前言 adb shell是Android开发者常用的一个工具,它可以让我们在电脑上通过USB或网络连接到Android设备,并执行一些命令或操作。但是,有时候我们可能不想让任何人都能随意使用adb s
adb shell是Android开发者常用的一个工具,它可以让我们在电脑上通过USB或网络连接到Android设备,并执行一些命令或操作。但是,有时候我们可能不想让任何人都能随意使用adb shell,而是需要一些授权或验证的机制,以保护我们的设备和数据。本文将介绍如何在基于rockchip rk3568 android11的系统上实现自定义的adb shell授权功能。
要实现自定义的adb shell授权功能,我们需要修改adb daemon的代码(),让它在接收到shell服务请求时,先检查是否已经通过了授权,如果没有,就返回一个错误信息,并提示用户输入一个随机生成的授权码。用户可以通过adb shell auth 命令来输入授权码,如果正确,就可以正常使用adb shell,否则就会被拒绝。
system/core/adb/client/commandline.cpp 这里是adb client端的,改这里没有 最开始走弯路.
system/core/adb/daemon/file_sync_service.cpp 这里是adb push/pull 逻辑,后面再研究
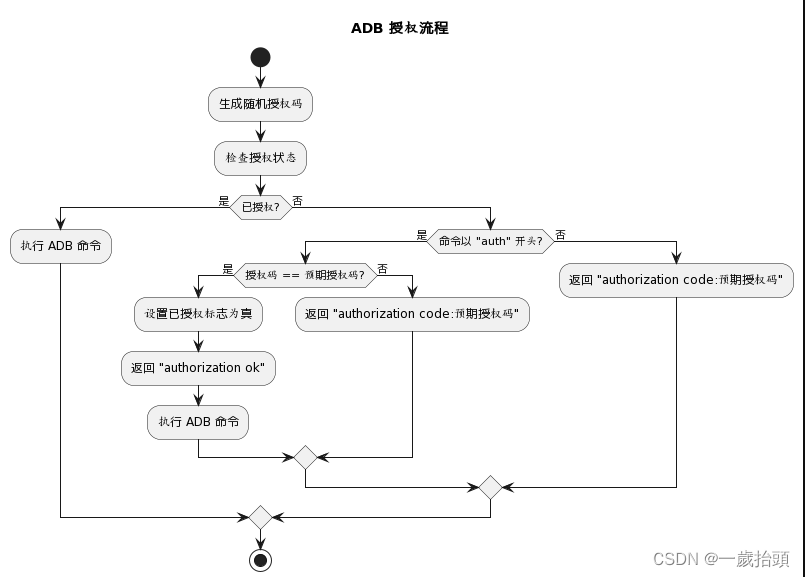
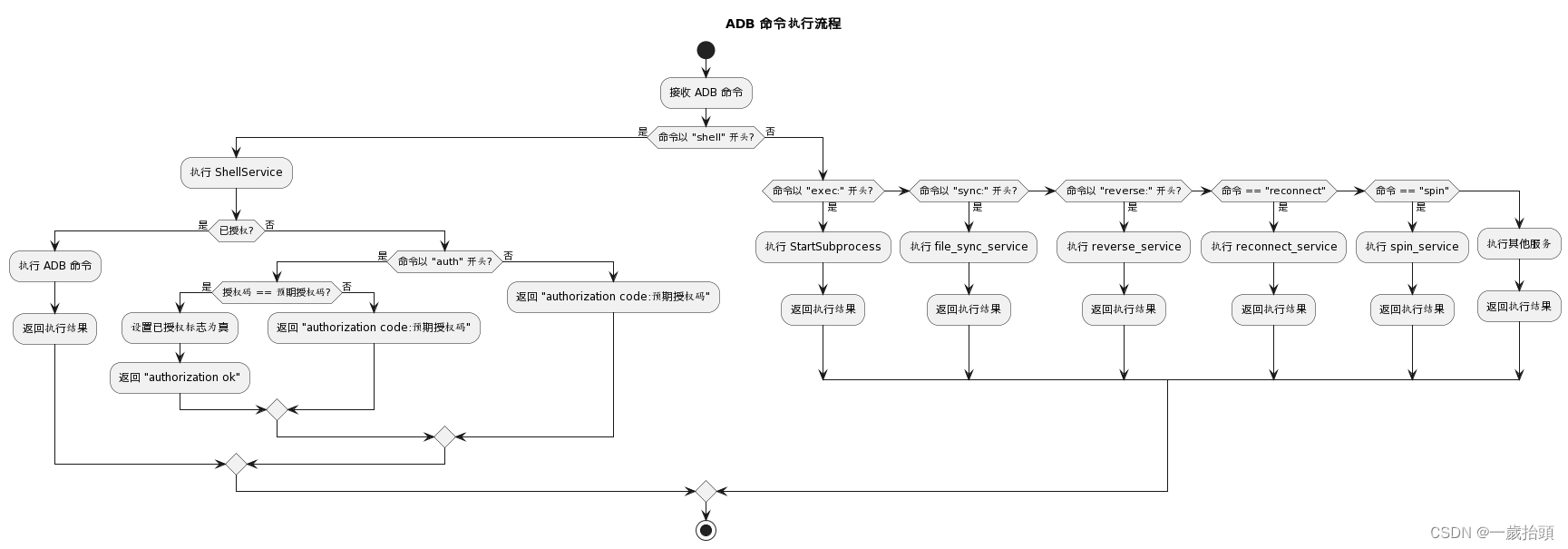
需要修改system/core/adb/daemon/services.cpp文件中的ShellService函数,增加一个CheckAuthorization函数来检查授权状态和处理授权码输入。CheckAuthorization函数的实现如下:
bool authorized = false;std::string GenerateRandomCode() { static std::string expected_code; // 在启动时生成随机码。 if (!expected_code.empty()) { return expected_code; } std::random_device rd; std::mt19937 gen(rd()); std::unifORM_int_distribution<> dis(0, 35); for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { int random = dis(gen); if (random < 10) { expected_code += '0' + random; } else { expected_code += 'a' + random - 10; } } return expected_code;}unique_fd CheckAuthorization(std::string_view command, SubprocessProtocol protocol) { std::string expected_code = GenerateRandomCode(); if (command.starts_with("auth")) { std::string auth_code = std::string(command.substr(strlen("auth"))); auth_code = android::base::Trim(auth_code); // remove leading/trailing whitespace if (auth_code == expected_code) { authorized = true; std::string message = "authorization ok"; return ReportError(protocol, message); } else { std::string message = android::base::StringPrintf("authorization code:%s", expected_code.c_str()); return ReportError(protocol, message); } } if (!authorized) { std::string message = android::base::StringPrintf("authorization code:%s", expected_code.c_str()); return ReportError(protocol, message); } return unique_fd{}; // Return an invalid fd if authorized}在ShellService函数中,在解析服务参数和命令之后,调用CheckAuthorization函数,并根据返回值判断是否继续执行shell服务:
unique_fd ShellService(std::string_view args, const atransport* transport) { size_t delimiter_index = args.find(':'); if (delimiter_index == std::string::npos) { LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid shell service arguments: " << args; return unique_fd{}; } // TODO: android::base::Split(const std::string_view&, ...) std::string service_args(args.substr(0, delimiter_index)); std::string command(args.substr(delimiter_index + 1)); // Defaults: // PTY for interactive, raw for non-interactive. // No protocol. // $TERM set to "dumb". SubprocessType type(command.empty() ? SubprocessType::kPty : SubprocessType::kRaw); SubprocessProtocol protocol = SubprocessProtocol::kNone; std::string terminal_type = "dumb"; for (const auto& arg : android::base::Split(service_args, ",")) { if (arg == "raw") { type = SubprocessType::kRaw; } else if (arg == "pty") { type = SubprocessType::kPty; } else if (arg == "v2") { protocol = SubprocessProtocol::kV2; } else if (arg.starts_with("TERM=")) { terminal_type = arg.substr(strlen("TERM=")); } else if (!arg.empty()) { // This is not an error to allow for future expansion. LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring unknown shell service argument: " << arg; } } unique_fd auth_fd = CheckAuthorization(command, protocol); if (auth_fd.get() != -1) { return auth_fd; } return StartSubprocess(command, terminal_type.c_str(), type, protocol);}还需要修改system/core/adb/Android.bp文件,去掉-Wexit-time-destructors的编译选项,因为我们使用了一个静态变量来存储授权码,它会在程序退出时触发析构函数,导致编译报错:
cc_defaults { name: "adb_defaults", cflags: [ "-Wall", "-Wextra", "-Werror",- "-Wexit-time-destructors",+ "-Wno-exit-time-destructors", "-Wno-unused-parameter", "-Wno-missing-field-initializers", "-Wthread-safety",修改完代码后,我们重新编译并刷入系统,然后连接设备并尝试使用adb shell。我们可以看到,如果没有输入正确的授权码,就会收到一个错误信息,并提示我们输入授权码。如果输入正确的授权码,就可以正常使用adb shell。测试结果如下:
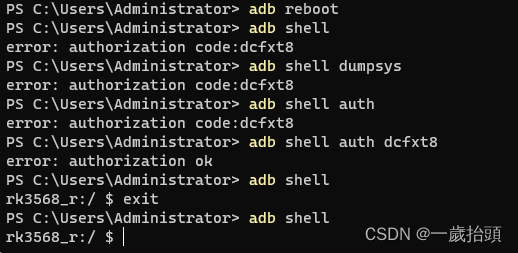
本文介绍了如何在基于rockchip rk3568 android11的系统上实现自定义的adb shell授权功能,主要是通过修改adb daemon的代码,增加一个CheckAuthorization函数来检查授权状态和处理授权码输入。这样可以提高设备的安全性,防止未经授权的人员使用adb shell。
这只是一个简单的示例,实际应用中可能需要更复杂的逻辑和更安全的机制。希望本文对你有所帮助。
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/SHH_1064994894/article/details/132101602
--结束END--
本文标题: Android系统 adb shell auth授权使用
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/429938.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-21
2023-10-28
2023-10-28
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0