admin模块:
admin提供了5种接口
list_display,
.png)
list_display_link,哪个字段可以链接

search_fields,搜索框
list_filter:用于筛选
acition:批处理
.png)


1.首先Django启动会自动加载配置文件

通过autodiscover_modules('文件名')会自动执行每一个应用下的文件
那么创建一个名为stark的应用(模拟admin的应用)和一个名为app01,app02的应用(正常测试应用)
在app01和app02下创建stark.py文件
在setting中为app01,app02,stark注册
点进StarkConfig

模仿admin,在StarkConfig中加入autodiscover_modules
测试一下,在app01,app02下的stark.py文件中,打印字符串


启动Django,运行效果:
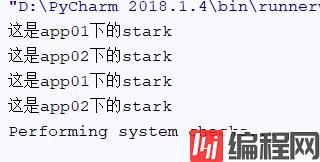
这样我们就实现了启动DjanGo的时候就运行我们自己定义的文件了
第一次打印是debug模式,不用管
2.路由分发
看看admin是怎么做的路由分发
点击site,如下图所示,site是一个类的实例化对象,同样这也是基于模板的单例

那么site.urls是什么?
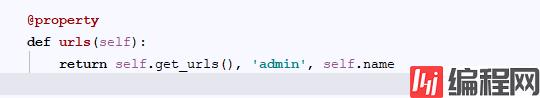
没错,urls就是AdminSite这个类中有property装饰的一个类而已,@property简单的来说就是外界可以通过点(.)的方式来获取这个函数的返回值,可以当做类的变量来处理
那么看看urls返回了什么
它返回了一个元组
这也是路由分发的根本原理
先说一下路由分发的本质:
路由分发的基本格式:url('正则表达式',([分发的路由],None,None))
一级分发:此时生成了两条路由

二级分发:此时生成了四条路由
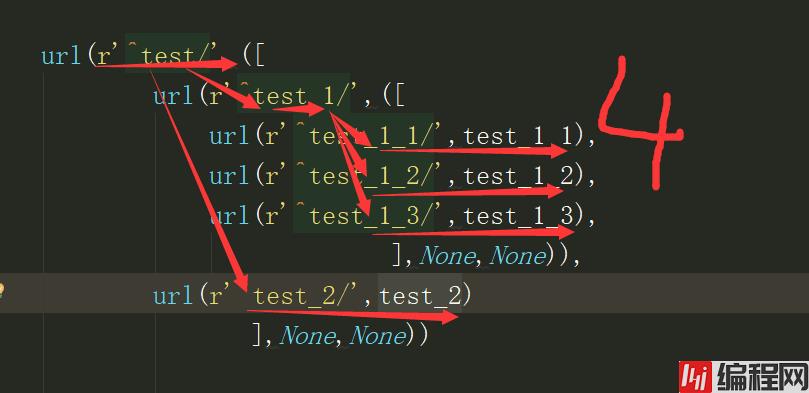
通过这样的原理,可以无限的分发,三级分发,四级分发等等
现在在看这句源码:

和基础格式([ ],None,None)是不是对应了起来,那么我们猜测self.get_urls()返回的是一个列表
检验一下:

