欢迎大家来学习本节内容,前几节我们已经学习了其他几种自定义控件,分别是Andriod 自定义控件之音频条及 Andriod 自定义控件之创建可以复用的组合控件还没有学习的同学请
欢迎大家来学习本节内容,前几节我们已经学习了其他几种自定义控件,分别是Andriod 自定义控件之音频条及 Andriod 自定义控件之创建可以复用的组合控件还没有学习的同学请先去学习下,因为本节将使用到上几节所讲述的内容。
在学习新内容之前,我们先来弄清楚两个问题:
1 . 什么是ViewGroup?
ViewGroup是一种容器。它包含零个或以上的View及子View。

2 . ViewGroup有什么作用?
ViewGroup内部可以用来存放多个View控件,并且根据自身的测量模式,来测量View子控件,并且决定View子控件的位置。这在下面会逐步讲解它是怎么测量及决定子控件大小和位置的。
ok,弄清楚了这两个问题,那么下面我们来学习下自定义ViewGroup吧。
首先和之前几节一样,先来继承ViewGroup,并重写它们的构造方法。
public class CustomViewGroup extends ViewGroup{
public CustomViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context,null);
}
public CustomViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs,0);
}
public CustomViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
}
在上面两个问题,我们知道,ViewGroup它是一个容器,它是用来存放和管理子控件的,并且子控件的测量方式是根据它的测量模式来进行的,所以我们必须重写它的onMeasure(),在该方法中进行对子View的大小进行测量,代码如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(children,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
其上代码,我们重写了onMeasure(),在方法里面,我们首先先获取ViewGroup中的子View的个数,然后遍历它所有的子View,得到每一个子View,调用measureChild()放来,来对子View进行测量。刚才提到子View的测量是根据ViewGroup所提供的测量模式来进行来,所以在measureChild()方法中,把ViewGroup的widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec和子View一起传进去了,我们可以跟进去看看是不是和我们所说的一样。
measureChild()方法源码:
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
measureChild()源码方法里面很好理解,它首先得到子View的LayoutParams,然后根据ViewGroup传递进来的宽高属性值和自身的LayoutParams 的宽高属性值及自身padding属性值分别调用getChildMeasureSpec()方法获取到子View的测量。由该方法我们也知道ViewGroup中在测量子View的大小时,测量结果分别是由父节点的测量模式和子View本身的LayoutParams及padding所决定的。
下面我们再来看看getChildMeasureSpec()方法的源码,看看它是怎么获取测量结果的。
getChildMeasureSpec()方法源码:
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
该方法也很好理解:首先是获取父节点(这里是ViewGroup)的测量模式和测量的大小,并根据测量的大小值与子View自身的padding属性值相比较取最大值得到一个size的值。
然后根据父节点的测量模式分别再来判定子View的LayoutParams属性值,根据LayoutParams的属性值从而获取到子View测量的大小和模式,知道了ziView的测量模式和大小就能决定子View的大小了。
ok,子View的测量我们已经完全明白了,那么接下来,我们再来分析一下ViewGroup是怎样给子View定位的,首先我们也是必须先重写onLayout()方法,代码如下:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int preHeight = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
int cHeight = children.getMeasuredHeight();
if(children.getVisibility() != View.GoNE){
children.layout(l, preHeight, r,preHeight += cHeight);
}
}
}
很好理解,给子View定位,首先必须知道有多少个子View才行,所以我们先得到子View的数量,然后遍历获取每个子View。其实在定位子View的layout()方法中,系统并没有给出具体的定位方法,而是给了我们最大的限度来自己定义,下面来看下layout源码:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy =
(ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
}
在上面一段代码中,最关键个就是setFrame(l, t, r, b);这个方法,它主要是来定位子View的四个顶点左右坐标的,然后关键的定位方法是在onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);这个方法中,跟进去看看
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
一看吓一跳,空的,哈哈,这也就是我上面说的,系统给了我们最大的自由,让我们自己根据需求去定义了。
而我这里是根据子View的高度让它们竖直顺序的排列下来。
View children = getChildAt(i);
int cHeight = children.getMeasuredHeight();
if(children.getVisibility() != View.GONE){
children.layout(l, preHeight, r,preHeight += cHeight);
定义一个记录上一个View的高度的变量,每次遍历以后都让它加上当前的View高度,由此就可以竖直依次地排列了每个子View,从而实现了子View的定义。
