今天小编给大家分享一下javascript中React面向组件编程实例代码分析的相关知识点,内容详细,逻辑清晰,相信大部分人都还太了解这方面的知识,所以分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后有所收获,下面我们一起来了解一下吧。
今天小编给大家分享一下javascript中React面向组件编程实例代码分析的相关知识点,内容详细,逻辑清晰,相信大部分人都还太了解这方面的知识,所以分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后有所收获,下面我们一起来了解一下吧。
表单的组件分类:
受控组件
非受控组件
多数情况下,推荐使用受控组件实现表单。在受控组件中,表单数据由组件控制。
另外一种是非受控组件,这种方式下表单组件由DOM自身控制。
受控组件通过 props 获取其当前值,并通过回调函数(比如 onChange )通知变化
表单状态发生变化时,都会通知 React,将状态交给 React 进行处理,比如可以使用 useState 存储
受控组件中,组件渲染出的状态与它的 value 或 checked 属性相对应
受控组件会更新 state 的流程
class Login extends React.Component { // 初始化状态 state = { username:'', // 用户名 passWord:'', // 密码 } // 保存用户名到状态中 saveUsername=(event)=>{ this.setState({username:event.target.value}) } // 保存密码到状态中 savePassword=(event)=>{ this.setState({password:event.target.value}) } // 表单提交的回调 handleSubmit=(event)=>{ event.preventDefault(); // 阻止默认事件 let {username,password} = this.state alert(`你输入的用户名是${username},密码是${password}`) } render(){ return( <div> <fORM action="https://www.baidu.com/" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}> 用户名:<input type="text" onChange={this.saveUsername} name="username" /> 密码:<input type="text" onChange={this.savePassword} name="password" /> <button type="submit">登录</button> </form> </div> ) }}非受控组件将数据存储在 DOM 中,而不是组件内,这比较类似于传统的 html 表单元素。
非受控组件的值不受组件自身的 state 和 props 控制
非受控组件使用 ref 从 DOM 中获取元素数据
class Login extends React.Component { handleSubmit=(event)=>{ // console.log(e>=event) event.preventDefault(); // 阻止默认事件 let {username,password} = this alert(`你输入的用户名是${username.value},密码是${password.value}`) } render(){ return( <div> <form action="Https://www.baidu.com/" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}> 用户名:<input type="text" ref={c=>this.username = c} name="username" /> 密码:<input type="text" ref={c=>this.password = c} name="password" /> <button type="submit">登录</button> </form> </div> ) }}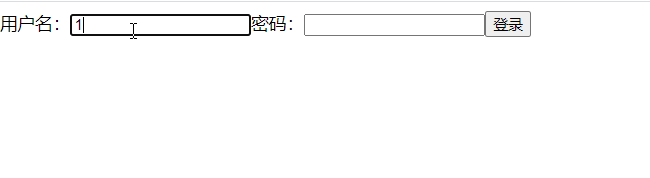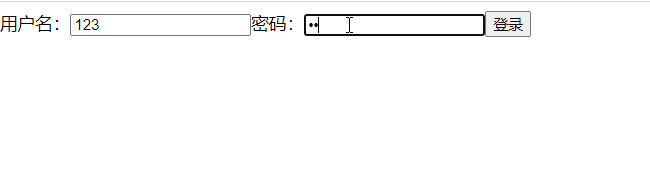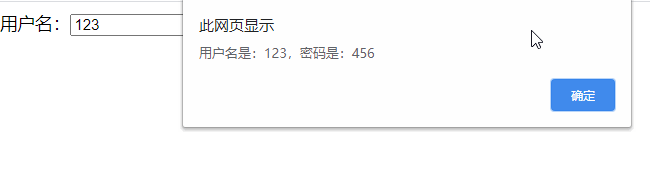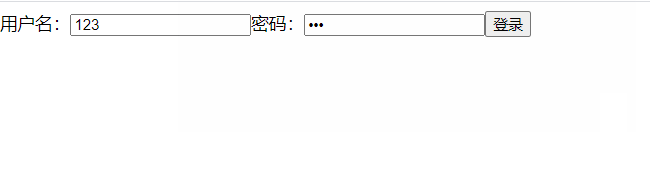
React 中的组件分为受控组件和非受控组件
受控组件的两个要点:
组件的 value 属性与 React 中的状态绑定
组件内声明了 onChange 事件处理 value 的变化
非受控组件更像是传统的 HTML 表单元素,数据存储在 DOM 中,而不是组件内部,获取数据的方式是通过 ref 引用
一些建议:
尽可能使用受控组件
受控组件是将状态交由 React 处理,可以是任何元素,不局限于表单元素
对于有大量表单元素的页面,使用受控组件会使程序变得繁琐难控,此时使用非受控组件更为明智
在受控组件中,数据流是单向的( state 是变化来源),因此在改变 state 时都应该使用 setState ,而不要强制赋值
Refs 不能用于函数式组件,因为函数式组件没有实例
在函数式组件内部,是可以使用 Refs 的
所谓的React生命周期,就是指组件从被创建出来,到被使用,最后被销毁的这么一个过程;
而在这个过程中,React提供了我们会自动执行的不同的钩子函数,我们称之为生命周期函数;
组件的生命周期大致分为三个阶段:组件挂载阶段,组件更新阶段,组件销毁卸载阶段
react在版本16.3前后存在两套生命周期,16.3之前为旧版,之后则是新版,虽有新旧之分,但主体上大同小异。
组件从创建到死亡它会经历一些特定的阶段。
React组件中包含一系列勾子函数(生命周期回调函数), 会在特定的时刻调用。
我们在定义组件时,会在特定的生命周期回调函数中,做特定的工作。