def get_urls(self):
from django.conf.urls import url, include
# Since this module gets imported in the application's root package,
# it cannot import models from other applications at the module level,
# and django.contrib.contenttypes.views imports ContentType.
from django.contrib.contenttypes import views as contenttype_views
def wrap(view, cacheable=False):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
return self.admin_view(view, cacheable)(*args, **kwargs)
wrapper.admin_site = self
return update_wrapper(wrapper, view)
# Admin-site-wide views.
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^$', wrap(self.index), name='index'),
url(r'^login/$', self.login, name='login'),
url(r'^logout/$', wrap(self.logout), name='logout'),
url(r'^passWord_change/$', wrap(self.password_change, cacheable=True), name='password_change'),
url(r'^password_change/done/$', wrap(self.password_change_done, cacheable=True),
name='password_change_done'),
url(r'^jsi18n/$', wrap(self.i18n_javascript, cacheable=True), name='jsi18n'),
url(r'^r/(?P<content_type_id>\d+)/(?P<object_id>.+)/$', wrap(contenttype_views.shortcut),
name='view_on_site'),
]
# Add in each model's views, and create a list of valid URLS for the
# app_index
valid_app_labels = []
for model, model_admin in self._reGIStry.items():
urlpatterns += [
url(r'^%s/%s/' % (model._meta.app_label, model._meta.model_name), include(model_admin.urls)),
]
if model._meta.app_label not in valid_app_labels:
valid_app_labels.append(model._meta.app_label)
# If there were ModelAdmins registered, we should have a list of app
# labels for which we need to allow access to the app_index view,
if valid_app_labels:
regex = r'^(?P<app_label>' + '|'.join(valid_app_labels) + ')/$'
urlpatterns += [
url(regex, wrap(self.app_index), name='app_list'),
]
return urlpatterns精简一下:
def get_urls(self):
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^$', wrap(self.index), name='index'),
url(r'^login/$', self.login, name='login'),
url(r'^logout/$', wrap(self.logout), name='logout'),
url(r'^password_change/$', wrap(self.password_change, cacheable=True), name='password_change'),
url(r'^password_change/done/$', wrap(self.password_change_done, cacheable=True),
name='password_change_done'),
url(r'^jsi18n/$', wrap(self.i18n_javascript, cacheable=True), name='jsi18n'),
url(r'^r/(?P<content_type_id>\d+)/(?P<object_id>.+)/$', wrap(contenttype_views.shortcut),
name='view_on_site'),
]
return urlpatterns所以下面这句实现了路由分发

那么接下来模仿这个格式进行路由的分发
admin.site是类实例化的对象
所以我们也在stark中创建一个类,并且用单例的方法实例化,在类中加入urls函数

在urls中

是不是很像,但是功能一点没写,现在先实现路由的分发
实现路由的分发要从get_urls()入手,在admin中

通过这句话,就能把user表加入路由中

所以除了get_urls之外,我们还需要register函数
先看看admin的register函数中写了什么
完整源码:

def register(self, model_or_iterable, admin_class=None, **options):
"""
Registers the given model(s) with the given admin class.
The model(s) should be Model classes, not instances.
If an admin class isn't given, it will use ModelAdmin (the default
admin options). If keyword arguments are given -- e.g., list_display --
they'll be applied as options to the admin class.
If a model is already registered, this will raise AlreadyRegistered.
If a model is abstract, this will raise ImproperlyConfigured.
"""
if not admin_class:
admin_class = ModelAdmin
if isinstance(model_or_iterable, ModelBase):
model_or_iterable = [model_or_iterable]
for model in model_or_iterable:
if model._meta.abstract:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'The model %s is abstract, so it cannot be registered with admin.' % model.__name__
)
if model in self._registry:
raise AlreadyRegistered('The model %s is already registered' % model.__name__)
# Ignore the registration if the model has been
# swapped out.
if not model._meta.swapped:
# If we got **options then dynamically construct a subclass of
# admin_class with those **options.
if options:
# For reasons I don't quite understand, without a __module__
# the created class appears to "live" in the wrong place,
# which causes issues later on.
options['__module__'] = __name__
admin_class = type("%sAdmin" % model.__name__, (admin_class,), options)
# Instantiate the admin class to save in the registry
self._registry[model] = admin_class(model, self)精简版
def register(self, model, admin_class=None, **options):
if not admin_class:
admin_class = ModelAdmin
self._registry[model] = admin_class(model)在解释之前,先看看ModelAdmin和self._registry是什么东西
ModelAdmin源码:

