Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
这篇文章主要介绍了python生成器和yield关键字怎么用,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。下列代码用于先体验普通列表推导式和生成器的差别:# def
这篇文章主要介绍了python生成器和yield关键字怎么用,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。
下列代码用于先体验普通列表推导式和生成器的差别:
# def add():# temp = ["姓名", "学号", "班级", "电话"]# dic = {}# lst = []# for item in temp:# inp = input("请输入{}:".fORMat(item))# if inp == "exit":# print("成功退出输入")# return False# else:# dic[item] = inp# lst.append(dic)# print("添加成功")# return lst## def show(lst):# print("-"*30)# print("姓名\t\t学号\t\t班级\t\t电话")# print("=" * 30)# for i in range(len(lst)):# for val in lst[i].values():# print(val, "\t", end="")# print()# print("-" * 30)## def search(total_lst):# name = input("请输入您要查询的学生姓名:")# flag = False# tmp = []# for i in range(len(total_lst)):# if total_lst[i]["姓名"] == name:# tmp.append(total_lst[i])# show(tmp)# flag = True# if not flag:# print("抱歉,没有找到该学生")## if __name__ == '__main__':# total_lst = []# while True:# flag = add()# if flag:# total_lst = total_lst + flag# else:# break# show(total_lst)# search(total_lst)## def show(lst):# print("="*30)# print("{:^25s}".format("输出F1赛事车手积分榜"))# print("=" * 30)# print("{:<10s}".format("排名"), "{:<10s}".format("车手"), "{:<10s}".format("积分"))# for i in range(len(lst)):# print("{:0>2d}{:<9s}".format(i+1, ""), "{:<10s}".format(lst[i][0]), "{:<10d}".format(lst[i][1]))## if __name__ == '__main__':# data = 'lisi 380,jack 256,bob 385,rose 204,alex 212'# data = data.split(",")# dic = {}# da = []# for i in range(len(data)):# da.append(data[i].split())# for i in range(len(da)):# dic[da[i][0]] = int(da[i][1])# data2 = sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda kv: (kv[1], kv[0]), reverse=True)# show(data2)# class Fun:# def __init__(self):# print("Fun:__init__()")# def test(self):# print("Fun")## class InheritFun(Fun):# def __init__(self):# print("InheritedFun.__init__()")# super().__init__()# def test(self):# super().test()# print("InheritedFun")# a = InheritFun()# a.test()# from math import *# class Circle:# def __init__(self, radius=1):# self.radius = radius# def getPerimeter(self):# return 2 * self.radius * pi# def getArea(self):# return self.radius * self.radius * pi# def setRadius(self, radius):# self.radius = radius## a=Circle(10)# print("{:.1f},{:.2f}".format(a.getPerimeter(), a.getArea()))# from math import *# class Root:# def __init__(self, a, b, c):# self.a = a# self.b = b# self.c = C# def getDiscriminant(self):# return pow(self.b, 2)-4*self.a*self.c# def getRoot1(self):# return (-self.b+pow(pow(self.b, 2)-4*self.a*self.c, 0.5))/(2*self.a)# def getRoot2(self):# return (-self.b - pow(pow(self.b, 2) - 4 * self.a * self.c, 0.5)) / (2 * self.a)# inp = input("请输入a,b,c: ").split(" ")# inp = list(map(int, inp))# Root = Root(inp[0], inp[1], inp[2])# print("判别式为:{:.1f}; x1:{:.1f}; x2:{:.1f}".format(Root.getDiscriminant(), Root.getRoot1(), Root.getRoot2()))# class Stock:# def __init__(self, num, name, pre_price, now_price):# self.num = num# self.name = name# self.pre_price = pre_price# self.now_price = now_price# def getCode(self):# return self.num# def getName(self):# return self.name# def getPriceYesterday(self):# return self.pre_price# def getPriceToday(self):# return self.now_price# def getChangePercent(self):# return (self.now_price-self.pre_price)/self.pre_price## sCode = input() #输入代码# sName = input() #输入名称# priceYesterday = float(input()) #输入昨日价格# priceToday = float(input()) #输入今日价格# s = Stock(sCode,sName,priceYesterday,priceToday)# print("代码:",s.getCode())# print("名称:",s.getName())# print("昨日价格:%.2f\n今天价格:%.2f" % (s.getPriceYesterday(),s.getPriceToday()))# print("价格变化百分比:%.2f%%" % (s.getChangePercent()*100))# from math import pi## class Shape:# def __init__(self, name='None', area=None, perimeter=None):# self.name = name# self.area = area# self.perimeter = perimeter# def calArea(self):# return self.area# def calPerimeter(self):# return self.perimeter# def display(self):# print("名称:%s 面积:%.2f 周长:%.2f" % (self.name, self.area, self.perimeter))## class Rectangle(Shape):# def __init__(self, width, height):# super().__init__()# self.width = width# self.height = height# def calArea(self):# self.area = self.height*self.width# return self.area# def calPerimeter(self):# self.perimeter = (self.height+self.width)*2# return self.perimeter# def display(self):# self.name = "Rectangle"# Rectangle.calArea(self)# Rectangle.calPerimeter(self)# super(Rectangle, self).display()## class Triangle(Shape):# def __init__(self, bottom, height, edge1, edge2):# super().__init__()# self.bottom = bottom# self.height = height# self.edge1 = edge1# self.edge2 = edge2# def calArea(self):# self.area = (self.bottom*self.height) / 2# return self.area# def calPerimeter(self):# self.perimeter = self.bottom+self.edge2+self.edge1# return self.perimeter# def display(self):# self.name = "Triangle"# Triangle.calArea(self)# Triangle.calPerimeter(self)# super(Triangle, self).display()## class Circle(Shape):# def __init__(self, radius):# super(Circle, self).__init__()# self.radius = radius# def calArea(self):# self.area = pi*pow(self.radius, 2)# return self.area# def calPerimeter(self):# self.perimeter = 2*pi*self.radius# return self.perimeter# def display(self):# self.name = "Circle"# Circle.calArea(self)# Circle.calPerimeter(self)# super(Circle, self).display()## rectangle = Rectangle(2, 3)# rectangle.display()## triangle = Triangle(3,4,4,5)# triangle.display()## circle = Circle(radius=1)# circle.display()## lst = list(map(lambda x: int(x), ['1', '2', '3']))# print(lst)## class Listnode(object):# def __init__(self):# self.val = None# self.next = None## #尾插法# def creatlist_tail(lst):# L = ListNode() #头节点# first_node = L# for item in lst:# p = ListNode()# p.val = item# L.next = p# L = p# return first_node# #头插法# def creatlist_head(lst):# L = ListNode() #头节点# for item in lst:# p = ListNode()# p.val = item# p.next = L# L = p# return L# #打印linklist# def print_ll(ll):# while True:# if ll.val:# print(ll.val)# if ll.next==None: #尾插法停止点# break# elif not ll.next: #头插法停止点# break# ll = ll.next# #题解# class Solution:# def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):# # write code here# res = []# while(listNode):# res.append(listNode.val)# listNode=listNode.next# return res[3:0:-1]## if __name__ == "__main__":# lst = [1, 2, 3]# linklist = creatlist_tail(lst)# solution = Solution()# res = solution.printListFromTailToHead(linklist)# print(res)# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# class Solution:# def __init__(self):# self.stack1 = []# self.stack2 = []# def push(self, node):# # write code here# self.stack1.append(node)# def pop(self):# # return xx# if self.stack2:# return self.stack2.pop()# else:# for i in range(len(self.stack1)):# self.stack2.append(self.stack1.pop())# return self.stack2.pop()## if __name__ == '__main__':# solution = Solution()# solution.push(1)# solution.push(2)# print(solution.pop())# print(solution.pop())# # binary search# def binary_search(lst, x):# lst.sort()# if len(lst) > 0:# pivot = len(lst) // 2# if lst[pivot] == x:# return True# elif lst[pivot] > x:# return binary_search(lst[:pivot], x)# elif lst[pivot] < x:# return binary_search(lst[pivot+1:], x)# return False## def binary_search3(lst, x):# lst.sort()# head = 0# tail = len(lst)# pivot = len(lst) // 2# while head <= tail:# if lst[pivot]>x:# tail = pivot# pivot = (head+tail) // 2# elif lst[pivot]<x:# head = pivot# pivot = (head+tail) // 2# elif lst[pivot] == x:# return True# return False# if __name__ == '__main__':# lst = [5, 3, 1, 8, 9]# print(binary_search(lst, 3))# print(binary_search(lst, 100))## print(binary_search(lst, 8))# print(binary_search(lst, 100))# 括号匹配# def bracket_matching(ans):# stack = []# flag = True# left = ['(', '{', '[']# right = [')', '}', ']']# for i in range(len(ans)):# if ans[i] in left:# stack.append(ans[i])# else:# tmp = stack.pop()# if left.index(tmp) != right.index(ans[i]):# flag = False# if stack:# flag = False# return flag## print(bracket_matching('({})()[[][]'))# print(bracket_matching('({})()[[]]'))# def longestValidParentheses(s):# maxlen = 0# stack = []# for i in range(len(s)):# if s[i] == '(':# stack.append(s[i])# if s[i] == ')' and len(stack) != 0:# stack.pop()# maxlen += 2# return maxlen# print(longestValidParentheses('()(()'))# def GetLongestParentheses(s):# maxlen = 0# start = -1# stack = []# for i in range(len(s)):# if s[i]=='(':# stack.append(i)# else:# if not stack:# start = i# else:# stack.pop()# if not stack:# maxlen = max(maxlen, i-start)# else:# maxlen = max(maxlen, i-stack[-1])# return maxlen# print(GetLongestParentheses('()(()'))# print(GetLongestParentheses('()(()))'))# print(GetLongestParentheses(')()())'))# import torch# a = torch.tensor([[[1,0,3],# [4,6,5]]])# print(a.size())# b = torch.squeeze(a)# print(b, b.size())# b = torch.squeeze(a,-1)# print(b, b.size())# b = torch.unsqueeze(a,2)# print(b, b.size())## print('-----------------')# x = torch.zeros(2, 1, 2, 1, 2)# print(x.size())# y = torch.squeeze(x)# print(y.size())# y = torch.squeeze(x, 0)# print(y.size())# y = torch.squeeze(x, 1)# print(y.size())# from typing import List# class Solution:# def duplicate(self, numbers: List[int]) -> int:# # write code here# dic = dict()# for i in range(len(numbers)):# if numbers[i] not in dic.keys():# dic[numbers[i]] = 1# else:# dic[numbers[i]] += 1# for key, value in dic.items():# if value > 1:# return key# return -1# if __name__ == '__main__':# solution = Solution()# print(solution.duplicate([2,3,1,0,2,5,3]))# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, data=0):# self.val = data# self.left = None# self.right = None### class Solution:# def TreeDepth(self , pRoot: TreeNode) -> int:# # write code here# if pRoot is None:# return 0# count = 0# now_layer =[pRoot]# next_layer = []# while now_layer:# for i in now_layer:# if i.left:# next_layer.append(i.left)# if i.right:# next_layer.append(i.right)# count +=1# now_layer, next_layer = next_layer,[]# return count## if __name__ == '__main__':# inp = [1,2,3,4,5,'#',6,'#','#',7]# bt = TreeNode(1)## bt.left = TreeNode(2)# bt.right = TreeNode(3)## bt.left.left = TreeNode(4)# bt.left.right = TreeNode(5)# bt.right.left = None# bt.right.right = TreeNode(6)## bt.left.left.left = None# bt.left.left.right = None# bt.left.right.left = TreeNode(7)## solution = Solution()# print('深度:', solution.TreeDepth(bt))# class