好了,讲了这么多,现在来看看效果吧,我们就拿之前做的自定义View作为它的子View吧:
custom_viewgroup.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.sanhuimusic.mycustomview.view.CustomViewGroup
Android:background="#999999"
xmlns:android="Http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/customViewGroup"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.sanhuimusic.mycustomview.view.CompositeViews
android:background="#999999"
android:id="@+id/topBar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
custom:titleText="@string/titleText"
custom:titleColor="#000000"
custom:titleTextSize="@dimen/titleTextSize"
custom:titleBackground="#999999"
custom:leftText="@string/leftText"
custom:leftTextColor="#FFFFFF"
custom:leftBackground="#666666"
custom:leftTextSize="@dimen/leftTextSize"
custom:rightText="@string/rightText"
custom:rightTextColor="#FFFFFF"
custom:rightBackground="#666666"
custom:rightTextSize="@dimen/rightTextSize"
/>
<com.sanhuimusic.mycustomview.view.AudioBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</com.sanhuimusic.mycustomview.view.CustomViewGroup>
MainActivity:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private CompositeViews topBar;
private Context mContext;
private CustomViewGroup mViewGroupContainer;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.custom_viewgroup);
mContext = this;
init();
}
private void init() {
mViewGroupContainer = (CustomViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.customViewGroup);
topBar = (CompositeViews)findViewById(R.id.topBar);
topBar.setOnTopBarClickListener(new CompositeViews.TopBarClickListener(){
@Override
public void leftClickListener() {
ToastUtil.makeText(MainActivity.this,"您点击了返回键",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void rightClickListener() {
ToastUtil.makeText(MainActivity.this,"您点击了搜索键",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
效果图:
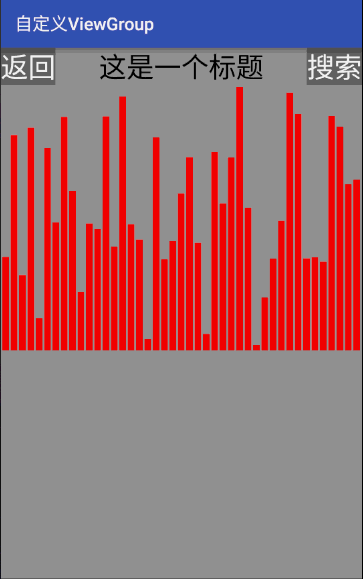
哈哈,是不是每个子View都按照我们所说的竖直依次排列下来了呢。正开心呢,然后突然冒出来一个想法,学习过Andriod 自定义控件之音频条这篇文章的你,会记得当时在定义全新的View时会遇到当我们的布局文件使用的是wrap_content时,View是不直接支持的,需要我们特殊的处理才能正确支持,而我们现在的 ViewGroup是不是也是这样的呢,赶快尝试一下。一尝试,坏了,果然不支持wrap_content。
所以,在自定义ViewGroup时,我们必须要注意以下几个问题:
1. 必须让ViewGroup支持wrap_content的情景下的布局。
2. 也需要支持本身的padding属性。
好,下面我们来一点一点的完善它。
1 . 我们让它先支持wrap_content。
这需要我们在onMeasure()方法中多出一些必要的改动。让它支持自身wrap_content那就需要我们对它惊醒测量,根据测量方式获取到测量大小,然后再调用setMeasuredDimension()决定显示大小。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(children,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
}
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int mWidth = 0;
int mHeight = 0;
int mMaxWidth = 0;
if(widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
mWidth += children.getMeasuredWidth();
mHeight += children.getMeasuredHeight();
}
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
} else if(widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
mMaxWidth = Math.max(mMaxWidth,children.getMeasuredWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(mMaxWidth,heightSpecSize);