class ModelAdmin(BaseModelAdmin):
"Encapsulates all admin options and functionality for a given model."
list_display = ('__str__',)
list_display_links = ()
list_filter = ()
list_select_related = False
list_per_page = 100
list_max_show_all = 200
list_editable = ()
search_fields = ()
date_hierarchy = None
save_as = False
save_as_continue = True
save_on_top = False
paginator = Paginator
preserve_filters = True
inlines = []
# Custom templates (designed to be over-ridden in subclasses)
add_fORM_template = None
change_form_template = None
change_list_template = None
delete_confirmation_template = None
delete_selected_confirmation_template = None
object_history_template = None
popup_response_template = None
# Actions
actions = []
action_form = helpers.ActionForm
actions_on_top = True
actions_on_bottom = False
actions_selection_counter = True
checks_class = ModelAdminChecks
def __init__(self, model, admin_site):
self.model = model
self.opts = model._meta
self.admin_site = admin_site
super(ModelAdmin, self).__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "%s.%s" % (self.model._meta.app_label, self.__class__.__name__)
def get_inline_instances(self, request, obj=None):
inline_instances = []
for inline_class in self.inlines:
inline = inline_class(self.model, self.admin_site)
if request:
if not (inline.has_add_permission(request) or
inline.has_change_permission(request, obj) or
inline.has_delete_permission(request, obj)):
continue
if not inline.has_add_permission(request):
inline.max_num = 0
inline_instances.append(inline)
return inline_instances
def get_urls(self):
from django.conf.urls import url
def wrap(view):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
return self.admin_site.admin_view(view)(*args, **kwargs)
wrapper.model_admin = self
return update_wrapper(wrapper, view)
info = self.model._meta.app_label, self.model._meta.model_name
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^$', wrap(self.changelist_view), name='%s_%s_changelist' % info),
url(r'^add/$', wrap(self.add_view), name='%s_%s_add' % info),
url(r'^(.+)/history/$', wrap(self.history_view), name='%s_%s_history' % info),
url(r'^(.+)/delete/$', wrap(self.delete_view), name='%s_%s_delete' % info),
url(r'^(.+)/change/$', wrap(self.change_view), name='%s_%s_change' % info),
# For backwards compatibility (was the change url before 1.9)
url(r'^(.+)/$', wrap(RedirectView.as_view(
pattern_name='%s:%s_%s_change' % ((self.admin_site.name,) + info)
))),
]
return urlpatterns
@property
def urls(self):
return self.get_urls()
@property
def media(self):
extra = '' if settings.DEBUG else '.min'
js = [
'core.js',
'vendor/Jquery/jquery%s.js' % extra,
'jquery.init.js',
'admin/RelatedObjectLookups.js',
'actions%s.js' % extra,
'urlify.js',
'prepopulate%s.js' % extra,
'vendor/xregexp/xregexp%s.js' % extra,
]
return forms.Media(js=['admin/js/%s' % url for url in js])
def get_model_perms(self, request):
"""
Returns a dict of all perms for this model. This dict has the keys
``add``, ``change``, and ``delete`` mapping to the True/False for each
of those actions.
"""
return {
'add': self.has_add_permission(request),
'change': self.has_change_permission(request),
'delete': self.has_delete_permission(request),
}
def get_fields(self, request, obj=None):
if self.fields:
return self.fields
form = self.get_form(request, obj, fields=None)
return list(form.base_fields) + list(self.get_readonly_fields(request, obj))
def get_form(self, request, obj=None, **kwargs):
"""
Returns a Form class for use in the admin add view. This is used by
add_view and change_view.
"""
if 'fields' in kwargs:
fields = kwargs.pop('fields')
else:
fields = flatten_fieldsets(self.get_fieldsets(request, obj))
excluded = self.get_exclude(request, obj)
exclude = [] if excluded is None else list(excluded)
readonly_fields = self.get_readonly_fields(request, obj)
exclude.extend(readonly_fields)
if excluded is None and hasattr(self.form, '_meta') and self.form._meta.exclude:
# Take the custom ModelForm's Meta.exclude into account only if the
# ModelAdmin doesn't define its own.
exclude.extend(self.form._meta.exclude)
# if exclude is an empty list we pass None to be consistent with the
# default on modelform_factory
exclude = exclude or None
# Remove declared form fields which are in readonly_fields.
new_attrs = OrderedDict(
(f, None) for f in readonly_fields
if f in self.form.declared_fields
)
form = type(self.form.__name__, (self.form,), new_attrs)
defaults = {
"form": form,
"fields": fields,
"exclude": exclude,
"formfield_callback": partial(self.formfield_for_dbfield, request=request),
}
defaults.update(kwargs)
if defaults['fields'] is None and not modelform_defines_fields(defaults['form']):
defaults['fields'] = forms.ALL_FIELDS
try:
return modelform_factory(self.model, **defaults)
except FieldError as e:
raise FieldError(
'%s. Check fields/fieldsets/exclude attributes of class %s.'
% (e, self.__class__.__name__)
)
def get_changelist(self, request, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the ChangeList class for use on the changelist page.
"""
from django.contrib.admin.views.main import ChangeList
return ChangeList
def get_object(self, request, object_id, from_field=None):
"""
Returns an instance matching the field and value provided, the primary
key is used if no field is provided. Returns ``None`` if no match is
found or the object_id fails validation.
"""
queryset = self.get_queryset(request)
model = queryset.model
field = model._meta.pk if from_field is None else model._meta.get_field(from_field)
try:
object_id = field.to_python(object_id)
return queryset.get(**{field.name: object_id})
except (model.DoesNotExist, ValidationError, ValueError):
return None
def get_changelist_form(self, request, **kwargs):
"""
Returns a Form class for use in the Formset on the changelist page.
"""
defaults = {
"formfield_callback": partial(self.formfield_for_dbfield, request=request),
}
defaults.update(kwargs)
if defaults.get('fields') is None and not modelform_defines_fields(defaults.get('form')):
defaults['fields'] = forms.ALL_FIELDS
return modelform_factory(self.model, **defaults)
def get_changelist_formset(self, request, **kwargs):
"""
Returns a FormSet class for use on the changelist page if list_editable
is used.
"""
defaults = {
"formfield_callback": partial(self.formfield_for_dbfield, request=request),
}
defaults.update(kwargs)
return modelformset_factory(
self.model, self.get_changelist_form(request), extra=0,
fields=self.list_editable, **defaults
)
def get_formsets_with_inlines(self, request, obj=None):
"""
Yields formsets and the corresponding inlines.
"""
for inline in self.get_inline_instances(request, obj):
yield inline.get_formset(request, obj), inline
def get_paginator(self, request, queryset, per_page, orphans=0, allow_empty_first_page=True):
return self.paginator(queryset, per_page, orphans, allow_empty_first_page)
def log_addition(self, request, object, message):
"""
Log that an object has been successfully added.
The default implementation creates an admin LogEntry object.
"""
from django.contrib.admin.models import LogEntry, ADDITION
return LogEntry.objects.log_action(
user_id=request.user.pk,
content_type_id=get_content_type_for_model(object).pk,
object_id=object.pk,
object_repr=force_text(object),
action_flag=ADDITION,
change_message=message,
)
def log_change(self, request, object, message):
"""
Log that an object has been successfully changed.
The default implementation creates an admin LogEntry object.
"""
from django.contrib.admin.models import LogEntry, CHANGE
return LogEntry.objects.log_action(
user_id=request.user.pk,
content_type_id=get_content_type_for_model(object).pk,
object_id=object.pk,
object_repr=force_text(object),
action_flag=CHANGE,
change_message=message,
)
def log_deletion(self, request, object, object_repr):
"""
Log that an object will be deleted. Note that this method must be
called before the deletion.
The default implementation creates an admin LogEntry object.
"""
from django.contrib.admin.models import LogEntry, DELETION
return LogEntry.objects.log_action(
user_id=request.user.pk,
content_type_id=get_content_type_for_model(object).pk,
object_id=object.pk,
object_repr=object_repr,
action_flag=DELETION,
)
def action_checkbox(self, obj):
"""
A list_display column containing a checkbox widget.
"""
return helpers.checkbox.render(helpers.ACTION_CHECKBOX_NAME, force_text(obj.pk))
action_checkbox.short_description = mark_safe('<input type="checkbox" id="action-toggle" />')
def get_actions(self, request):
"""
Return a dictionary mapping the names of all actions for this
ModelAdmin to a tuple of (callable, name, description) for each action.
"""
# If self.actions is explicitly set to None that means that we don't
# want *any* actions enabled on this page.
if self.actions is None or IS_POPUP_VAR in request.GET:
return OrderedDict()
actions = []
# Gather actions from the admin site first
for (name, func) in self.admin_site.actions:
description = getattr(func, 'short_description', name.replace('_', ' '))
actions.append((func, name, description))
# Then gather them from the model admin and all parent classes,
# starting with self and working back up.
for klass in self.__class__.mro()[::-1]:
class_actions = getattr(klass, 'actions', [])
# Avoid trying to iterate over None
if not class_actions:
continue
actions.extend(self.get_action(action) for action in class_actions)
# get_action might have returned None, so filter any of those out.
actions = filter(None, actions)
# Convert the actions into an OrderedDict keyed by name.
actions = OrderedDict(
(name, (func, name, desc))
