本篇内容主要讲解“SpringBoot参数怎么校验”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“springBoot参数怎么校验”吧!使用传统方式的弊端public String&nb
本篇内容主要讲解“SpringBoot参数怎么校验”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“springBoot参数怎么校验”吧!
public String addUser(User user) { if (user == null || user.getId() == null || user.getAccount() == null || user.getPassword() == null || user.getEmail() == null) { return "对象或者对象字段不能为空"; } if (StringUtils.isEmpty(user.getAccount()) || StringUtils.isEmpty(user.getPassword()) || StringUtils.isEmpty(user.getEmail())) { return "不能输入空字符串"; } if (user.getAccount().length() < 6 || user.getAccount().length() > 11) { return "账号长度必须是6-11个字符"; } if (user.getPassword().length() < 6 || user.getPassword().length() > 16) { return "密码长度必须是6-16个字符"; } if (!Pattern.matches("^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+(\\.[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)+$", user.getEmail())) { return "邮箱格式不正确"; } // 参数校验完毕后这里就写上业务逻辑 return "success"; }这样做确实没有什么问题,而且排版也工整,但代码太繁琐了,如果有几十个字段要校验,那这个方法里面将会变得非常臃肿,实在不够优雅。下面我们就来讲讲如何使用最优雅的方式来解决。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId></dependency>| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @AssertFalse | 被注解的元素必须为 false |
| @AssertTrue | 被注解的元素必须为 true |
| @DecimalMax(value) | 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) | 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Digits (integer, fraction) | 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Null | 被注解的元素必须为空 |
| @NotNull | 被注解的元素必须不为空 |
| @Min(value) | 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max, min) | 被注解的元素的长度必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注解的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注解的元素必须是一个未来的日期 |
| @Pattern(value) | 被注解的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
下面我们以此来在业务中实现
@Datapublic class User { @NotNull(message = "用户id不能为空") private Long id; @NotNull(message = "用户账号不能为空") @Size(min = 6, max = 11, message = "账号长度必须是6-11个字符") private String account; @NotNull(message = "用户密码不能为空") @Size(min = 6, max = 11, message = "密码长度必须是6-16个字符") private String passWord; @NotNull(message = "用户邮箱不能为空") @Email(message = "邮箱格式不正确") private String email;}@RestControllerpublic class UserController { @PostMapping("/addUser") public void addUser(@RequestBody @Valid User user) {//业务 }}import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;import org.springframework.WEB.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;import java.util.stream.Collectors;@RestControllerAdvicepublic class ExceptionConfig { @ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class) public String handleValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) { // 从异常对象中拿到ObjectError对象 ObjectError objectError = e.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().get(0); // 然后提取错误提示信息进行返回 return objectError.getDefaultMessage(); } @ExceptionHandler(value = ConstraintViolationException.class) public String handleConstraintViolationException(ConstraintViolationException e) { // 从异常对象中拿到ObjectError对象 return e.getConstraintViolations() .stream() .map(ConstraintViolation::getMessage) .collect(Collectors.toList()).get(0); }}
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;@RestController@Validatedpublic class TestController { @GetMapping("/test") public void test(@NotNull(message = "id不能为空") Integer id) { }}然后我们使用apipost测试
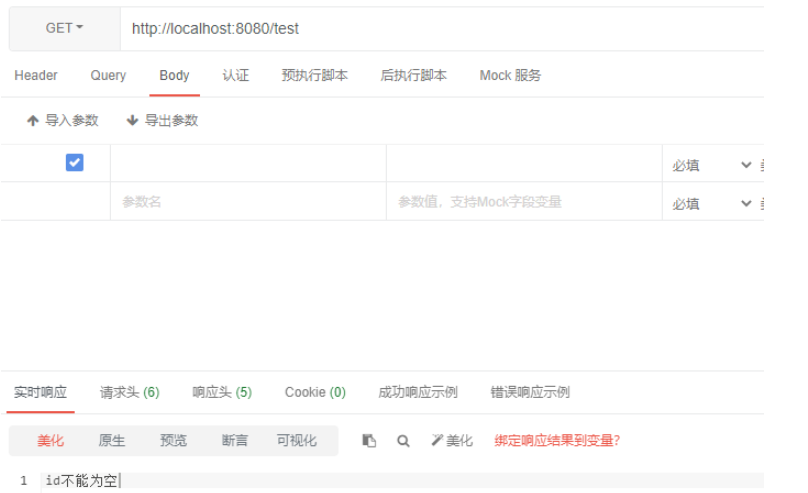
场景:在新增时我们需要id为空,但修改时我们又需要id不为空,总不可能搞两个类吧,这时候分组校验的用处就来了
