这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Java Runtime的使用方法是什么,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。前言最近做项目框架,需要在框架结束的时候,关闭服务器连接,清除部分
这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Java Runtime的使用方法是什么,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
最近做项目框架,需要在框架结束的时候,关闭服务器连接,清除部分框架运行lock文件,这里就想到了shutdownhook,顺便学了学Runtime的使用
demo示例,证明在程序正常结束的时候会调用,如果kill -9 那肯定就不会调用了
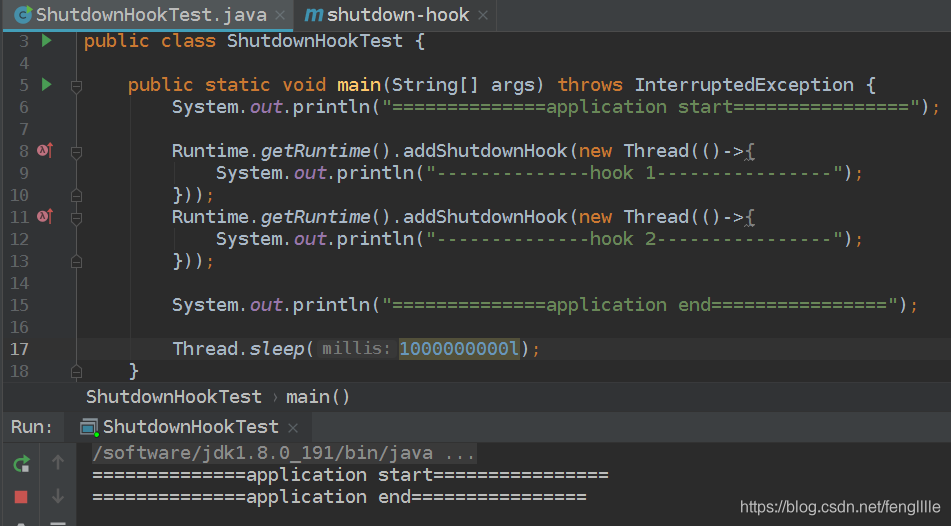
public class ShutdownHookTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("==============application start================"); Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(()->{ System.out.println("--------------hook 1----------------"); })); Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(()->{ System.out.println("--------------hook 2----------------"); })); System.out.println("==============application end================"); }}正常运行结束,结果如下
==============application start================
==============application end================
--------------hook 1----------------
--------------hook 2----------------
Process finished with exit code 0
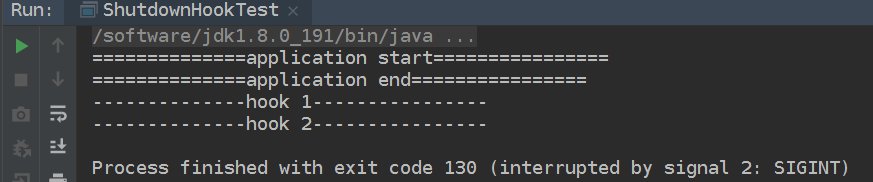
如果暂停,点击下图左下角的正方形红图标,停止正在运行的应用
结果如下,shutdownhook已执行。
shutdownhook可以处理程序正常结束的时候,删除文件,关闭连接等
demo示例如下,比如ls
public class ShutdownHookTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException { Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("ls"); try (InputStream fis = process.getInputStream(); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr)) { String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } }}结果如下
而正常执行结果
但是这个方法有远程执行风险,即在浏览器端通过这个方法执行特定指令,比如执行rm -rf *,结果就很……
但是遇见管道符之后就会失效,什么办法解决,sh -c,但是不能直接用,否则获取到的是TTY窗口信息
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("sh -c ps aux|grep java"); try (InputStream fis = process.getInputStream(); InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr)) { String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } }结果????