ListNode:# def __init__(self):# self.val = None# self.next = None## def creatlist_tail(lst):# L = ListNode()# first_node = L# for item in lst:# p = ListNode()# p.val = item# L.next = p# L = p# return first_node## def show(node:ListNode):# print(node.val,end=' ')# if node.next is not None:# node = show(node.next)## class Solution:# def ReverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:# # write code here# res = None# while head:# nextnode = head.next# head.next = res# res = head# head = nextnode# return res## if __name__ == '__main__':# lst = [1,2,3]# linklist = creatlist_tail(lst)# show(linklist)# print()# solution = Solution()# show(solution.ReverseList(linklist))# 字典推导式# a = ['a', 'b', 'c']# b = [4, 5, 6]# dic = {k:v for k,v in zip(a,b)}# print(dic)#列表推导式# l = [i for i in range(10)]# print(l)#### # 生成器推导式# l1 = (i for i in range(10))# print(type(l1)) # 输出结果:<class 'generator'># for i in l1:# print(i)# print('{pi:0>10.1f}'.format(pi=3.14159855))# print("'","center".center(40),"'")# print("center".center(40,'-'))# print("center".zfill(40))# print("center".ljust(40,'-'))# print("center".rjust(40,'-'))# s = "Python is easy to learn, easy to use."# print(s.find('to',0,len(s)))# print(s.find('es'))# num = [1,2,3]# print("+".join(str(i) for i in num),"=",sum(num))# print(''.center(40,'-'))## import torch# from torch import nn# import numpy as np## # 一维BN# d1 = torch.rand([2,3,4]) #BCW# bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(3, momentum=1)# res = bn1(d1)# print(res.shape)## #二维BN(常用)# d2 = torch.rand([2,3,4,5]) #BCHW# bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(3, momentum=1)# res = bn2(d2)# print(res.shape)# print(bn2.running_mean) #3个chanel均值# print(bn2.running_var) #3个chanel方差### a = np.array(d2.tolist())# mean = np.mean(a,axis=(0,2,3))# print(mean)### def batchnorm_forward(x, gamma, beta, bn_param):# """# Forward pass for batch normalization## Input:# - x: Data of shape (N, D)# - gamma: Scale parameter of shape (D,)# - beta: Shift parameter of shape (D,)# - bn_param: Dictionary with the following keys:# - mode: 'train' or 'test'# - eps: Constant for numeric stability# - momentum: Constant for running mean / variance# - running_mean: Array of shape(D,) giving running mean of features# - running_var Array of shape(D,) giving running variance of features# Returns a tuple of:# - out: of shape (N, D)# - cache: A tuple of values needed in the backward pass# """# mode = bn_param['mode']# eps = bn_param.get('eps', 1e-5)# momentum = bn_param.get('momentum', 0.9)## N, D = x.shape# running_mean = bn_param.get('running_mean', np.zeros(D, dtype=x.dtype))# running_var = bn_param.get('running_var', np.zeros(D, dtype=x.dtype))## out, cache = None, None## if mode == 'train':# sample_mean = np.mean(x, axis=0) # np.mean([[1,2],[3,4]])->[2,3]# sample_var = np.var(x, axis=0)# out_ = (x - sample_mean) / np.sqrt(sample_var + eps)## running_mean = momentum * running_mean + (1 - momentum) * sample_mean# running_var = momentum * running_var + (1 - momentum) * sample_var## out = gamma * out_ + beta# cache = (out_, x, sample_var, sample_mean, eps, gamma, beta)# elif mode == 'test':# # scale = gamma / np.sqrt(running_var + eps)# # out = x * scale + (beta - running_mean * scale)# x_hat = (x - running_mean) / (np.sqrt(running_var + eps))# out = gamma * x_hat + beta# else:# raise ValueError('Invalid forward batchnorm mode "%s"' % mode)## # Store the updated running