Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
nginx+uwsgi+djangorestframework+flower+celery+redis配置如下:nginx server配置, 没有https,注释掉ssl开头配置即可.server { &
nginx+uwsgi+djangorestframework+flower+celery+redis配置如下:
nginx server配置, 没有https,注释掉ssl开头配置即可.
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost; # 域名
ssl_certificate your crt; # 证书crt
ssl_certificate_key your key; # 证书key
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:AES256-SHA256:RC4:HIGH:!MD5:!aNULL:!eNULL:!NULL:!DH:!EDH:!AESGCM;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# 指定项目路径uwsgi
location / {
include weixin_uwsgi_params; # 导入一个Nginx模块他是用来和uWSGI进行通讯的
uwsgi_connect_timeout 180; # 设置连接uWSGI超时时间
uwsgi_pass unix:/data/www/weixin_api/weixin.sock; # 指定uwsgi的sock文件所有动态请求就会直接丢给他
}
# 指定静态文件路径
location /static/ {
alias /data/www/weixin_api/static/;
}
}安装uwsgi
pip3 install uwsgi
创建一个uwsgi.ini配置文件,配置如下:
# uwsgi使用配置文件启动
[uwsgi]
# 项目目录
chdir=/data/www/weixin_api/
# 指定项目的application
wsgi-file=weixin_api/weixin/wsgi.py
# 指定sock的文件路径
Socket=/data/www/weixin_api/weixin.sock
# 进程个数
workers=8
pidfile=/data/www/weixin_api/script/uwsgi.pid
# 指定IP端口
Http=0.0.0.0:8006
# 指定静态文件
static-map=/static=/data/www/weixin_api/static
# 启动uwsgi的用户名和用户组
uid=root
gid=root
# 启用主进程
master=true
# 自动移除unix Socket和pid文件当服务停止的时候
vacuum=true
# 序列化接受的内容,如果可能的话
thunder-lock=true
# 启用线程
enable-threads=true
# 设置自中断时间
harakiri=30
# 设置缓冲
post-buffering=8192
# 设置日志目录
daemonize=/data/www/weixin_api/script/uwsgi.log
wsgi-file = /data/www/weixin_api/weixin/wsgi.pyuwsgi的关闭与启动,可以写一个shell脚本来控制
创建一个uwsgi_restart.sh,如下:
#!/bin/bash
API_INI="/data/www/API_rest_framework/script/uwsgi.ini"
WEIXIN_INI="/data/www/weixin_api/script/uwsgi.ini"
UWSGI="/usr/local/python36/bin/uwsgi"
PSID="ps aux | grep "uwsgi"| grep -v "grep" | wc -l"
if [ ! -n "$1" ]
then
content="Usages: sh uwsGIServer.sh [start|stop|restart]"
echo -e "\033[31m $content \033[0m"
exit 0
fi
if [ $1 = start ]
then
if [ `eval $PSID` -gt 4 ]
then
content="uwsgi is running!"
echo -e "\033[32m $content \033[0m"
exit 0
else
$UWSGI $API_INI
$UWSGI $WEIXIN_INI
content="Start uwsgi service [OK]"
echo -e "\033[32m $content \033[0m"
fi
elif [ $1 = stop ];then
if [ `eval $PSID` -gt 4 ];then
killall -9 uwsgi
fi
content="Stop uwsgi service [OK]"
echo -e "\033[32m $content \033[0m"
elif [ $1 = restart ];then
if [ `eval $PSID` -gt 4 ];then
killall -9 uwsgi
fi
$UWSGI --ini $API_INI
$UWSGI --ini $WEIXIN_INI
content="Restart uwsgi service [OK]"
echo -e "\033[32m $content \033[0m"
else
content="Usages: sh uwsgiserver.sh [start|stop|restart]"
echo -e "\033[31m $content \033[0m"
fidjangorestframework安装
pip3 install Django
pip3 install djanGorestframework
在settings配置文件的 installed_apps添加rest_framework