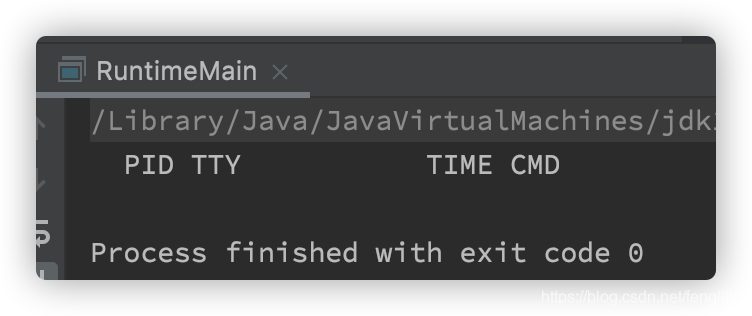
sh -c的参数要分离,不然runtime会认为是一个参数
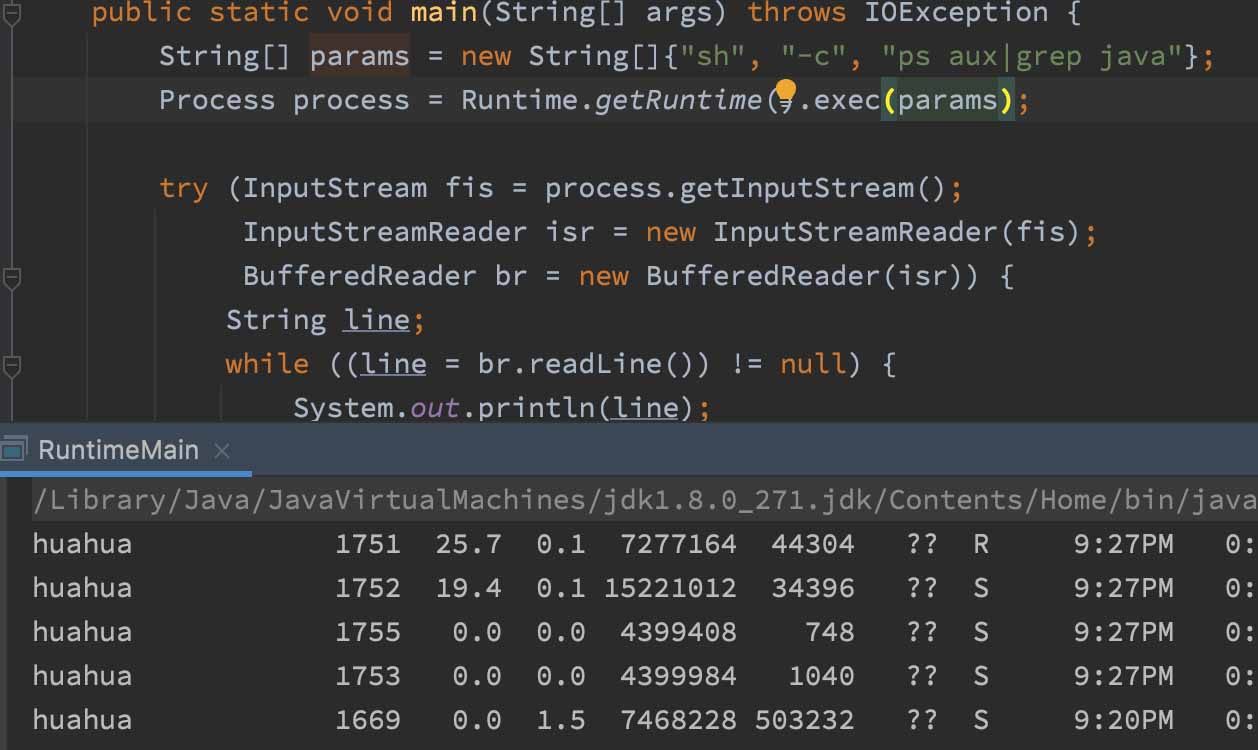
跟踪代码,使用ProcessImpl来执行指令
public Process exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir) throws IOException { return new ProcessBuilder(cmdarray) .environment(envp) .directory(dir) .start(); }ProcessBuilder
// Only for use by ProcessBuilder.start() static Process start(String[] cmdarray, java.util.Map<String,String> environment, String dir, ProcessBuilder.Redirect[] redirects, boolean redirectErrorStream) throws IOException { assert cmdarray != null && cmdarray.length > 0; // Convert arguments to a contiguous block; it's easier to do // memory management in Java than in C. byte[][] args = new byte[cmdarray.length-1][]; int size = args.length; // For added NUL bytes for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { args[i] = cmdarray[i+1].getBytes(); size += args[i].length; } byte[] argBlock = new byte[size]; int i = 0; for (byte[] arg : args) { System.arraycopy(arg, 0, argBlock, i, arg.length); i += arg.length + 1; // No need to write NUL bytes explicitly } int[] envc = new int[1]; byte[] envBlock = ProcessEnvironment.toEnvironmentBlock(environment, envc); int[] std_fds; FileInputStream f0 = null; FileOutputStream f1 = null; FileOutputStream f2 = null; try { if (redirects == null) { std_fds = new int[] { -1, -1, -1 }; } else { std_fds = new int[3]; if (redirects[0] == Redirect.PIPE) std_fds[0] = -1; else if (redirects[0] == Redirect.INHERIT) std_fds[0] = 