Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
点睛在我们实际开发的时候,经常会遇到在Bean在使用之前或者止呕做一些必要的操作,spring对Bean的生命周期的操作提供了支持。在使用Java配置和注解配置下提供如下两种方式:Java配置方式:使用@Bean的initMethod和de
点睛
在我们实际开发的时候,经常会遇到在Bean在使用之前或者止呕做一些必要的操作,spring对Bean的生命周期的操作提供了支持。在使用Java配置和注解配置下提供如下两种方式:
Java配置方式:使用@Bean的initMethod和destroyMethod(相当于XML配置init-method和destory-method)。
注解方式:利用jsR-250的@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy。
示例
被注入Bean
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.prepost;
public class BeanWayService { public BeanWayService() { System.out.println("初始化構造函数-BeanWayService"); } public void init() { System.out.println("@Bean-init-Method");
} public void destroy() { System.out.println("@Bean-destory-Method"); }
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.prepost;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class JSR250WayService { public JSR250WayService() { System.out.println("初始化構造函数-JSR250WayService"); } @PostConstruct //1 在构造函数执行完之后执行 public void init() { System.out.println("JSR250-init-Method"); } @PreDestroy //2 在Bean销毁之前执行 public void destroy() { System.out.println("JSR250-destory-Method"); }
}
|
配置类
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.prepost;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration @ComponentScan("hightlight_spirng4.ch2.prepost") public class PrePostConfig { // initMethod 和destroyMethod 指定BeanWayService 类的init 和destroy // 方法在构造之后、Bean 销毁之前执行。 @Bean(initMethod="init",destroyMethod="destroy") public BeanWayService beanWayService() { return new BeanWayService(); }
@Bean public JSR250WayService jsr250WayService() { return new JSR250WayService(); } }
|
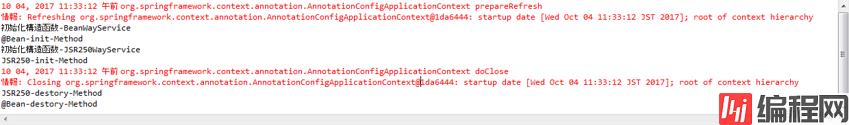
运行
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.prepost;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrePostConfig.class);
BeanWayService beanWayService = context.getBean(BeanWayService.class); JSR250WayService JSR250WayService = context.getBean(JSR250WayService.class);
context.close(); } } |
结果

点睛
Profile为在不同环境下使用不同的配置提供了支持(开发环境下的配置和生产环境下的配置肯定是不同的,例如数据库配置)
通过设定Environment的ActiveProfile来设定当前context需要使用的配置环境。在开发中使用@Profile注解类或者方法,达到在不同情况下选择实例化不同的Bean。
通过设定JVM的spring.profiles.active参数来设置配置环境。
示例
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.profile;
public class DemoBean {
public DemoBean(String content) { super(); this.content=content; }
private String content;
public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; }
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.profile;
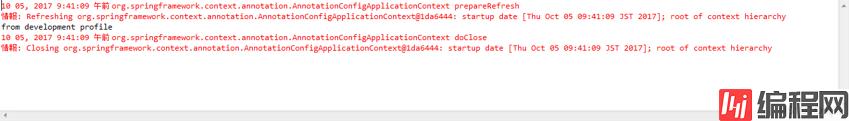
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; @Configuration public class ProfileConfig { @Bean @Profile("dev") //1 public DemoBean deveDemoBean() { return new DemoBean("from development profile"); }
@Bean @Profile("prod") //2 public DemoBean proDemoBean() { return new DemoBean("from production profile"); } }
|
结果
点睛
Spring的事件(Application Event)为Bean与Bean之间的消息通信提供了支持。当一个Bean处理完一个任务之后,希望另一个Bean知道并能做相应的处理,这时外面见需要让另外一个Bean监听当前Bean所发送的事件。
Spring的事件需要遵循如下流程:
自定义事件,继承ApplicationEvent。
定义事件监听器,实现ApplicationListener。
使用容器发布事件。
示例
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class DemoEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String msg;
public DemoEvent(Object source,String msg) { super(source); this.msg=msg; }
public String getMsg() { return msg; }
public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; }
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class DemoListener implements ApplicationListener<DemoEvent> { //1
@Override public void onApplicationEvent(DemoEvent event) { //2 String msg=event.getMsg(); System.out.println("我(bean-demoListener)接受到了bean-demoPublisher发布的消息:" + msg); System.out.println("发生事件的对象是:" + event.getSource());
}
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.event;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class DemoPublisher { @Autowired //1 ApplicationContext context;
public void publish(String msg) { context.publishEvent(new DemoEvent(this, msg)); //2 } }
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.event;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration @ComponentScan("hightlight_spirng4.ch2.event") public class EventConfig {
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch2.event;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
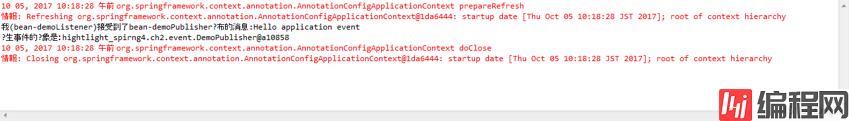
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(EventConfig.class); DemoPublisher publisher = context.getBean(DemoPublisher.class); publisher.publish("Hello application event"); context.close();
}
}
|
结果
点睛
Spring的依赖注入最大的亮点就是所有的Bean对Spring容器的存在是没有意识的。即你可以将你的容器替换成别的容器,如Google Guice,只是Bean之间的耦合度很低。
但是在实际项目中,你不可避免的要用到Spring容器本身的功能资源,这时你的Bean必须要意识到Spring容器的存在,才能调用Spring所提供的资源,着就是所谓的Spring Aware。其实Spring Aware本来就是Spring设计用来框架内部使用的,若使用了Spring Aware,你的Bean将会和Spring框架耦合。
Spring提供的Aware接口如下所示:
BeanNameAware | 获得到容器中Bean名称 |