import lombok.Data;import javax.validation.constraints.Email;import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;import javax.validation.constraints.Size;@Datapublic class User { public interface Insert{ } public interface Update{ } @NotNull(message = "用户id不能为空",groups = Update.class) @Null(message = "用户id必须为空",groups = Integer.class) private Long id; private String account; private String password; private String email;}@PostMapping("/add")public void add(@RequestBody @Validated(User.Insert.class) User user) {}添加时就用User.Insert.class,修改时就用User.Update.class
场景:当type为1时,需要参数a不为空,当type为2时,需要参数b不为空。
import com.example.demo.provider.CustomSequenceProvider;import lombok.Data;import org.hibernate.validator.group.GroupSequenceProvider;import javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty;import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;@Data@GroupSequenceProvider(value = CustomSequenceProvider.class)public class CustomGroup { @Pattern(regexp = "[A|B]" , message = "类型不必须为 A|B") private String type; @NotEmpty(message = "参数A不能为空" , groups = {WhenTypeIsA.class}) private String paramA; @NotEmpty(message = "参数B不能为空", groups = {WhenTypeIsB.class}) private String paramB; public interface WhenTypeIsA { } public interface WhenTypeIsB { }}import com.example.demo.controller.CustomGroup;import org.hibernate.validator.spi.group.DefaultGroupSequenceProvider;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class CustomSequenceProvider implements DefaultGroupSequenceProvider<CustomGroup> { @Override public List<Class<?>> getValidationGroups(CustomGroup fORM) { List<Class<?>> defaultGroupSequence = new ArrayList<>(); defaultGroupSequence.add(CustomGroup.class); if (form != null && "A".equals(form.getType())) { defaultGroupSequence.add(CustomGroup.WhenTypeIsA.class); } if (form != null && "B".equals(form.getType())) { defaultGroupSequence.add(CustomGroup.WhenTypeIsB.class); } return defaultGroupSequence; }}@PostMapping("/add")public void add(@RequestBody @Validated CustomGroup user) {}虽然官方提供的校验注解已经满足很多情况了,但还是无法满足我们业务的所有需求,比如校验手机号码,下面我就以校验手机号码来做一个示例。
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Constraint(validatedBy = PhoneValidator.class)public @interface Phone { String message() default "手机号码格式有误"; Class<?>[] groups() default {}; Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};}注:groups和payload是必须要写的,Constraint是使用哪个类来进行校验。
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;import java.util.regex.Pattern;public class PhoneValidator implements ConstraintValidator<Phone, Object> { @Override public boolean isValid(Object telephone, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) { String pattern = "^1[3|4|5|6|7|8|9]\\d{9}$"; return Pattern.matches(pattern, telephone.toString()); }}最后直接用到参数前面或者实体类变量上面即可。
当某个对象中还包含了对象需要进行校验,这个时候我们需要用嵌套校验。
@Datapublic class TestAA { @NotEmpty(message = "id不能为空") private String id; @NotNull @Valid private Job job; @Data public class Job { @NotEmpty(message = "content不能为空") private String content; }}Spring Validation默认会校验完所有字段,然后才抛出异常。可以通过配置,开启Fali Fast模式,一旦校验失败就立即返回。
import org.hibernate.validator.HibernateValidator;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.validation.Validation;import javax.validation.Validator;import javax.validation.ValidatorFactory;@Configurationpublic class FailFastConfig { @Bean public Validator validator() { ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class) .configure() // 快速失败模式 .failFast(true) .buildValidatorFactory(); return validatorFactory.getValidator(); }}SpringBoot 2.3.x 移除了validation依赖需要手动引入依赖。
到此,相信大家对“SpringBoot参数怎么校验”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是编程网网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
--结束END--
本文标题: SpringBoot参数怎么校验
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/329366.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0