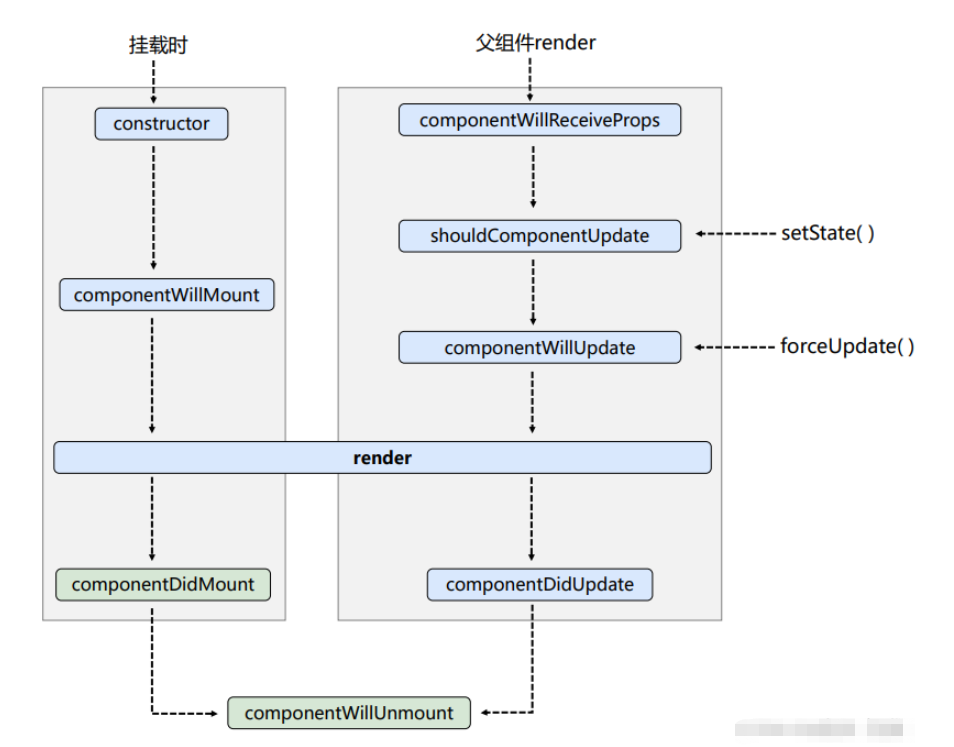
初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发—初次渲染
constructor()
componentWillMount()
render()
componentDidMount()
更新阶段: 由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发
shouldComponentUpdate()
componentWillUpdate()
render()
componentDidUpdate()
卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtnode()触发
componentWillUnmount()
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>生命周期旧</title></head><body> <!-- 准备好一个容器 --> <div id="test"></div> <!-- 引入 React 核心库 --> <script src="../js/react.development.js"></script> <!-- 引入 react-dom 用于支持 react 操作 DOM --> <script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script> <!-- 引入babel: 1. es6 ==> ES5 2. jsx ==> js --> <script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script> <script type="text/babel"> class Count extends React.Component { state = { count:0 } add = ()=>{ // 获取原状态 let {count} = this.state // 更新状态 this.setState({count:count+1}) } death = ()=>{ ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test')) } force = ()=>{ this.forceUpdate() // 强制更新 } // 数据更新的 ‘阀门~' shouldComponentUpdate() { console.log("Count --- shouldComponentUpdate"); return true // 这里必须有返回4值,其次返回值默认是true } // 组件将要更新的钩子 componentWillUpdate() { console.log("Count ---- componentWillUpdate"); } // 组件更新完成的钩子 componentDidUpdate() { console.log("Count ---- componentDidUpdate"); } render(){ console.log("render"); let {count} = this.state return( <div> <h3>当前求和为:{count}</h3> <button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button> <button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button> <button onClick={this.force}>不更改任何状态中的数据,强制更新</button> </div> ) } } // 父组件 class A extends React.Component { state = {carName:'小三轮'} changeCar = ()=>{ this.setState({carName:"宾利"}) } render(){ console.log('A ---- render'); return( <div> <div>我是A组件</div> <button onClick={this.changeCar}>换车</button> <B carName={this.state.carName}></B> </div> ) } } // 子组件 class B extends A { // 组件将要接收新的props的钩子 componentWillReceiveProps(){ console.log('B ---- componentWillReceiveProps'); } // 数据更新的 ‘阀门~' shouldComponentUpdate() { console.log("B --- shouldComponentUpdate"); return true // 这里必须有返回4值,其次返回值默认是true } // 组件将要更新的钩子 componentWillUpdate() { console.log("B ---- componentWillUpdate"); } // 组件更新完成的钩子 componentDidUpdate() { console.log("B ---- componentDidUpdate"); } render(){ console.log('B ---- render'); return( <div> 我是B组件,接收到的车是:{this.props.carName} </div> ) } } ReactDOM.render(<A />,document.getElementById('test')) </script></body></html>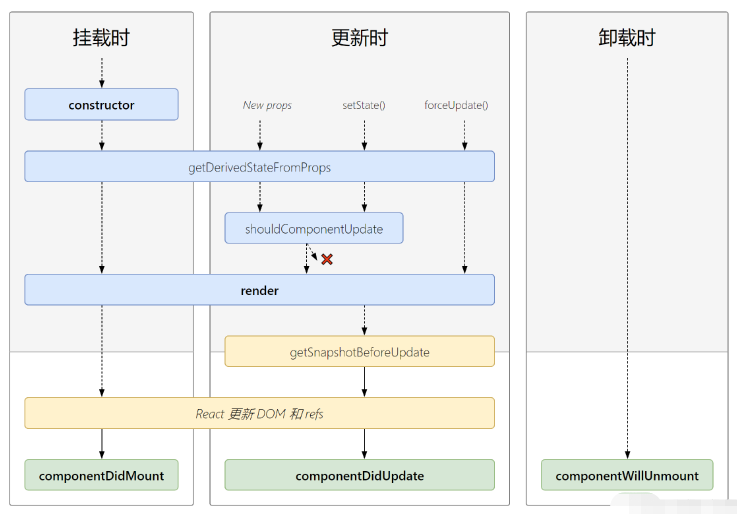
初始化阶段: 由ReactDOM.render()触发—初次渲染
constructor()
getDerivedStateFromProps
render()
componentDidMount()