means back into bn_param# bn_param['running_mean'] = running_mean# bn_param['running_var'] = running_var## return out, cache## import numpy as np# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt### def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):## x1 = dets[:, 0]# y1 = dets[:, 1]# x2 = dets[:, 2]# y2 = dets[:, 3]# scores = dets[:, 4]# areas = (x2-x1+1)*(y2-y1+1)# res = []# index = scores.argsort()[::-1]# while index.size>0:# i = index[0]# res.append(i)# x11 = np.maximum(x1[i],x1[index[1:]])# y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])# x22 = np.minimum(x2[i],x2[index[1:]])# y22 = np.minimum(y2[i],y2[index[1:]])## w = np.maximum(0,x22-x11+1)# h = np.maximum(0,y22-y11+1)## overlaps = w * h# iou = overlaps/(areas[i]+areas[index[1:]]-overlaps)## idx = np.where(iou<=thresh)[0]# index = index[idx+1]# print(res)# return res## def plot_boxs(box,c):# x1 = box[:, 0]# y1 = box[:, 1]# x2 = box[:, 2]# y2 = box[:, 3]## plt.plot([x1,x2],[y1,y1],c)# plt.plot([x1,x2],[y2,y2],c)# plt.plot([x1,x1],[y1,y2],c)# plt.plot([x2,x2],[y1,y2],c)## if __name__ == '__main__':# boxes = np.array([[100, 100, 210, 210, 0.72],# [250, 250, 420, 420, 0.8],# [220, 220, 320, 330, 0.92],# [230, 240, 325, 330, 0.81],# [220, 230, 315, 340, 0.9]])# plt.figure()# ax1 = plt.subplot(121)# ax2 = plt.subplot(122)# plt.sca(ax1)# plot_boxs(boxes,'k')## res = py_cpu_nms(boxes,0.7)# plt.sca(ax2)# plot_boxs(boxes[res],'r')# plt.show()# 2 3 3 4# 1 2 3# 4 5 6# 1 2 3 4# 5 6 7 8# 9 10 11 12# lst1, lst2 = [], []# n1,m1,n2,m2 = map(int,input().split())# for i in range(n1):# nums = list(map(int,input().split())) #输入一行数据# lst1.append(nums)# for i in range(n2):# nums = list(map(int,input().split()))# lst2.append(nums)# res = []# for i in range(n1):# res.append([])# for j in range(m2):# lst4 = []# lst3 = lst1[i]# for k in range(n2):# lst4.append(lst2[k][j])# res_num = sum(map(lambda x,y:x*y,lst3,lst4))# res[i].append(res_num)# print(res)## import numpy as np# print('numpy:',np.dot(lst1,lst2))#定义残差块# import torch# import torch.nn as nn# import torch.nn.functional as F## class ResBlock(nn.Module):# def __init__(self,inchanel,outchanel,stride=1):# super(ResBlock,self).__init__()# self.left = nn.Sequential(# nn.Conv2d(inchanel,outchanel,kernel_size=3,stride=stride,padding=1,bias=False),# nn.BatchNorm2d(outchanel),# nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# nn.Conv2d(outchanel,outchanel,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),# nn.BatchNorm2d(outchanel)# )# self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()# if stride!=1 or inchanel!=outchanel:# self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(# nn.Conv2d(inchanel,outchanel,kernel_size=1,stride=stride,padding=1,bias=False),# nn.BatchNorm2d(outchanel)# )# def forward(self,x):# out = self.left(x)# out = out + self.shortcut(x)# out = F.relu(out)## return out## class ResNet(nn.Module):# def __init__(self,Resblock,num_classes=10):# super(ResNet,self).