AudioPolicy&AudioFlinger初始化总体框架初始化步骤简介初始化步骤详细流程分析1、loadConfig()2、ini
AudioFlinger和AudioPolicy两者是Android Audio框架层最主要的两个服务,他们两个是Android框架层的本地服务,在init.rc中启动;
AudioPolicyManager负责音频策略定制者,说白了就相当于Audio系统的司令。
AudioFlinger负责与底层audio alsa进行交互的实现者,那么它就是Audio系统的军官,干苦力的;
总体框架:
两个服务都属于audiOServer进程,严格意义上来说audioserver通过init进程fork出来的,所以它是linux系统中的一个进程。
AudioFlinger:media.audio_flinger
AudioPolicyService:media.audio_policy
 //编译后生成的so命名会根据module name 以及soc名字生成e.g. audio.[module name].[soc name]
//如IMX8的:audio.primary.imx8.so
Speaker
Speaker
//输出混音线程
//输出设备节点
//音频路由
2、initialize()
//编译后生成的so命名会根据module name 以及soc名字生成e.g. audio.[module name].[soc name]
//如IMX8的:audio.primary.imx8.so
Speaker
Speaker
//输出混音线程
//输出设备节点
//音频路由
2、initialize()
好了,上面的都是开胃菜,这个才是硬菜。
来,看下这个大概步骤,心中有谱,码海不慌。
主要是三个步骤:
2.1初始音频路由引擎
audio_policy::EngineInstance *engineInstance = audio_policy::EngineInstance::getInstance();
2.2、加载so 并且打开设备节点
mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(hwModule->getName())
2.3、打开输出流
status_t status = outputDesc->open(nullptr, profileType, address, AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT, AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE,&output);
怕你不信,所以贴了部分代码出来:
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp
status_t AudioPolicyManager::initialize() {
//1、初始音频路由引擎
// Once policy config has been parsed, retrieve an instance of the engine and initialize it.
audio_policy::EngineInstance *engineInstance = audio_policy::EngineInstance::getInstance();
if (!engineInstance) {
ALOGE("%s: Could not get an instance of policy engine", __FUNCTION__);
return NO_INIT;
}
// Retrieve the Policy Manager Interface
mEngine = engineInstance->queryInterface();
if (mEngine == NULL) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to get Policy Engine Interface", __FUNCTION__);
return NO_INIT;
}
mEngine->setObserver(this);
status_t status = mEngine->initCheck();
for (const auto& hwModule : mHwModulesAll) {
//2、加载so 并且打开设备节点
hwModule->setHandle(mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(hwModule->getName()));
mHwModules.push_back(hwModule);
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
// except for direct output streams that are only opened when they are actually
// required by an app.
// This also validates mAvailableOutputDevices list
for (const auto& outProfile : hwModule->getOutputProfiles()) {
//经过一系列有效判断后 创建输出相关参数
sp outputDesc = new SwAudioOutputDescriptor(outProfile,
mpClientInterface);
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = outProfile->getSupportedDevices();
const DeviceVector &devicesForType = supportedDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
String8 address = devicesForType.size() > 0 ? devicesForType.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
audio_io_handle_t output = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
//3、打开输出流
status_t status = outputDesc->open(nullptr, profileType, address,
AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT, AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE, &output);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGW("Cannot open output stream for device %08x on hw module %s",
outputDesc->mDevice,
hwModule->getName());
} else {
for (const auto& dev : supportedDevices) {
ssize_t index = mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(dev);
// give a valid ID to an attached device once confirmed it is reachable
if (index >= 0 && !mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->isAttached()) {
//这个很重要的变量,保存了可用的输出设备,后续会进一步说明
mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->attach(hwModule);
}
}
if (mPrimaryOutput == 0 &&
outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY) {
mPrimaryOutput = outputDesc;
}
addOutput(output, outputDesc);
setOutputDevice(outputDesc, profileType, true, 0, NULL, address);
}
}//end inner for
}//end out for
}
// make sure all attached devices have been allocated a unique ID
好了,是不是也挺简单的,就三步。
2.1、初始音频路由引擎2.1.1 创建路由
audio_policy::EngineInstance
这块有可配置路由和默认路由之分,音频流是根据路由策略进行打开相应的音频路由通路的。这部分内容需要领开一篇进行分析。这是一块很重要的内容,这里暂不展开分析。
loadHwModule(hwModule->getName());
参数是由上面步骤初始配置文件得到,hwModule->getName():如IMX8的根据配置文件:audio.primary.imx8.so
会在vendor/lib/hw/加载文件,如果找不到会依次在system/lib/hw/进行查找。
详细步骤如下:
//注意这个返回值是audio_module_handle_t,这是个线程,这个很重要
//因为后续的播放录音Track都是挂到这个audio_module_handle_t上去的,这个是个线程
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule(const char *name){
1==>进一步调用loadHwModule_l(name);
2====> 再进一步调用到DevicesFactoryHal的openDevice方法打开驱动设备
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
int rc = mDevicesFactoryHal->openDevice(name, &dev);
3=======>调用本地通讯方式的DeviceFactroy实现
//frameworks\av\media\libaudiohal\2.0\DevicesFactoryHalLocal.cpp
status_t DevicesFactoryHalLocal::openDevice(const char *name, sp *device)
3.1=======>继续调用到load_audio_interface
//frameworks\av\media\libaudiohal\2.0\DevicesFactoryHalLocal.cpp
static status_t load_audio_interface(const char *if_name, audio_hw_device_t **dev){
const hw_module_t *mod;
int rc;
rc = hw_get_module_by_class(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, &mod);
if (rc) {
ALOGE("%s couldn't load audio hw module %s.%s (%s)", __func__,
AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, strerror(-rc));
Goto out;
}
rc = audio_hw_device_open(mod, dev);
return rc;
}
4=========>最终会调用到audio.h的方法open,audio_hw_device_open方法会调用设备的open方法
//hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio.h
static inline int audio_hw_device_open(const struct hw_module_t* module,
struct audio_hw_device** device){
return module->methods->open(module, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE,
TO_HW_DEVICE_T_OPEN(device));
}
5==========>最后会调用到
//最终会调用到各自厂商实现的hal层的open方法,代码路径就不放了
static int adev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
到这里,音频设备打开就完毕了;
额外说明一下:mDevicesFactoryHal的初始化:
1、
// mDevicesFactoryHal初始化是在AudioFlinger初始化的时候进行的:
//frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/AudioFlinger.cpp
mDevicesFactoryHal = DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create();
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DevicesFactoryHalInterface.cpp
sp DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create() {
if (hardware::audio::V4_0::IDevicesFactory::getService() != nullptr) {
return new V4_0::DevicesFactoryHalHybrid();
}
if (hardware::audio::V2_0::IDevicesFactory::getService() != nullptr) {
return new DevicesFactoryHalHybrid();
}
return nullptr;
}
DevicesFactoryHalHybrid:Hybrid混合,包含了本地通讯方式,也包含了HIDL通讯方式:
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/impl/DevicesFactoryHalHybrid.cpp
DevicesFactoryHalHybrid::DevicesFactoryHalHybrid(sp hidlFactory)
: mLocalFactory(new DevicesFactoryHalLocal()),
mHidlFactory(new DevicesFactoryHalHidl(hidlFactory)) {
}
status_t DevicesFactoryHalHybrid::openDevice(const char *name, sp *device) {
if (mHidlFactory != 0 && strcmp(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_A2DP, name) != 0 &&
strcmp(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_HEARING_AID, name) != 0) {
return mHidlFactory->openDevice(name, device);
}
return mLocalFactory->openDevice(name, device);
}