更新阶段: 由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发
getDerivedStateFromProps
shouldComponentUpdate()
render()
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
componentDidUpdate()
卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
componentWillUnmount()
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>生命周期新</title></head><body> <!-- 准备好一个容器 --> <div id="test"></div> <!-- 引入 React 核心库 --> <script src="../js/17.0.1/react.development.js"></script> <!-- 引入 react-dom 用于支持 react 操作 DOM --> <script src="../js/17.0.1/react-dom.development.js"></script> <!-- 引入babel:1. ES6 ==> ES52. jsx ==> js --> <script src="../js/17.0.1/babel.min.js"></script> <script type="text/babel"> class Count extends React.Component { state = { count:0 } add = ()=>{ // 获取原状态 let {count} = this.state // 更新状态 this.setState({count:count+1}) } death = ()=>{ ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test')) } force = ()=>{ this.forceUpdate() // 强制更新 } // 数据更新的 ‘阀门~' shouldComponentUpdate() { console.log("Count --- shouldComponentUpdate"); return true // 这里必须有返回4值,其次返回值默认是true } // 组件将要更新的钩子 componentWillUpdate() { console.log("Count ---- componentWillUpdate"); } // 组件更新完成的钩子 componentDidUpdate() { console.log("Count ---- componentDidUpdate"); } render(){ console.log("render"); let {count} = this.state return( <div> <h3>当前求和为:{count}</h3> <button onClick={this.add}>点我+1</button> <button onClick={this.death}>卸载组件</button> <button onClick={this.force}>不更改任何状态中的数据,强制更新</button> </div> ) } } // 父组件 class A extends React.Component { state = {carName:'小三轮'} constructor(props) { state } changeCar = ()=>{ this.setState({carName:"宾利"}) } static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) { // 这里必须要一个返回值 ==> state or null // 这里的state会覆盖掉原本的状态,并且后续也无法修改 // 能将外部的接收的props 赋值给组件自身的 state // 如果你希望自身的state一直,全部依赖于外部的props,那么可以使用这个生命周期函数 return {carName:"QQ"} } // 获取护具更新前的快照,能拿到旧的props和state // 必须有返回值 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate = (prevProps, prevState) => { } render(){ console.log('A ---- render'); return( <div> <div>我是A组件</div> <button onClick={this.changeCar}>换车</button> <B carName={this.state.carName}></B> </div> ) } } // 子组件 class B extends A { // 组件将要接收新的props的钩子 UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(){ console.log('B ---- componentWillReceiveProps'); } // 数据更新的 ‘阀门~' shouldComponentUpdate() { console.log("B --- shouldComponentUpdate"); return true // 这里必须有返回4值,其次返回值默认是true } // 将要挂载时 UNSAFE_componentWillMount() { console.log("Count --- componentWillUnMount"); } // 组件将要更新的钩子 UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate() { console.log("B ---- componentWillUpdate"); } // 组件更新完成的钩子 componentDidUpdate() { console.log("B ---- componentDidUpdate"); } render(){ console.log('B ---- render'); return( <div> 我是B组件,接收到的车是:{this.props.carName} </div> ) } } ReactDOM.render(<A />,document.getElementById('test')) </script></body></html>新生命周期中去掉了三个 will 钩子,分别为 componentWillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate;