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'application.apps.ApplicationConfig',
'rest_framework',
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': "rest_framework.versioning.URLPathVersioning",
'DEFAULT_VERSION': 'v1',
'ALLOWED_VERSIONS': ['v1', 'v2'],
'VERSION_PARAM': 'version',
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination',
'PAGE_SIZE': 100, # 默认分页大小
'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': ('rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer', ),
}接口代码示例:
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from django.http import jsonResponse
class UploadFile(APIView):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
请求到来之后,都要执行dispatch方法,dispatch方法根据请求方式不同触发 get/post/方法
"""
return super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
pass
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
passcelery介绍
实时处理和任务调度的分布式任务队列。
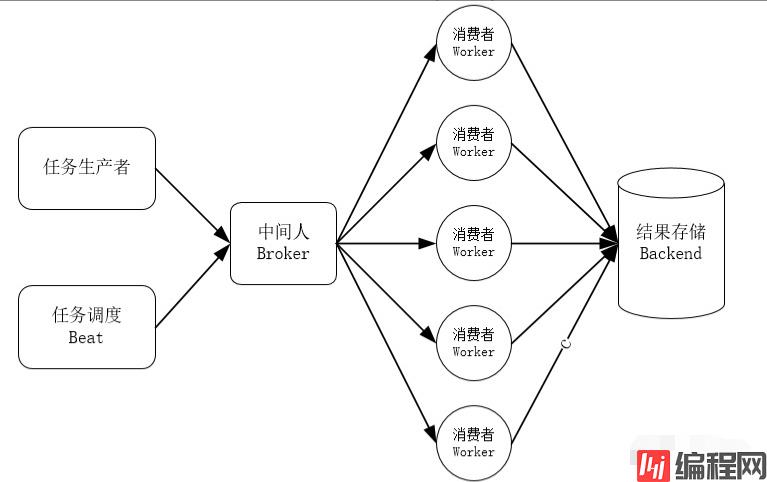
用户使用 Celery 产生任务,借用中间人来传递任务,任务执行单元从中间人那里消费任务。任务执行单元可以单机部署,也可以分布式部署,因此 Celery 是一个高可用的生产者消费者模型的异步任务队列。你可以将你的任务交给 Celery 处理,也可以让 Celery 自动按 crontab 那样去自动调度任务,然后去做其他事情,你可以随时查看任务执行的状态,也可以让 Celery 执行完成后自动把执行结果告诉你。
使用Celery的常见场景如下:
1.高并发的请求任务。互联网已经普及,人们的衣食住行中产生的交易都可以线上进行,这就避免不了某些时间极高的并发任务请求,如公司中常见的购买理财、学生缴费,在理财产品投放市场后、开学前的一段时间,交易量猛增,确认交易时间较长,此时可以把交易请求任务交给 Celery 去异步执行,执行完再将结果返回给用户。用户提交后不需要等待,任务完成后会通知到用户(购买成功或缴费成功),提高了网站的整体吞吐量和响应时间,几乎不需要增加硬件成本即可满足高并发。
2.定时任务。在云计算,大数据,集群等技术越来越普及,生产环境的机器也越来越多,定时任务是避免不了的,如果每台机器上运行着自己的 crontab 任务,管理起来相当麻烦,例如当进行灾备切换时,某些 crontab 任务可能需要单独手工调起,给运维人员造成极大的麻烦,有了 Celery ,你可以集中管理所有机器的定时任务,而且灾备无论何时切换,crontab 任务总能正确的执行。
3.异步任务。 一些耗时较长的操作,比如 I/O 操作,网络请求,可以交给 Celery 去异步执行,用户提交后可以做其他事情,当任务完成后将结果返回用户即可,可提高用户体验。比如发送短信/邮件、推送消息、清理/设置缓存等
Celery 的优点
1. 纯 python 编写,开源。这已经是站在巨人的肩膀上了,虽然 Celery 是由纯 Python 编写的,但协议可以用任何语言实现。迄今,已有 Ruby 实现的 RCelery 、node.js 实现的 node-celery 以及一个 PHP 客户端 ,语言互通也可以通过 using WEBhooks 实现。
2. 灵活的配置。默认的配置已经满足绝大多数需求,因此你不需要编写配置文件基本就可以使用,当然如果有个性化地定制,你可以选择使用配置文件,也可以将配置写在源代码文件里。
3. 方便监控。任务的所有状态,均在你的掌握之下。
4. 完善的错误处理。
5. 灵活的任务队列和任务路由。你可以非常方便地将一个任务运行在你指定的队列上,这叫任务路由。
Celery 的架构:
Celery支持不同的方式存储任务的结果,包括RabbitMQ,AMQP,Redis,memcached,mongoDB,sqlAlchemy等
celery使用-安装:
环境是:Centos-7.6 + python-3.6.8 + redis-5.0.4
pip install celery
pip install eventlet
pip install redis
目录结构,在django settings目录下,创建一个celery.py文件
├── weixin
│ ├── celery.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── __pycache__
│ ├── settings.py
│ ├── urls.py
│ └── wsgi.py
celery.py内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import absolute_import, unicode_literals
import os
from celery import Celery
# set the default Django settings module for the 'API' program.
os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'weixin.settings')
app = Celery('celery')
# 设置时区
app.conf.timezone = 'Asia/Shanghai'
