Android Service类与生命周期 Service是Android四大组件与Activity最相似的组件,都代表可执行的程序,区别在于Service一直在后
Android Service类与生命周期
Service是Android四大组件与Activity最相似的组件,都代表可执行的程序,区别在于Service一直在后台运行且没有用户界面。
1.Service的类图和生命周期
先来看看Service的类图:
接下来看看Service的生命周期:
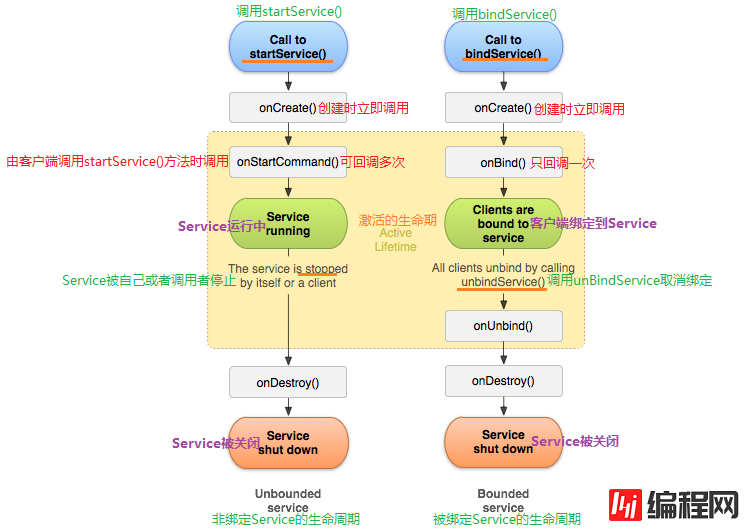
2.开发Service
(1)开发Service需要两步:
第1步:定义子类,继承Service
第2步:在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置Service
(2)创建Service
public class MyService extends Service {
// 必须实现,绑定该Service时被回调
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
// Service被创建时回调
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// 定义相关业务逻辑
System.out.println("Service is Created");
}
// Service被启动时回调
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// 定义相关业务逻辑
System.out.println("Service is Started");
return START_STICKY;
}
// Service被关闭之前回调
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service is Destroyed");
}
}
(3)配置Service
<application
...
<!-- 配置一个Service组件 -->
<service android:name=".MyService">
<intent-filter>
<!-- 为该Service组件的intent-filter配置action -->
<action android:name="com.GC.service.MY_SERVICE" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
接下来就可以运行Service了。
(4)启动和停止Service(一般方式)
// 创建启动Service的Intent
final Intent intent = new Intent();
// 为Intent设置Action属性
intent.setAction("com.gc.service.MY_SERVICE");
...
// 启动指定Serivce
startService(intent);
...
// 停止指定Serivce
stopService(intent);
当程序使用startService()、stopService()启动、关闭Service时,Service与访问者之间无法进行通信、数据交换,故下面介绍另一种方式启动和停止Service。
(5)启动和停止Service(绑定Service并与之通信)
如果Service和访问者之间需要进行方法调用或数据交换,则应该使用bindService()和unbindService()方法启动、停止Service。
bindService(Intent intent, ServiceConnection conn, int flags),三个参数如下:
intent:指定要启动的Service
conn:用于监听访问者与Service之间的连接情况,当访问者与Service之间连接成功时将回调该ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)方法;反之回调该ServiceConnection对象的onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)方法(主动调用unbindService方法断开连接时则不回调)
flags:指定绑定时是否创建Service,0:不自动创建;BIND_AUTO_CREATE:自动创建
注意:ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected方法中有一个IBinder对象,该对象即可实现与绑定Service之间的通信。
在绑定本地Service的情况下,onBind(Intent intent)方法所返回的IBinder对象将会传给ServiceConnection对象里onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)方法的service参数,这样访问者就可以通过该IBinder对象与Service进行通信。
实际开发通常会采用继承Binder(IBinder的实现类)的方式实现自己的IBinder对象。
public class MyService extends Service {
private int count;
// 定义onBinder方法所返回的对象
private MyBinder binder = new MyBinder();
// 通过继承Binder来实现IBinder类
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
public int getCount() {
return count; // 获取Service的运行状态
}
}
// 必须实现,绑定该Service时被回调
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
System.out.println("Service is Binded");
return binder; // 返回IBinder对象
}
// Service被创建时回调
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service is Created");
count = 100;
}
// Service被断开连接时回调
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
System.out.println("Service is Unbinded");
return true;
}
// Service被关闭之前回调
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service is Destroyed");
}
}
接下来定义一个Activity来绑定该Service,并在该Activity中通过MyBinder对象访问Service的内部状态。
在该Activity绑定该Service后,该Activity还可以通过MyBinder对象来获取Service的运行状态。对于Service的onBind(Intent intent)方法返回的IBinder对象来说,Service允许客户端通过该IBinder对象来访问Service内部的数据,这样即可实现客户端与Service之间的通信。
public class MyServiceTest extends Activity {
// Service的IBinder对象
MyService.MyBinder binder;
// 定义一个ServiceConnection对象
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
// 当该Activity与Service连接成功时回调
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// 获取Service的onBind方法所返回的MyBinder对象
binder = (MyService.MyBinder) service;
}
// 当该Activity与Service断开连接时回调
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
...
// 创建启动Service的Intent
final Intent intent = new Intent();
// 为Intent设置Action属性
intent.setAction("com.gc.service.MY_SERVICE");
// 绑定指定Serivce
bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
...
binder.getCount(); // 获取Serivce的count值
...
// 解除绑定Serivce
unbindService(conn);
}
}
感谢阅读,希望能帮助到大家,谢谢大家对本站的支持!
您可能感兴趣的文章:详解Android中的ServiceAndroid IntentService详解及使用实例Android 如何保证service在后台不被killandroid使用NotificationListenerService监听通知栏消息Android实现微信自动向附近的人打招呼(AccessibilityService)Android AccessibilityService实现微信抢红包插件Android Service中使用Toast无法正常显示问题的解决方法Android基于service实现音乐的后台播放功能示例Android Service的启动过程分析
--结束END--
本文标题: Android Service类与生命周期详细介绍
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/28237.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-21
2023-10-28
2023-10-28
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0