} else if(heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
mHeight += children.getMeasuredHeight();
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize,mHeight);
}
}
我们再原来的基础上添加了可以支持wrap_content的代码,然后根据具体的情况进行获取大小。分为三种情况:
当宽高属性都为wrap_content时,分别获取到子View的宽高并相加取得总宽高,在调用setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight)直接设置即可; 当宽属性都为wrap_content时,分别获取到子View的宽并获取其中最大值,在调用setMeasuredDimension(mMaxWidth,heightSpecSize)直接设置即可; 当高属性都为wrap_content时,分别获取到子View的高并相加取得总高,在调用setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize,mHeight)直接设置即可。好,来看看是否可以达到我们的要求。

显然已达到目标。
2 . 需要支持本身的padding属性。
首先我们先获取到padding值,如下:
leftPadding = getPaddingLeft();
topPadding = getPaddingTop();
rightPadding = getPaddingRight();
bottomPadding = getPaddingBottom();然后分别在设置大小的地方给加上这些属性值,如下:
if(widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
mWidth += children.getMeasuredWidth();
mHeight += children.getMeasuredHeight();
}
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth + leftPadding + rightPadding, mHeight
+ topPadding + bottomPadding);
} else if(widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
mMaxWidth = Math.max(mMaxWidth,children.getMeasuredWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(mMaxWidth + leftPadding + rightPadding, heightSpecSize + topPadding + bottomPadding);
} else if(heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
mHeight += children.getMeasuredHeight();
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize + leftPadding + rightPadding, mHeight + topPadding + bottomPadding);
}
最后在onlayout()方法中给添加属性值:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int preHeight = topPadding;
for(int i = 0 ; i < childCount ; i ++){
View children = getChildAt(i);
int cHeight = children.getMeasuredHeight();
if(children.getVisibility() != View.GONE){
children.layout(l + leftPadding, preHeight, r + rightPadding, preHeight += cHeight);
}
}
}
代码很简单,不再让preHeight = 0 了,而是直接设置为topPadding,最后在layout中也把属性值添加进来,看看结果。
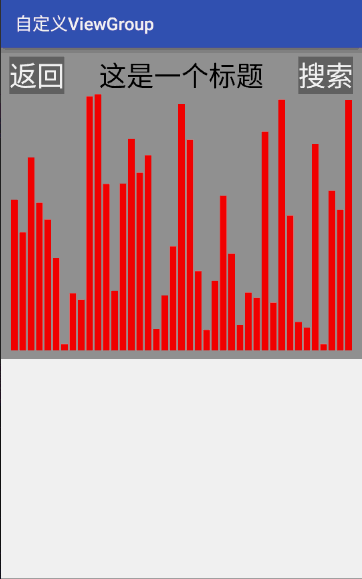
其实除了以上两个问题需要注意的,还有其他也是需要关注的,比如说是支持子View的margin属性等,大致和解决padding属性一样的思路,大家可以尝试实现下。
好了,整个自定义ViewGroup的内容都讲完了,当然我们只是讲述了UI的显示,并没有谈及到功能的添加和实现。从上面可以看出,自定义ViewGroup要比自定义View复杂很多,但是只要一步一步的来完善还是可以实现不同的UI展示的。
从这几节自定义控件学习中,大家一定学到了很多知识,然后对自定义控件也不是那么怕了,同时也可以实现自己想要的各种UI啦,接下来我会总结下自定义控件中所需要使用的其他技术和知识下,让大家更好的加深印象。
好,今天就学习到这里吧,happy!
您可能感兴趣的文章:从源码解析Android中View的容器ViewGroupAndroid中标签容器控件的实例详解Android应用开发中自定义ViewGroup视图容器的教程Android自定义ViewGroup实现标签流容器FlowLayoutAndroid中实现多行、水平滚动的分页的Gridview实例源码android listview 水平滚动和垂直滚动的小例子Android使用RecyclerView实现水平滚动控件Android实现Activity水平和垂直滚动条的方法详解Android使GridView横向水平滚动的实现方式Android使用Recyclerview实现图片水平自动循环滚动效果Android开发实现自定义水平滚动的容器示例
--结束END--
本文标题: Android自定义控件之继承ViewGroup创建新容器
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/23007.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-21
2023-10-28
2023-10-28
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
2023-10-27
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0