这篇文章主要讲解了“Java之io流原理及流的分类是什么”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Java之IO流原理及流的分类是什么”吧!一、概述I/O是Input/Output的缩写
这篇文章主要讲解了“Java之io流原理及流的分类是什么”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Java之IO流原理及流的分类是什么”吧!

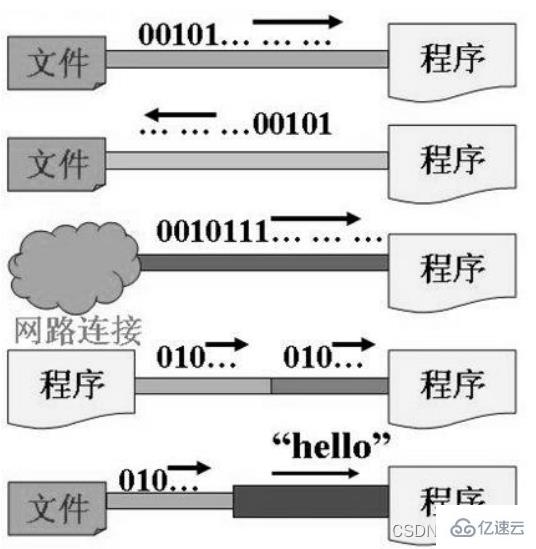
I/O是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理设备之间的数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等。
输入
input:读取外部数据(磁 盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。输出
output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设 备中。
Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流(
stream)” 的方式进行。
java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不种类的数据,并通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
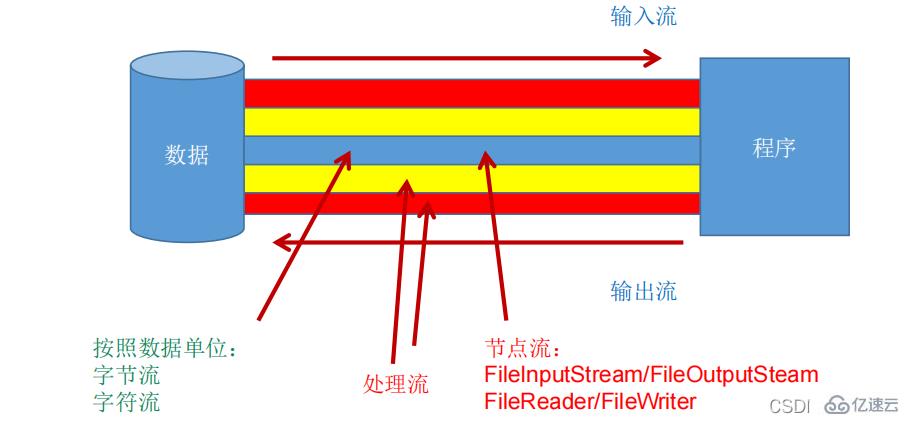
按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8
bit),字符流(16bit)
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
节点流:直接从数据源或目的地读写数据
处理流:不直接连接到数据源或目的地,而是“连接”在已存在的流(节点流或处理流)之上,通过对数据的处理为程序提供更为强大的读写功能。
Java的IO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从以上4个抽象基类派生的,由这4个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
| (抽象基类) | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
IO 流体系体系: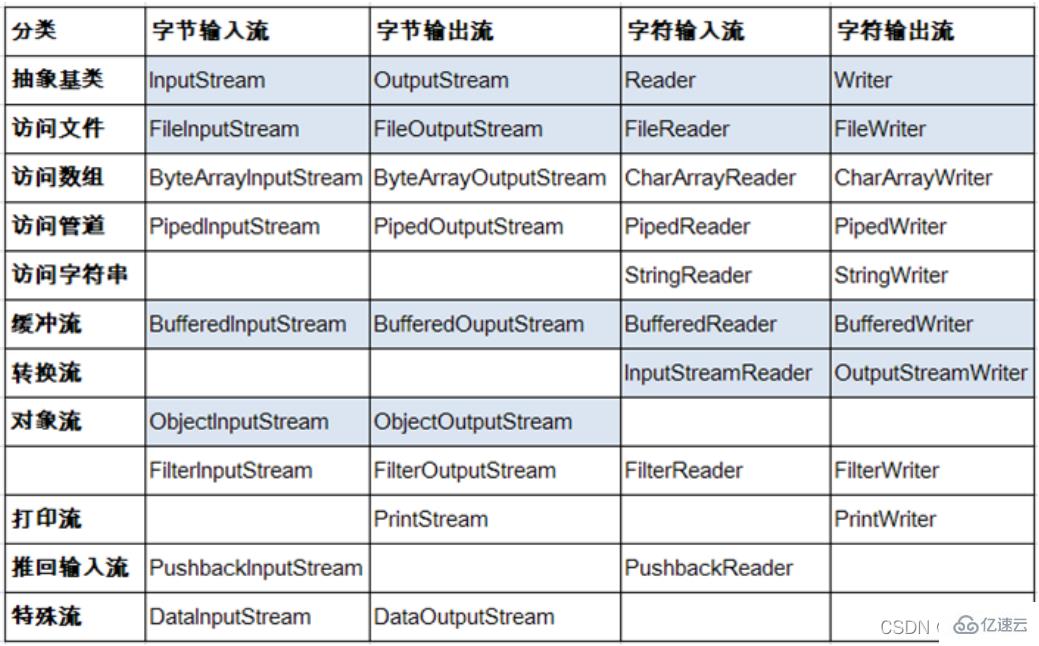
概述
典型实现:
FileInputStream
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
int read() | 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。返回 0 到 255 范围内的 int 字节值。如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。 |
int read(byte[] b) | 从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。如果因为已经到达流末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。否则以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。 |
int read(byte[] b, int off,int len) | 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组。尝试读取 len 个字节,但读取的字节也可能小于该值。以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数。如果因为流位于文件末尾而没有可用的字节,则返回值 -1。 |
public void close() throws IOException | 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源 |
典型实现类:FileInputStream
代码演示:
@Test public void testFileInputStream() { FileInputStream fis = null; try { //1. 造文件 File file = new File("hello.txt"); //2.造流 fis = new FileInputStream(file); //3.读数据 byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len;//记录每次读取的字节的个数 while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ String str = new String(buffer,0,len); System.out.print(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fis != null){ //4.关闭资源 try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }概述
典型实现类:
FileReader
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
int read() | 读取单个字符。作为整数读取的字符,范围在 0 到 65535 之间 (0x00-0xffff)(2个字节的Unicode码),如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1 |
int read(char[] cbuf) | 将字符读入数组。如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1。否则返回本次读取的字符数。 |
int read(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) | 将字符读入数组的某一部分。存到数组cbuf中,从off处开始存储,最多读len个字符。如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1。否则返回本次读取的字符数。 |
public void close() throws IOException | 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。 |
典型实现类:FileReader