for func, name, desc in actions
)
return actions
def get_action_choices(self, request, default_choices=BLANK_CHOICE_DASH):
"""
Return a list of choices for use in a form object. Each choice is a
tuple (name, description).
"""
choices = [] + default_choices
for func, name, description in six.itervalues(self.get_actions(request)):
choice = (name, description % model_format_dict(self.opts))
choices.append(choice)
return choices
def get_action(self, action):
"""
Return a given action from a parameter, which can either be a callable,
or the name of a method on the ModelAdmin. Return is a tuple of
(callable, name, description).
"""
# If the action is a callable, just use it.
if callable(action):
func = action
action = action.__name__
# Next, look for a method. Grab it off self.__class__ to get an unbound
# method instead of a bound one; this ensures that the calling
# conventions are the same for functions and methods.
elif hasattr(self.__class__, action):
func = getattr(self.__class__, action)
# Finally, look for a named method on the admin site
else:
try:
func = self.admin_site.get_action(action)
except KeyError:
return None
if hasattr(func, 'short_description'):
description = func.short_description
else:
description = capfirst(action.replace('_', ' '))
return func, action, description
def get_list_display(self, request):
"""
Return a sequence containing the fields to be displayed on the
changelist.
"""
return self.list_display
def get_list_display_links(self, request, list_display):
"""
Return a sequence containing the fields to be displayed as links
on the changelist. The list_display parameter is the list of fields
returned by get_list_display().
"""
if self.list_display_links or self.list_display_links is None or not list_display:
return self.list_display_links
else:
# Use only the first item in list_display as link
return list(list_display)[:1]
def get_list_filter(self, request):
"""
Returns a sequence containing the fields to be displayed as filters in
the right sidebar of the changelist page.
"""
return self.list_filter
def get_list_select_related(self, request):
"""
Returns a list of fields to add to the select_related() part of the
changelist items query.
"""
return self.list_select_related
def get_search_fields(self, request):
"""
Returns a sequence containing the fields to be searched whenever
somebody submits a search query.
"""
return self.search_fields
def get_search_results(self, request, queryset, search_term):
"""
Returns a tuple containing a queryset to implement the search,
and a boolean indicating if the results may contain duplicates.
"""
# Apply keyword searches.
def construct_search(field_name):
if field_name.startswith('^'):
return "%s__istartswith" % field_name[1:]
elif field_name.startswith('='):
return "%s__iexact" % field_name[1:]
elif field_name.startswith('@'):
return "%s__search" % field_name[1:]
else:
return "%s__icontains" % field_name
use_distinct = False
search_fields = self.get_search_fields(request)
if search_fields and search_term:
orm_lookups = [construct_search(str(search_field))
for search_field in search_fields]
for bit in search_term.split():
or_queries = [models.Q(**{orm_lookup: bit})
for orm_lookup in orm_lookups]
queryset = queryset.filter(reduce(operator.or_, or_queries))
if not use_distinct:
for search_spec in orm_lookups:
if lookup_needs_distinct(self.opts, search_spec):
use_distinct = True
break
return queryset, use_distinct
def get_preserved_filters(self, request):
"""
Returns the preserved filters querystring.
"""
match = request.resolver_match
if self.preserve_filters and match:
opts = self.model._meta
current_url = '%s:%s' % (match.app_name, match.url_name)
changelist_url = 'admin:%s_%s_changelist' % (opts.app_label, opts.model_name)
if current_url == changelist_url:
preserved_filters = request.GET.urlencode()
else:
preserved_filters = request.GET.get('_changelist_filters')
if preserved_filters:
return urlencode({'_changelist_filters': preserved_filters})
return ''
def construct_change_message(self, request, form, formsets, add=False):
"""
Construct a JSON structure describing changes from a changed object.
"""
return construct_change_message(form, formsets, add)
def message_user(self, request, message, level=messages.INFO, extra_tags='',
fail_silently=False):
"""
Send a message to the user. The default implementation
posts a message using the django.contrib.messages backend.
Exposes almost the same api as messages.add_message(), but accepts the
positional arguments in a different order to maintain backwards
compatibility. For convenience, it accepts the `level` argument as
a string rather than the usual level number.
"""
if not isinstance(level, int):
# attempt to get the level if passed a string
try:
level = getattr(messages.constants, level.upper())
except AttributeError:
levels = messages.constants.DEFAULT_TAGS.values()
levels_repr = ', '.join('`%s`' % l for l in levels)
raise ValueError(
'Bad message level string: `%s`. Possible values are: %s'
% (level, levels_repr)
)
messages.add_message(request, level, message, extra_tags=extra_tags, fail_silently=fail_silently)
def save_form(self, request, form, change):
"""
Given a ModelForm return an unsaved instance. ``change`` is True if
the object is being changed, and False if it's being added.
"""
return form.save(commit=False)
def save_model(self, request, obj, form, change):
"""
Given a model instance save it to the database.
"""
obj.save()
def delete_model(self, request, obj):
"""
Given a model instance delete it from the database.
"""
obj.delete()
def save_formset(self, request, form, formset, change):
"""
Given an inline formset save it to the database.
"""
formset.save()
def save_related(self, request, form, formsets, change):
"""
Given the ``HttpRequest``, the parent ``ModelForm`` instance, the
list of inline formsets and a boolean value based on whether the
parent is being added or changed, save the related objects to the
database. Note that at this point save_form() and save_model() have
already been called.
"""
form.save_m2m()
for formset in formsets:
self.save_formset(request, form, formset, change=change)
def render_change_form(self, request, context, add=False, change=False, form_url='', obj=None):
opts = self.model._meta
app_label = opts.app_label
preserved_filters = self.get_preserved_filters(request)
form_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, form_url)
view_on_site_url = self.get_view_on_site_url(obj)
context.update({
'add': add,
'change': change,
'has_add_permission': self.has_add_permission(request),
'has_change_permission': self.has_change_permission(request, obj),
'has_delete_permission': self.has_delete_permission(request, obj),
'has_file_field': True, # FIXME - this should check if form or formsets have a FileField,
'has_absolute_url': view_on_site_url is not None,
'absolute_url': view_on_site_url,
'form_url': form_url,
'opts': opts,
'content_type_id': get_content_type_for_model(self.model).pk,
'save_as': self.save_as,
'save_on_top': self.save_on_top,
'to_field_var': TO_FIELD_VAR,
'is_popup_var': IS_POPUP_VAR,
'app_label': app_label,
})
if add and self.add_form_template is not None:
form_template = self.add_form_template
else:
form_template = self.change_form_template
request.current_app = self.admin_site.name
return TemplateResponse(request, form_template or [
"admin/%s/%s/change_form.html" % (app_label, opts.model_name),
"admin/%s/change_form.html" % app_label,
"admin/change_form.html"
], context)
def response_add(self, request, obj, post_url_continue=None):
"""
Determines the HttpResponse for the add_view stage.
"""
opts = obj._meta
pk_value = obj._get_pk_val()
preserved_filters = self.get_preserved_filters(request)
obj_url = reverse(
'admin:%s_%s_change' % (opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
args=(quote(pk_value),),
current_app=self.admin_site.name,
)
# Add a link to the object's change form if the user can edit the obj.
if self.has_change_permission(request, obj):
obj_repr = format_html('<a href="{}">{}</a>', urlquote(obj_url), obj)
else:
obj_repr = force_text(obj)
msg_dict = {
'name': force_text(opts.verbose_name),
'obj': obj_repr,
}
# Here, we distinguish between different save types by checking for
# the presence of keys in request.POST.
if IS_POPUP_VAR in request.POST:
to_field = request.POST.get(TO_FIELD_VAR)
if to_field:
attr = str(to_field)
else:
attr = obj._meta.pk.attname
value = obj.serializable_value(attr)
popup_response_data = json.dumps({
'value': six.text_type(value),
'obj': six.text_type(obj),
})
return TemplateResponse(request, self.popup_response_template or [
'admin/%s/%s/popup_response.html' % (opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
'admin/%s/popup_response.html' % opts.app_label,
'admin/popup_response.html',
], {
'popup_response_data': popup_response_data,
})
elif "_continue" in request.POST or (
# Redirecting after "Save as new".
"_saveasnew" in request.POST and self.save_as_continue and
self.has_change_permission(request, obj)
):
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was added successfully. You may edit it again below.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
if post_url_continue is None:
post_url_continue = obj_url
post_url_continue = add_preserved_filters(
{'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts},
post_url_continue
)
return HttpResponseRedirect(post_url_continue)
elif "_addanother" in request.POST:
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was added successfully. You may add another {name} below.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
redirect_url = request.path