app.conf.enable_utc = False
#app.conf.enable_utc = True
# Using a string here means the worker don't have to serialize
# the configuration object to child processes.
# - namespace='CELERY' means all celery-related configuration keys
# should have a `CELERY_` prefix.
# 使用django的settings设置
app.config_from_object('django.conf:settings')
# Load task modules from all registered Django app configs.
# Celery 会自动发现模块
app.autodiscover_tasks()
@app.task(bind=True)
def debug_task(self):
print('Request: {0!r}'.fORMat(self.request))同目录下面更改__init__.py的内容如下:
from __future__ import absolute_import, unicode_literals
# This will make sure the app is always imported when
# Django starts so that shared_task will use this app.
from .celery import app as celery_app
__all__ = ['celery_app']在django settings最后添加内容如下:
# django celery settings
# 如redis中设置有密码,则需加上passWord,后面的/5 指的是使用redis的哪个库
BROKER_URL = 'redis://:password@127.0.0.1:9999/5'
CELERY_RESULT_BACKEND = 'redis://:password@127.0.0.1:9999/5'
CELERY_ACCEPT_CONTENT = ['json']
CELERY_TASK_SERIALIZER = 'json'
CELERY_RESULT_SERIALIZER = 'json'
#CELERY_ENABLE_UTC = False
#CELERY_TIMEZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'
# celery worker并发数
CELERYD_CONCURRENCY = 20
# 非常重要,有些情况下可以防止死锁
CELERYD_FORCE_EXECV = True
# 每个worker最大执行任务数
CELERYD_MAX_TASKS_PER_CHILD = 100创建celery job,目录结构如下:
├── celery_job
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── send_mail.py
创建一个send_mail.py内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.mime.application import MIMEApplication
from celery import task
@task(bind=True)
def send_email(self, html_path, file_name_path, send_to_user, send_mail_subject, send_mail_body):
"""
发送邮件
:param file_name_path: html存放路径
:param send_to_user: 收件人
:param send_mail_subject: 邮件主题
:param send_mail_body: excel是否转html
:return:
"""
send_to_user = send_to_user.split(',')
if send_mail_body != 'True':
html_content = ""
else:
with open(html_path, encoding='utf-8', mode='r') as fp:
html_content = fp.read()
fp.close()
mail_info = {
"from": "发件人邮箱",
"to": "收件人邮箱",
"hostname": "smtp hostname",
"username": "邮箱账号",
"password": '邮箱密码',
"mail_subject": send_mail_subject, # 邮件主题名字