__init__()# self.inchanel = 64# self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(# nn.Conv2d(3,64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),# nn.BatchNorm2d(64),# nn.ReLU()# )# self.layer1 = self.make_layer(ResBlock,64,2,1)# self.layer2 = self.make_layer(ResBlock, 128, 2, 2)# self.layer3 = self.make_layer(ResBlock, 256, 2, 2)# self.layer4 = self.make_layer(ResBlock, 512, 2, 2)# self.fc = nn.Linear(512,num_classes)## def make_layer(self,ResBlock,channels,num_blocks,stride):# strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks-1)# layers = []# for stride in strides:# layers.append(ResBlock(self.inchanel,channels,stride))# self.inchanel=channels# return nn.Sequential(*layers)# def forward(self,x):# out = self.conv1(x)# out = self.layer1(out)# out = self.layer2(out)# out = self.layer3(out)# out = self.layer4(out)# out = F.avg_pool2d(out,4)# out = out.view(out.size(0),-1)# out = self.fc(out)# return out# import torch# import torch.nn as nn# import torch.nn.functional as F## class ASPP(nn.Module):# def __init__(self,in_channel=512,depth=256):# super(ASPP,self).__init__()# self.mean = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1))# self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,depth,1,1)# self.atrous_block1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,depth,1,1)# self.atrous_block6 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,depth,3,1,padding=6,dilation=6)# self.atrous_block12 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,depth,3,1,padding=12,dilation=12)# self.atrous_block18 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,depth,3,1,padding=18,dilation=18)# self.conv1x1_output = nn.Conv2d(depth*5,depth,1,1)# def forward(self,x):# size = x[2:]# pool_feat = self.mean(x)# pool_feat = self.conv(pool_feat)# pool_feat = F.upsample(pool_feat,size=size,mode='bilinear')## atrous_block1 = self.atrous_block1(x)# atrous_block6 = self.atrous_block6(x)# atrous_block12 = self.atrous_block12(x)# atrous_block18 = self.atrous_block18(x)## out = self.conv1x1_output(torch.cat([pool_feat,atrous_block1,atrous_block6,# atrous_block12,atrous_block18],dim=1))# return out#牛顿法求三次根# def sqrt(n):# k = n# while abs(k*k-n)>1e-6:# k = (k + n/k)/2# print(k)## def cube_root(n):# k = n# while abs(k*k*k-n)>1e-6:# k = k + (k*k*k-n)/3*k*k# print(k)# sqrt(2)# cube_root(8)# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# import random## import numpy as np# from matplotlib import pyplot### class K_Means(object):# # k是分组数;tolerance‘中心点误差';max_iter是迭代次数# def __init__(self, k=2, tolerance=0.0001, max_iter=300):# self.k_ = k# self.tolerance_ = tolerance# self.max_iter_ = max_iter## def fit(self, data):# self.centers_ = {}# for i in range(self.k_):# self.centers_[i] = data[random.randint(0,len(data))]# # print('center', self.centers_)# for i in range(self.max_iter_):# self.clf_ = {} #用于装归属到每个类中的点[k,len(data)]# for i in range(self.k_):# self.clf_[i] = []# # print("质点:",self.centers_)# for feature in data:# distances = [] #装中心点到每个点的距离[k]# for center in self.centers_:# # 欧拉距离# distances.append(np.linalg.norm(feature - self.centers_[center]))# classification = distances.index(min(distances))# self.clf_[classification].append(feature)## # print("分组情况:",self.clf_)# prev_centers = dict(self.centers_)## for c in self.clf_:# self.centers_[c] = np.average(self.clf_[c], axis=0)## # '中心点'是否在误差范围# optimized = True# for center in self.centers_:# org_centers = prev_centers[center]# cur_centers = self.centers_[center]# if np.sum((cur_centers - org_centers) / org_centers * 100.0) > self.tolerance_:# optimized = False# if optimized:# break## def predict(self, p_data):# distances = [np.linalg.norm(p_data - self.centers_[center]) for center in self.centers_]# index = distances.index(min(distances))# return index### if __name__ == '__main__':# x = np.array([[1, 2], [1.5, 1.8], [5, 8], [8, 8], [1, 0.6], [9, 11]])# k_means = K_Means(k=2)# k_means.fit(x)# for