FLAGS.batch_size*5)
#############################################################
#建立卷积神经网络,并将数据集的image通过神经网络,获得prediction。
#############################################################
inputs = tf.cast(inputs,tf.float32)
inputs_reshape = tf.reshape(inputs,[-1,28,28,1])
Conv_Net = Net.Conv_Net()
logits = Conv_Net.net(inputs_reshape)
#############################################################
# 利用prediction和实际label获得loss。
#############################################################
# 获得损失值
loss = Conv_Net.get_loss(labels = labels,logits = logits)
decay_steps = int(dataset.num_samples / FLAGS.batch_size *
FLAGS.num_epochs_per_decay)
# 学习率指数下降
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(FLAGS.learning_rate,
global_step,
decay_steps,
FLAGS.learning_rate_decay_factor,
staircase=False,
name='exponential_decay_learning_rate')
#############################################################
# 利用优化器完成梯度下降并保存模型。
#############################################################
# 优化器
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)
# 构建训练对象
train_op = slim.learning.create_train_op(loss, optimizer,
summarize_gradients=False)
# gpu使用比率
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=FLAGS.gpu_memory_fraction,
allow_growth = True)
# 参数配置
config = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=False,
gpu_options=gpu_options)
# 保存方式
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5,
keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=1.0,
write_version=2,
pad_step_number=False)
# 托管训练
slim.learning.train(
train_op,
logdir=FLAGS.train_dir,
master='',
is_chief=True,
number_of_steps = FLAGS.max_number_of_steps,
log_every_n_steps = FLAGS.log_every_n_steps,
save_summaries_secs= FLAGS.save_summaries_secs,
saver=saver,
save_interval_secs = FLAGS.save_interval_secs,
session_config=config,
sync_optimizer=None)
在完成数据集的构建后,直接运行CNN.py就可以开始训练。训练的graph如下:
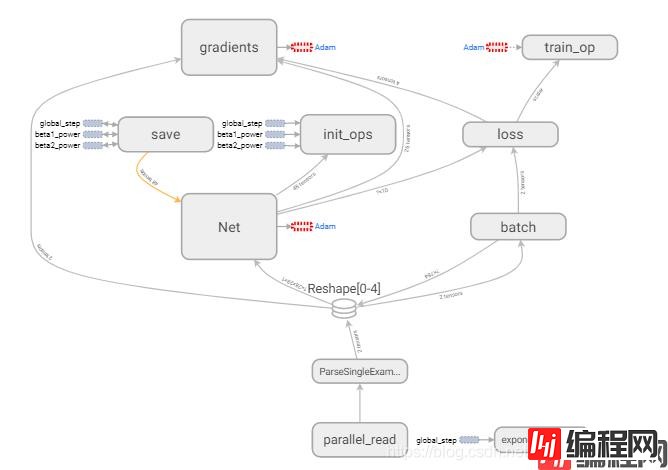
Net的内容为(这里的layer3忘了改成layer2了,试了很多结构,这个比较好):

输出的logs为:
……
INFO:tensorflow:global step 17899: loss = 1.4701 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 17999: loss = 1.4612 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18099: loss = 1.4612 (0.051 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18199: loss = 1.4612 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18299: loss = 1.4668 (0.048 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18399: loss = 1.4615 (0.039 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18499: loss = 1.4612 (0.050 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18599: loss = 1.4812 (0.050 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18699: loss = 1.4612 (0.060 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18799: loss = 1.4712 (0.050 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18899: loss = 1.4712 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 18999: loss = 1.4716 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19199: loss = 1.4613 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19299: loss = 1.4619 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19399: loss = 1.4732 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19499: loss = 1.4612 (0.050 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19599: loss = 1.4614 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19699: loss = 1.4612 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19799: loss = 1.4612 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19899: loss = 1.4612 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:global step 19999: loss = 1.4612 (0.040 sec/step)
INFO:tensorflow:Stopping Training.
INFO:tensorflow:Finished training! Saving model to disk.
以上就是Python神经网络使用slim函数训练保存模型的详细内容,更多关于slim函数训练保存模型的资料请关注编程网其它相关文章!
--结束END--
本文标题: python神经网络slim常用函数训练保存模型
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/117687.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0