新生命周期中新增了两个钩子,分别为 getDerivedStateFromProps(从 props 中得到衍生的 state )和 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate。
render:初始化渲染或更新渲染调用
componentDidMount:开启监听, 发送ajax请求
componentWillUnmount:做一些收尾工作, 如: 清理定时器
componentWillMount
componentWillReceiveProps
componentWillUpdate
警告:
现在使用会出现警告,下一个大版本需要加上
UNSAFE_前缀才能使用,以后可能会被彻底废弃,不建议使用。
如果一个函数符合下面2个规范中的任何一个,那么它就属于一个高阶函数
若A函数,接收的参数是一个函数,那么A就可以称为高阶函数
若A函数,它的返回值依然是一个函数,那么A就可以称为高阶函数
常见的高阶函数:Promise,setTimeout,arr.map(数组方法)
通过函数继续调用,返回值为函数的方式,实现多次接受参数,最后统一处理的函数编码形式
function sum(a){ return (b)=>{ return (c)=>{ return a + b + c } }}const result = sum(1)(2)(3)console.log(result);class Login extends React.Component { // 初始化状态 state = { username:'', // 用户名 password:'', // 密码 } // 保存表单数据到状态中 saveFormDate=(dataType,event)=>{ // 标识当前标签 this.setState({[dataType]:event.target.value}) } // 表单提交的回调 handleSubmit=(event)=>{ event.preventDefault(); // 阻止默认事件 let {username,password} = this.state alert(`你输入的用户名是${username},密码是${password}`) } render(){ return( <div> <form action="https://www.baidu.com/" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}> 用户名:<input type="text" onChange={(event)=>this.saveFormDate('username',event)} name="username" /> 密码:<input type="text" onChange={(event)=>this.saveFormDate('password',event)} name="password" /> <button type="submit">登录</button> </form> </div> ) }}class Login extends React.Component { // 初始化状态 state = { username:'', // 用户名 password:'', // 密码 } // 保存表单数据到状态中 saveFormDate=(dataType)=>{ // 标识当前标签 return (event)=>{ // 这里的回调谁执行? input标签的 onChange事件 this.setState({[dataType]:event.target.value}) } } // 表单提交的回调 handleSubmit=(event)=>{ event.preventDefault(); // 阻止默认事件 let {username,password} = this.state alert(`你输入的用户名是${username},密码是${password}`) } render(){ return( <div> <form action="https://www.baidu.com/" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}> 用户名:<input type="text" onChange={this.saveFormDate('username')} name="username" /> 密码:<input type="text" onChange={this.saveFormDate('password')} name="password" /> <button type="submit">登录</button> </form> </div> ) }}以上就是“JavaScript中React面向组件编程实例代码分析”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家阅读完这篇文章都有很大的收获,小编每天都会为大家更新不同的知识,如果还想学习更多的知识,请关注编程网精选频道。
--结束END--
本文标题: JavaScript中React面向组件编程实例代码分析
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/354611.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0