到这里,mDevicesFactoryHal的初始化介绍就完毕了。
但是Android 10以后是mDevicesFactoryHal的初始化是这样实现的:
//frameworks/av/media/libaudiohal/DevicesFactoryHalInterface.cpp
sp DevicesFactoryHalInterface::create() {
return createPreferredImpl(
"android.hardware.audio", "IDevicesFactory");
}
通过是从服务中根据名称"android.hardware.audio", "IDevicesFactory"获取的,暂不深究。
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/managerdefault/AudioPolicyManager.cpp AudioPolicyManager::initialize()
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = outProfile->getSupportedDevices();
const DeviceVector &devicesForType = supportedDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
String8 address = devicesForType.size() > 0 ? devicesForType.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
audio_io_handle_t output = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
status_t status = outputDesc->open(nullptr, profileType, address,
AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT, AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_NONE, &output);
//frameworks/av/services/audiopolicy/common/managerdefinitions/src/AudioOutputDescriptor.cpp
status_t SwAudioOutputDescriptor::open(const audio_config_t *config,
const DeviceVector &devices,
audio_stream_type_t stream,
audio_output_flags_t flags,
audio_io_handle_t *output)
{
mDevices = devices;
sp device = devices.getDeviceForOpening();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(device == nullptr,
"%s failed to get device descriptor for opening "
"with the requested devices, all device types: %s",
__func__, dumpDeviceTypes(devices.types()).c_str());
audio_config_t lConfig;
if (config == nullptr) {
lConfig = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
lConfig.sample_rate = mSamplingRate;
lConfig.channel_mask = mChannelMask;
lConfig.fORMat = mFormat;
} else {
lConfig = *config;
}
// if the selected profile is offloaded and no offload info was specified,
// create a default one
if ((mProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD) &&
lConfig.offload_info.format == AUDIO_FORMAT_DEFAULT) {
flags = (audio_output_flags_t)(flags | AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD);
lConfig.offload_info = AUDIO_INFO_INITIALIZER;
lConfig.offload_info.sample_rate = lConfig.sample_rate;
lConfig.offload_info.channel_mask = lConfig.channel_mask;
lConfig.offload_info.format = lConfig.format;
lConfig.offload_info.stream_type = stream;
lConfig.offload_info.duration_us = -1;
lConfig.offload_info.has_video = true; // conservative
lConfig.offload_info.is_streaming = true; // likely
}
mFlags = (audio_output_flags_t)(mFlags | flags);
ALOGV("opening output for device %s profile %p name %s",
mDevices.toString().c_str(), mProfile.get(), mProfile->getName().c_str());
status_t status = mClientInterface->openOutput(mProfile->getModuleHandle(),
output,
&lConfig,
device,
&mLatency,
mFlags);
mClientInterface:是在AudioPolicyManager调用的时候传进去的
AudioPolicyClientInterface *mpClientInterface; // audio policy client interface
到了AudioPolicyClientInterface 这个就明朗了,调用如下:
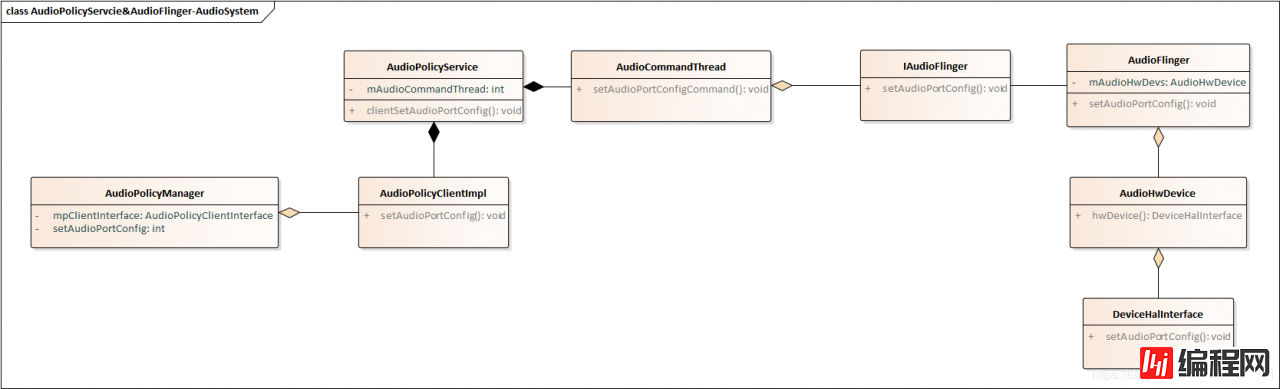
大概流程就是AudioPolicyManager–>AudioPolicyService–>AudioFlinger–>audio hal层了。至此,output 输出流打开成功。
最后将已经打开的输出流和输出设备保存到相应的数组里面,后续有流需要播出的时候直接进行查找,如果查找不到会尝试向底层查询,如果查询支持将会打开,如果查询不到,则会将其流类型改变并且将其加入到默认输出流里面进行播放处理。
小结:
这里的一切都是为音频播放做准备,后续将介绍音频路由部分。
--结束END--
本文标题: Android P Audio系统笔记:AudioPolicy&AudioFlinger初始化
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/29677.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-21
2023-10-28
2023-10-28
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0