BeanFactoryAware | 获得当前Bean Factory,这样可以调用容器的服务 |
ApplicationContextAware* | 当前ApplicationContext,这样可以调用容器的服务 |
MessageSourceAware | 获得messagesource,这样可以获得文本信息 |
ApplicationEventPublisherAware | 应用事件发布器,可以发布事件 |
ResourceLoaderAware | 获得资源加载器,可以获得外部资源文件 |
Spring Aware的目的是为了让Bean获得Spring容器的服务。因为ApplicationContext接口集成了MessageSource接口、ApplicationEventPublisher接口和ResourceLoader接口,所以Bean继承ApplicationContextAware可以获得Spring容器的所有服务,但原则上我们还是用到什么接口,就实现什么接口。
示例
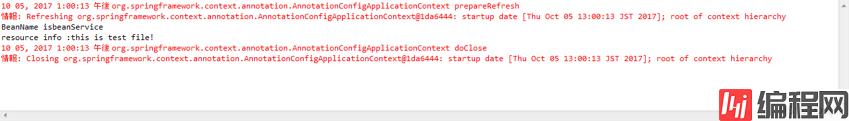
准备。新建test.txt,内容随意,给下面的外部资源加载使用。
Spring Aware演示Bean。
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.aware;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class BeanService implements BeanNameAware, ResourceLoaderAware {//1 private String BeanName; private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@Override public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {//2 this.resourceLoader=resourceLoader;
}
@Override public void setBeanName(String name) {//3 this.BeanName=name; }
public void outputResult() { System.out.println("BeanName is "+BeanName); Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource("classpath:hightlight_spirng4/ch3/aware/test.txt"); try { System.out.println("resource info :"+IOUtils.toString(resource.getInputStream(), "utf-8")); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.aware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration @ComponentScan("hightlight_spirng4.ch3.aware") public class AwareConfig {
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.aware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AwareConfig.class); BeanService bean=context.getBean(BeanService.class); bean.outputResult(); context.close();
}
}
|
结果
点睛
Spring通过任务执行器(TaskExecutor)来实现多线程和并发编程。使用RhreadPoolTaskExecutor可实现一个基于线程池的TaskExecutor。而实际开发中人物一般式非阻碍的,即异步的,所以我们要在配置类中通过@EnableAsync开始起对一部人物的支持,并通过在实际执行的Bean的方法中使用@Async注解来声明其是一个异步任务。
示例
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskexecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurer; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; @Configuration @ComponentScan("hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskexecutor") @EnableAsync //1 开启异步任务支持 //2配置类实现AsyncConfigurer 接口并重写getAsyncExecutor 方法,并返回一个ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ,这样我们就获得了一个基于线程池TaskExecutor。 public class TaskExecutorConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(5); taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(10); taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(25); taskExecutor.initialize(); return taskExecutor; }
@Override public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; }
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskexecutor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service public class AsyncTaskService { @Async public void executeAsyncTask(Integer i) { System.out.println("Async task: "+i); } @Async public void executeAsyncTaskPlus(Integer i) { System.out.println("Async task i+1: "+(i+1)); } }
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskexecutor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TaskExecutorConfig.class); AsyncTaskService bean=context.getBean(AsyncTaskService.class); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { bean.executeAsyncTask(i); bean.executeAsyncTaskPlus(i); } context.close(); } }
|
结果并发执行并不是顺序的
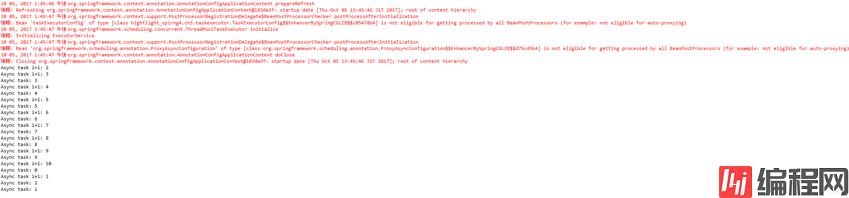
点睛
从Spring3.1开始,计划任务在Spring中的实现变得异常的简单。首先通过在配置类注解@EnableScheduling来开启对计划任务的支持,然后在执行计划任务的方法上注解@Scheduled,声明这是一个计划任务。
Sring通过@Scheduled支持多种类型的任务计划,包含cron、fixDelay、fixRate等。
示例
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskscheduler;
import java.text.SimpleDateFORMat; import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service public class ScheduledTaskService { private static final SimpleDateFormat dateformat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
//声明该方法是计划任务,使用fixedRate属性每隔固定时间执行 @Scheduled(fixedRate=5000) public void reportCurrentTime() { System.out.println("每隔5秒执行一次:"+dateformat.format(new Date())); } //可按照指定时间执行,每天11点28分执行。cron是UNIX和类UNIX系统下的定时任务 @Scheduled(cron="0 28 11 ? * *") public void fixTimeExecut() { System.out.println("指定时间执行:"+dateformat.format(new Date())); }
}
|
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskscheduler;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@Configuration @ComponentScan("hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskscheduler") @EnableScheduling //开启对计划任务的支持 public class TaskScheduledConfig {
} |
package hightlight_spirng4.ch3.taskscheduler;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TaskScheduledConfig.class); ScheduledTaskService bean=context.getBean(ScheduledTaskService.class); bean.reportCurrentTime(); bean.fixTimeExecut(); context.close(); } }
|
结果

--结束END--
本文标题: Spring Boot学习记3
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/184104.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0