"mail_text": html_content,
"mail_encoding": "utf-8",
"mail_port": '587',
}
try:
msg = MIMEMultipart()
msg["Subject"] = mail_info.get('mail_subject')
msg["From"] = mail_info.get('from')
msg["To"] = ','.join(mail_info.get('to'))
part = MIMEText(mail_info.get('mail_text'), _subtype='html', _charset='utf-8')
msg.attach(part)
# xlsx类型附件
part = MIMEApplication(open(file_name_path, 'rb').read())
part.add_header('Content-Disposition', 'attachment', filename='{}.xlsx'.format(send_mail_subject))
msg.attach(part)
s = smtplib.SMTP(mail_info.get('hostname'), mail_info.get('mail_port'), timeout=20)
s.ehlo()
s.starttls()
s.login(mail_info.get('username'), mail_info.get('password')) # 登陆服务器
s.sendmail(mail_info.get('username'), mail_info.get('to'), msg.as_string()) # 发送邮件
# return {'status': 'success', 'msg': 'Send mail success'}
return True
except Exception as e:
"""
邮件发送失败,使用retry进行重试
retry的参数可以有:
exc:指定抛出的异常
throw:重试时是否通知worker是重试任务
eta:指定重试的时间/日期
countdown:在多久之后重试(每多少秒重试一次)
max_retries:最大重试次数
"""
raise self.retry(exc=e, countdown=10, max_retries=6)django views配置视图函数
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from django.http import JsonResponse
import hashlib
import os
from application.celery_job.send_mail import send_email
class DataReport(APIView):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.key = 'your key'
# 允许访问接口的邮箱
self.auth_user = ['xxxxx', 'xxxxx']
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
def get(self, request):
return JsonResponse({'status': 'error', 'msg': 'Is not get API'})
def post(self, request):
print(request.data)
domain_name = request.META['HTTP_HOST'] # 获取域名
token = request.data.get('token') # token
excel_file = request.FILES.get("excel_file") # 获取文件内容
send_mail = request.data.get("send_mail") # 是否发邮件(True or False)
send_to_user = request.data.get('send_to_user') # 收件人邮箱(一个或多个)
send_mail_subject = request.data.get('send_mail_subject') # 邮件主题
send_mail_body = request.data.get('send_mail_body') # 邮件正文_html(True or False)
if not token:
return JsonResponse({'status': 'error', 'msg': 'Token cannot be empty'})
ret = self.auth_token(token)
if not ret:
return JsonResponse({'status': 'error', 'msg': 'Auth token error'})