@Test public void testFileReader(){ FileReader fr = null; try { //1.实例化File类的对象,指明要操作的文件 File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前Module //2.提供具体的流 fr = new FileReader(file); //3.数据的读入 //read():返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 //方式一:// int data = fr.read();// while(data != -1){// System.out.print((char)data);// data = fr.read();// } //方式二:语法上针对于方式一的修改 int data; while((data = fr.read()) != -1){ System.out.print((char)data); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.流的关闭操作// try {// if(fr != null)// fr.close();// } catch (IOException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// } //或 if(fr != null){ try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //对read()操作升级:使用read的重载方法 @Test public void testFileReader1() { FileReader fr = null; try { //1.File类的实例化 File file = new File("hello.txt"); //2.FileReader流的实例化 fr = new FileReader(file); //3.读入的操作 //read(char[] cbuf):返回每次读入cbuf数组中的字符的个数。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len; while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ //方式一: //错误的写法// for(int i = 0;i < cbuf.length;i++){// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);// } //正确的写法// for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);// } //方式二: //错误的写法,对应着方式一的错误的写法// String str = new String(cbuf);// System.out.print(str); //正确的写法 String str = new String(cbuf,0,len); System.out.print(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fr != null){ //4.资源的关闭 try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }概述
典型实现:
FileOutputStream
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
void write(int b) | 将指定的字节写入此输出流。write 的常规协定是:向输出流写入一个字节。要写入的字节是参数 b 的八个低位。b 的 24 个高位将被忽略。 即写入0~255范围的。 |
void write(byte[] b) | 将 b.length 个字节从指定的 byte 数组写入此输出流。write(b) 的常规协定是:应该与调用 write(b, 0, b.length) 的效果完全相同。 |
void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) | 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流。 |
public void flush()throws IOException | 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节,调用此方法指示应将这些字节立即写入它们预期的目标。 |
public void close() throws IOException | 关闭此输出流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。 |
主要实现类:FileInputOutputStream
@Test public void testFileInputOutputStream() { FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { // File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); File destFile = new File("爱情与友情2.jpg"); // fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //复制的过程 byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len; while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ fos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fos != null){ // try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fis != null){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }概述
典型实现:
FileWriter
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
void write(int c) | 写入单个字符。要写入的字符包含在给定整数值的 16 个低位中,16 高位被忽略。 即写入0 到 65535 之间的Unicode码。 |
void write(char[] cbuf) | 写入字符数组。 |
void write(char[] cbuf,int off,int len) | 写入字符数组的某一部分。从off开始,写入len个字符 |
void write(String str) | 写入字符串。 |
void write(String str,int off,int len) | 写入字符串的某一部分。 |
void flush() | 刷新该流的缓冲,则立即将它们写入预期目标。 |
public void close() throws IOException | 关闭此输出流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。 |
主要实现类:FileWriter
概述
输出操作,对应的
File可以不存在的。并不会报异常
File对应的硬盘中的文件如果不存在,在输出的过程中,会自动创建此文件。
File对应的硬盘中的文件如果存在:
如果流使用的构造器是:
FileWriter(file,false) / FileWriter(file):对原有文件的覆盖如果流使用的构造器是:
FileWriter(file,true):不会对原有文件覆盖,而是在原有文件基础上追加内容
代码演示
//从内存中写出数据到硬盘的文件里。 @Test public void testFileWriter() { FileWriter fw = null; try { //1.提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件 File file = new File("hello1.txt"); //2.提供FileWriter的对象,用于数据的写出 fw = new FileWriter(file,false); //3.写出的操作 fw.write("I have a dream!\n"); fw.write("you need to have a dream!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.流资源的关闭 if(fw != null){ try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }代码演示:
实现对文本的复制操作
@Test public void testFileReaderFileWriter() { FileReader fr = null; FileWriter fw = null; try { //1.创建File类的对象,指明读入和写出的文件 File srcFile = new File("hello.txt"); File destFile = new File("hello2.txt"); //不能使用字符流来处理图片等字节数据// File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg");// File destFile = new File("爱情与友情1.jpg"); //2.创建输入流和输出流的对象 fr = new FileReader(srcFile); fw = new FileWriter(destFile); //3.数据的读入和写出操作 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len;//记录每次读入到cbuf数组中的字符的个数 while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ //每次写出len个字符 fw.write(cbuf,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.关闭流资源 //方式一:// try {// if(fw != null)// fw.close();// } catch (IOException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// }finally{// try {// if(fr != null)// fr.close();// } catch (IOException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// }// } //方式二: try { if(fw != null) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(fr != null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }}实现对图片的复制操作
@Test public void testFileInputOutputStream() { FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { // File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); File destFile = new File("爱情与友情2.jpg"); // fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //复制的过程 byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len; while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ fos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fos != null){ // try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fis != null){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //指定路径下文件的复制 public void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath){ FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try { // File srcFile = new File(srcPath); File destFile = new File(destPath); // fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //复制的过程 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ fos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fos != null){ // try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(fis != null){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } @Test public void testCopyFile(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\01-视频.avi"; String destPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\02-视频.avi";// String srcPath = "hello.txt";// String destPath = "hello3.txt"; copyFile(srcPath,destPath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//618 }}定义文件路径时,注意:可以用“
/”或者“\\”。
在写入一个文件时,如果使用构造器
FileOutputStream(file),则目录下有同名文 件将被覆盖。 如果使用构造器FileOutputStream(file,true),则目录下的同名文件不会被覆盖, 在文件内容末尾追加内容。
在读取文件时,必须保证该文件已存在,否则报异常。
字节流操作字节,比如:
.mp3,.avi,.rmvb,.mp4,.jpg,.doc,.ppt
字符流操作字符,只能操作普通文本文件。最常见的文本文件:
txt,.java,.c,.cpp等语言的源代码。尤其注意.doc,excel,ppt这些不是文本文件。
概述
建立一个流对象,将已存在的一个文件加载进流。
java FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File(“Test.txt”));创建一个临时存放数据的数组。
java char[] ch = new char[1024];调用流对象的读取方法将流中的数据读入到数组中。
java fr.read(ch);关闭资源。
java fr.close();
代码演示
FileReader fr = null;try {fr = new FileReader(new File("c:\\test.txt"));char[] buf = new char[1024];int len;while ((len = fr.read(buf)) != -1) {System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, len));}} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("read-Exception :" + e.getMessage());} finally {if (fr != null) {try {fr.close();} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("close-Exception :" + e.getMessage());} } }概述