center in k_means.centers_:# pyplot.scatter(k_means.centers_[center][0], k_means.centers_[center][1], marker='*', s=150)## for cat in k_means.clf_:# for point in k_means.clf_[cat]:# pyplot.scatter(point[0], point[1], c=('r' if cat == 0 else 'b'))## predict = [[2, 1], [6, 9]]# for feature in predict:# cat = k_means.predict(feature)# pyplot.scatter(feature[0], feature[1], c=('r' if cat == 0 else 'b'), marker='x')## pyplot.show()# def pred(key, value):# if key == 'math':# return value>=40# else:# return value>=60# def func(dic,pred):# # temp = []# # for item in dic:# # if not pred(item,dic[item]):# # temp.append(item)# # for item in temp:# # del dic[item]# # return dic## for k in list(dic.keys()):# if dic[k]<60:# del dic[k]# return dic## if __name__ == '__main__':# dic={'math':66,'c':78,'c++':59,'python':55}# dic = func(dic,pred)# print(dic)## class TreeNode:# def __init__(self):# self.left = None# self.right = None# self.data = None## def insert(tree,x):# temp = TreeNode()# temp.data = x# if tree.data>x:# if tree.left == None:# tree.left = temp# else:# insert(tree.left,x)# else:# if tree.right == None:# tree.right = temp# else:# insert(tree.right,x)## def print_tree(node):# if node is None:# return 0# print_tree(node.left)# print(node.data)# print_tree(node.right)### def sort(lst):# tree = TreeNode()# tree.data = lst[0]# for i in range(1, len(lst)):# insert(tree,lst[i])# print_tree(tree)## sort([5,2,4])# from collections import Iterable, Iterator### class Person(object):# """定义一个人类"""## def __init__(self):# self.name = list()# self.name_num = 0## def add(self, name):# self.name.append(name)## def __iter__(self):# return self# def __next__(self):# # 记忆性返回数据# if self.name_num < len(self.name):# ret = self.name[self.name_num]# self.name_num += 1# return ret# else:# raise StopIteration## person1 = Person()# person1.add("张三")# person1.add("李四")# person1.add("王五")## print("判断是否是可迭代的对象:", isinstance(person1, Iterable))# print("判断是否是迭代器:", isinstance(person1,Iterator))# for name in person1:# print(name)# nums = []# a = 0# b = 1# i = 0# while i < 10:# nums.append(a)# a,b = b,a+b# i += 1# for i in nums:# print(i)## class Fb():# def __init__(self):# self.a = 0# self.b = 1# self.i = 0# def __iter__(self):# return self# def __next__(self):# res = self.a# if self.i<10:# self.a,self.b = self.b,self.a+self.b# self.i += 1# return res# else:# raise StopIteration## fb = Fb()# for i in fb:# print(i)import timedef get_time(func): def wraper(*args, **kwargs): start_time = time.time() result = func(*args, **kwargs) end_time = time.time() print("Spend:", end_time - start_time) return result return wraper@get_timedef _list(n): l = [i*i*i for i in range(n)]@get_timedef _generator(n): ge = (i*i*i for i in range(n))@get_timedef _list_print(l1): for i in l1: print(end='')@get_timedef _ge_print(ge): for i in ge: print(end='')n = 100000print('list 生成耗时:')_list(n)print('生成器 生成耗时:')_generator(n)l1 = [i*i*i for i in range(n)]ge = (i*i*i for i in range(n))# print(l1)# print(ge)print('list遍历耗时:')_list_print(l1)print('生成器遍历耗时:')_ge_print(ge)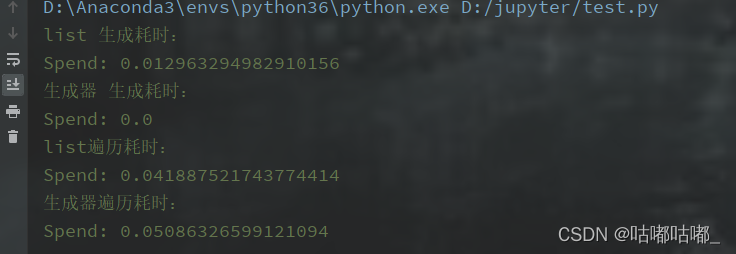
结论:
生成速度:生成器>列表
for_in_循环遍历:1、速度方面:列表>生成器;2、内存占用方面:列表<生成器
总的来说,生成器就是用于降低内存消耗的。
感谢你能够认真阅读完这篇文章,希望小编分享的“python生成器和yield关键字怎么用”这篇文章对大家有帮助,同时也希望大家多多支持编程网,关注编程网Python频道,更多相关知识等着你来学习!
--结束END--
本文标题: python生成器和yield关键字怎么用
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/307061.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0