if send_mail:
if not send_to_user:
return JsonResponse({'status': 'error', 'msg': 'The recipient cannot be empty'})
if not send_mail_subject:
return JsonResponse({'status': 'error', 'msg': 'Mail subject cannot be empty'})
# 发送邮件
if send_mail:
result3 = send_email.delay(html_path, file_name_path, send_to_user, send_mail_subject, send_mail_body)
task_id = result3.task_id
return JsonResponse({'status': 'success', 'task_id': task_id})
def auth_token(self, token):
"""
验证token是否有效
:param token:
:return: True or False
"""
# 加密后的token_list
token_list = []
for i in self.auth_user:
m = hashlib.md5(i[::-1][::2].encode('utf-8'))
m.update(self.key.encode('utf-8'))
token_list.append(m.hexdigest())
for i in token_list:
if i == token:
return True
else:
return Falsedjango urls配置访问路径
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from application.views.weixin_api.data_report import DataReport
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.views import static
from django.conf import settings
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^static/(?P<path>.*)$', static.serve, {'document_root': settings.STATIC_ROOT}, name='static'),
url(r'^data_report$', DataReport().as_view(), name='data_report'),
]启动程序:
nginx : /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
uwsgi: /usr/local/python36/bin/uwsgi --ini /data/www/project/script/uwsgi.ini
redis: /usr/local/redis/redis-server /usr/local/redis/redis.conf
## -c 20 指得是并发数为20
celery: celery -A /data/www/project/weixin worker -l info -c 20 -P eventlet
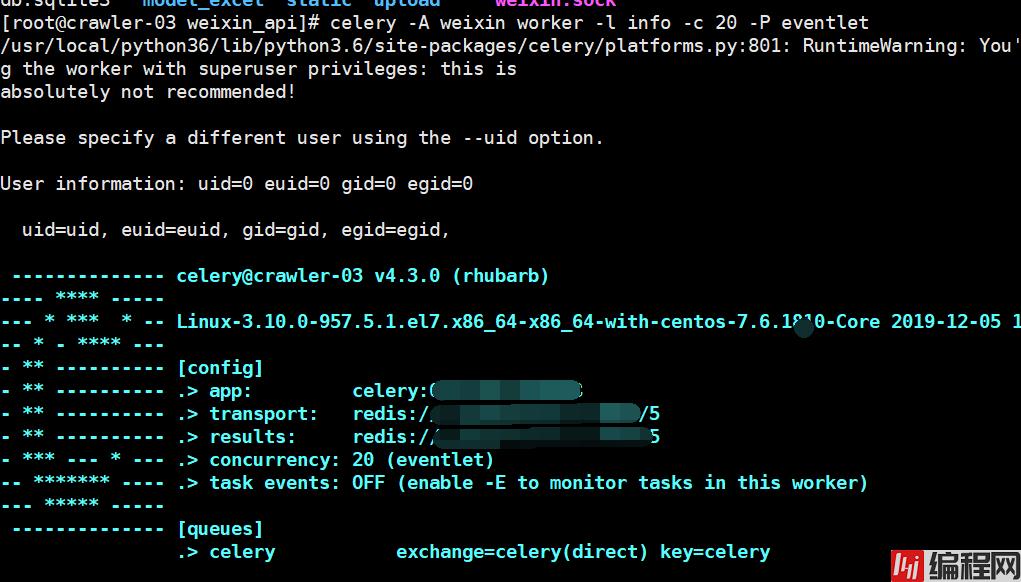
安装flower: 实时监控celery任务状态
pip install flower
启动flower
# --max_tasks 为页面允许存储的最大数
flower --port=7788 --broker=redis://:password@123@127.0.0.1:9999/5 --broker_api=redis://:password@127.0.0.1:9999/5 --max_tasks=1000000
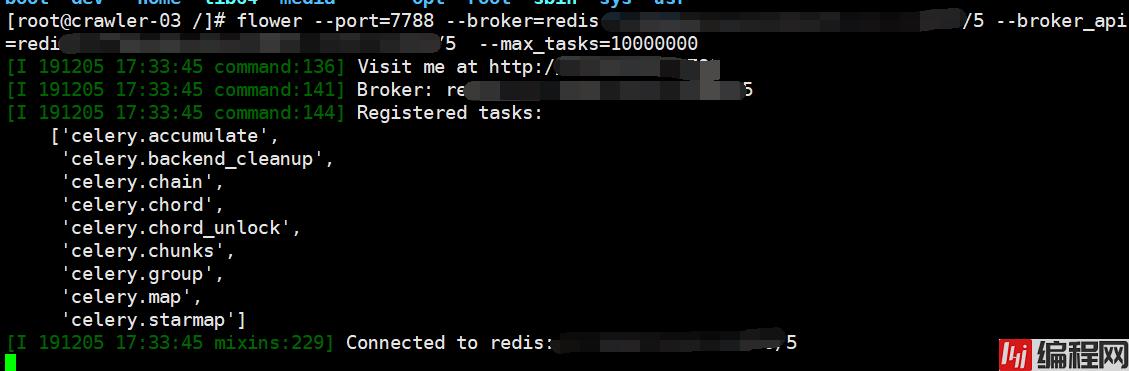
执行任务,查看flower监控的状态:
访问页面: http://ip:7788
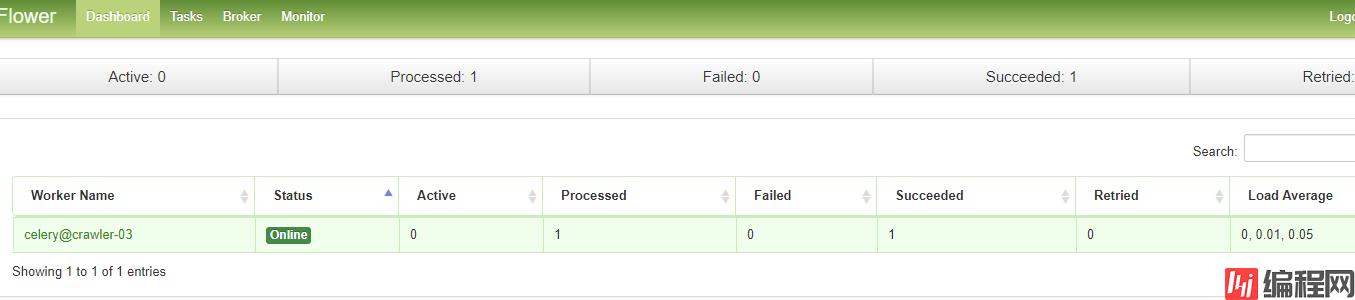
查看任务状态
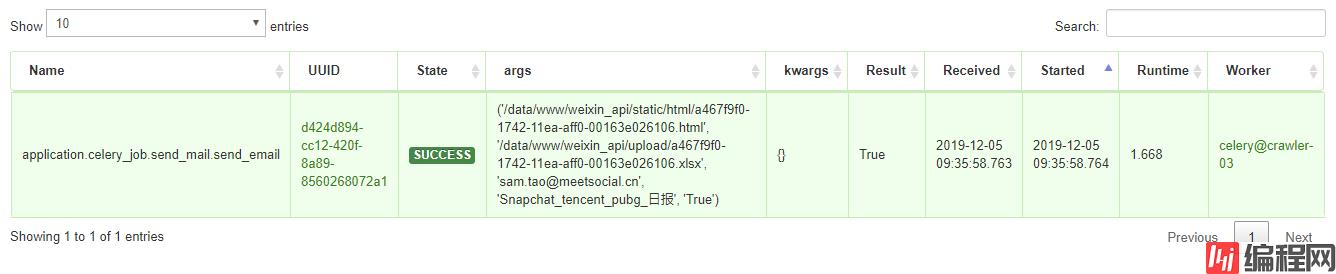
--结束END--
本文标题: nginx+uwsgi+djangorestframework+flower+celery+redis
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/193545.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0