创建流对象,建立数据存放文件
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File(“Test.txt”));
2.调用流对象的写入方法,将数据写入流fw.write(“atguigu-songhongkang”);
3.关闭流资源,并将流中的数据清空到文件中。fw.close();
代码演示
FileWriter fw = null;try {fw = new FileWriter(new File("Test.txt"));fw.write("atguigu-songhongkang");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (fw != null)try {fw.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} }为了提高数据读写的速度,Java api提供了带缓冲功能的流类,在使用这些流类时,会创建一个内部缓冲区数组,缺省使用8192个字节(8Kb)的缓冲区。
缓冲流要“套接”在相应的节点流之上,根据数据操作单位可以把缓冲流分为:
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直接访问缓冲区
当使用
BufferedInputStream读取字节文件时,BufferedInputStream会一次性从文件中读取8192个(8Kb),存在缓冲区中,直到缓冲区装满了,才重新从文件中读取下一个8192个字节数组。
向流中写入字节时,不会直接写到文件,先写到缓冲区中直到缓冲区写满,
BufferedOutputStream才会把缓冲区中的数据一次性写到文件里。使用方法flush()可以强制将缓冲区的内容全部写入输出流
关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反。只要关闭最外层流即可,关闭最外层流也 会相应关闭内层节点流
flush()方法的使用:手动将buffer中内容写入文件
如果是带缓冲区的流对象的close()方法,不但会关闭流,还会在关闭流之前刷新缓冲区,关闭后不能再写出
@Test public void BufferedStreamTest() throws FileNotFoundException { BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); File destFile = new File("爱情与友情3.jpg"); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[10]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len);// bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos != null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略.// fos.close();// fis.close(); } } @Test public void testCopyFileWithBuffered(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\01-视频.avi"; String destPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\03-视频.avi"; copyFileWithBuffered(srcPath,destPath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//618 - 176 } //实现文件复制的方法 public void copyFileWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){ BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File(srcPath); File destFile = new File(destPath); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos != null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略.// fos.close();// fis.close(); } } @Test public void testBufferedReaderBufferedWriter(){ BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { //创建文件和相应的流 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("dbcp.txt"))); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("dbcp1.txt"))); //读写操作 //方式一:使用char[]数组// char[] cbuf = new char[1024];// int len;// while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){// bw.write(cbuf,0,len);// // bw.flush();// } //方式二:使用String String data; while((data = br.readLine()) != null){ //方法一:// bw.write(data + "\n");//data中不包含换行符 //方法二: bw.write(data);//data中不包含换行符 bw.newLine();//提供换行的操作 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 if(bw != null){ try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }}转换流提供了在字节流和字符流之间的转换
Java API提供了两个转换流:
InputStreamReader:将InputStream转换为Reader
OutputStreamWriter:将Writer转换为OutputStream
字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效。
很多时候我们使用转换流来处理文件乱码问题。实现编码和 解码的功能。
概述
实现将字节的输入流按指定字符集转换为字符的输入流。
需要和
InputStream“套接”。
构造器
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in) |
public InputSreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName) |
概述
实现将字符的输出流按指定字符集转换为字节的输出流。
需要和
OutputStream“套接”。
(2)构造器
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) |
public OutputSreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charsetName) |
代码演示1:
@Test public void test1() throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.txt");// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系统默认的字符集 //参数2指明了字符集,具体使用哪个字符集,取决于文件dbcp.txt保存时使用的字符集 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");//使用系统默认的字符集 char[] cbuf = new char[20]; int len; while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ String str = new String(cbuf,0,len); System.out.print(str); } isr.close(); }代码演示2:
@Test public void test2() throws Exception { //1.造文件、造流 File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt"); File file2 = new File("dbcp_gbk.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8"); OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk"); //2.读写过程 char[] cbuf = new char[20]; int len; while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ osw.write(cbuf,0,len); } //3.关闭资源 isr.close(); osw.close(); }}
System.in和System.out分别代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备
默认输入设备是:键盘,输出设备是:显示器
System.in的类型是InputStream,System.out的类型是PrintStream,其是OutputStream的子类,FilterOutputStream的子类
重定向:通过System类的setIn,setOut方法对默认设备进行改变。
public static void setIn(InputStream in)
public static void setOut(PrintStream out)
public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader br = null; try { InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in); br = new BufferedReader(isr); while (true) { System.out.println("请输入字符串:"); String data = br.readLine(); if ("e".equalsIgnoreCase(data) || "exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) { System.out.println("程序结束"); break; } String upperCase = data.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upperCase); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (br != null) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }实现将基本数据类型的数据格式转化为字符串输出
打印流:
PrintStream和PrintWriter
提供了一系列重载的
print()和println()方法,用于多种数据类型的输出
PrintStream和PrintWriter的输出不会抛出IOException异常
PrintStream和PrintWriter有自动flush功能
PrintStream打印的所有字符都使用平台的默认字符编码转换为字节。 在需要写入字符而不是写入字节的情况下,应该使用PrintWriter类。
System.out返回的是PrintStream的实例
@Test public void test2() { PrintStream ps = null; try { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\IO\\text.txt")); // 创建打印输出流,设置为自动刷新模式(写入换行符或字节 '\n' 时都会刷新输出缓冲区) ps = new PrintStream(fos, true); if (ps != null) {// 把标准输出流(控制台输出)改成文件 System.setOut(ps); } for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) { // 输出ASCII字符 System.out.print((char) i); if (i % 50 == 0) { // 每50个数据一行 System.out.println(); // 换行 } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (ps != null) { ps.close(); } } }为了方便地操作Java语言的基本数据类型和String的数据,可以使用数据流。
数据流有两个类:(用于读取和写出基本数据类型、String类的数据)
DataInputStream
DataOutputStream分别“套接”在
InputStream和OutputStream子类的流上
DataInputStream中的方法:
boolean readBoolean() |
byte readByte() char |
readChar() |
float readFloat() |
double readDouble() |
long readLong() |
int readInt() |
short readShort() |
String readUTF() |
void readFully(byte[] b) |
补充:DataOutputStream中的方法:将上述的方法的read改为相应的write即可
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Java之IO流原理及流的分类是什么”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Java之IO流原理及流的分类是什么这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是编程网,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
--结束END--
本文标题: Java之IO流原理及流的分类是什么
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/342176.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0