0; else { f0 = new FileInputStream(redirects[0].file()); std_fds[0] = fdAccess.get(f0.getFD()); } if (redirects[1] == Redirect.PIPE) std_fds[1] = -1; else if (redirects[1] == Redirect.INHERIT) std_fds[1] = 1; else { f1 = new FileOutputStream(redirects[1].file(), redirects[1].append()); std_fds[1] = fdAccess.get(f1.getFD()); } if (redirects[2] == Redirect.PIPE) std_fds[2] = -1; else if (redirects[2] == Redirect.INHERIT) std_fds[2] = 2; else { f2 = new FileOutputStream(redirects[2].file(), redirects[2].append()); std_fds[2] = fdAccess.get(f2.getFD()); } } return new UNIXProcess (toCString(cmdarray[0]), argBlock, args.length, envBlock, envc[0], toCString(dir), std_fds, redirectErrorStream); } finally { // In theory, close() can throw IOException // (although it is rather unlikely to happen here) try { if (f0 != null) f0.close(); } finally { try { if (f1 != null) f1.close(); } finally { if (f2 != null) f2.close(); } } } }new UNIXProcess 环境
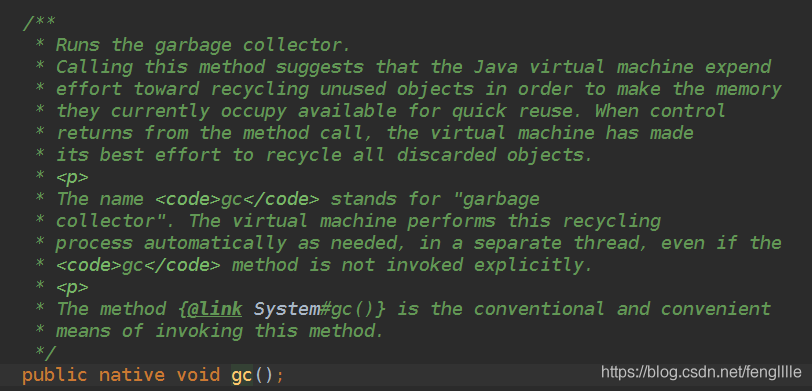
final class UNIXProcess extends Process {Runtime用处非常多,偏底层
比如GC调用
加载jar文件
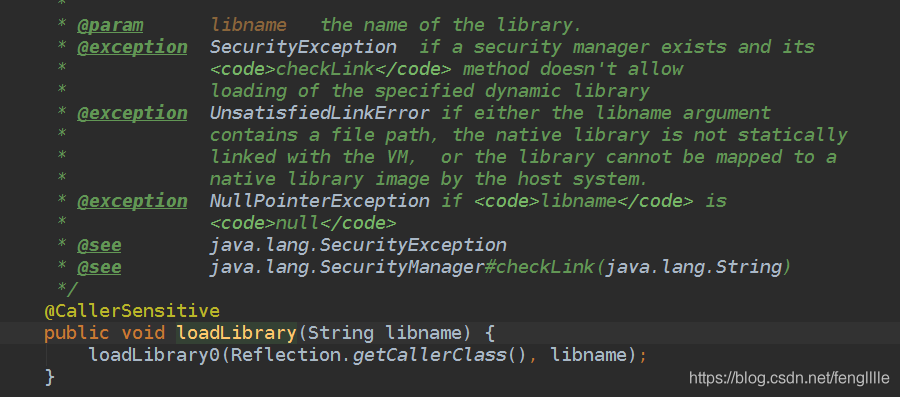
Runtime功能强大,但需要合理利用,很多攻击是通过Runtime执行的漏洞
但是使用shutdownhook还是很方便的,用来做停止任务的后续处理。
关于Java Runtime的使用方法是什么就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
--结束END--
本文标题: Java Runtime的使用方法是什么
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/301987.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
2024-05-24
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0