redirect_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, redirect_url)
return HttpResponseRedirect(redirect_url)
else:
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was added successfully.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
return self.response_post_save_add(request, obj)
def response_change(self, request, obj):
"""
Determines the HttpResponse for the change_view stage.
"""
if IS_POPUP_VAR in request.POST:
opts = obj._meta
to_field = request.POST.get(TO_FIELD_VAR)
attr = str(to_field) if to_field else opts.pk.attname
# Retrieve the `object_id` from the resolved pattern arguments.
value = request.resolver_match.args[0]
new_value = obj.serializable_value(attr)
popup_response_data = json.dumps({
'action': 'change',
'value': six.text_type(value),
'obj': six.text_type(obj),
'new_value': six.text_type(new_value),
})
return TemplateResponse(request, self.popup_response_template or [
'admin/%s/%s/popup_response.html' % (opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
'admin/%s/popup_response.html' % opts.app_label,
'admin/popup_response.html',
], {
'popup_response_data': popup_response_data,
})
opts = self.model._meta
pk_value = obj._get_pk_val()
preserved_filters = self.get_preserved_filters(request)
msg_dict = {
'name': force_text(opts.verbose_name),
'obj': format_html('<a href="{}">{}</a>', urlquote(request.path), obj),
}
if "_continue" in request.POST:
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was changed successfully. You may edit it again below.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
redirect_url = request.path
redirect_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, redirect_url)
return HttpResponseRedirect(redirect_url)
elif "_saveasnew" in request.POST:
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was added successfully. You may edit it again below.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
redirect_url = reverse('admin:%s_%s_change' %
(opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
args=(pk_value,),
current_app=self.admin_site.name)
redirect_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, redirect_url)
return HttpResponseRedirect(redirect_url)
elif "_addanother" in request.POST:
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was changed successfully. You may add another {name} below.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
redirect_url = reverse('admin:%s_%s_add' %
(opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
current_app=self.admin_site.name)
redirect_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, redirect_url)
return HttpResponseRedirect(redirect_url)
else:
msg = format_html(
_('The {name} "{obj}" was changed successfully.'),
**msg_dict
)
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
return self.response_post_save_change(request, obj)
def response_post_save_add(self, request, obj):
"""
Figure out where to redirect after the 'Save' button has been pressed
when adding a new object.
"""
opts = self.model._meta
if self.has_change_permission(request, None):
post_url = reverse('admin:%s_%s_changelist' %
(opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
current_app=self.admin_site.name)
preserved_filters = self.get_preserved_filters(request)
post_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, post_url)
else:
post_url = reverse('admin:index',
current_app=self.admin_site.name)
return HttpResponseRedirect(post_url)
def response_post_save_change(self, request, obj):
"""
Figure out where to redirect after the 'Save' button has been pressed
when editing an existing object.
"""
opts = self.model._meta
if self.has_change_permission(request, None):
post_url = reverse('admin:%s_%s_changelist' %
(opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
current_app=self.admin_site.name)
preserved_filters = self.get_preserved_filters(request)
post_url = add_preserved_filters({'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, post_url)
else:
post_url = reverse('admin:index',
current_app=self.admin_site.name)
return HttpResponseRedirect(post_url)
def response_action(self, request, queryset):
"""
Handle an admin action. This is called if a request is POSTed to the
changelist; it returns an HttpResponse if the action was handled, and
None otherwise.
"""
# There can be multiple action forms on the page (at the top
# and bottom of the change list, for example). Get the action
# whose button was pushed.
try:
action_index = int(request.POST.get('index', 0))
except ValueError:
action_index = 0
# Construct the action form.
data = request.POST.copy()
data.pop(helpers.ACTION_CHECKBOX_NAME, None)
data.pop("index", None)
# Use the action whose button was pushed
try:
data.update({'action': data.getlist('action')[action_index]})
except IndexError:
# If we didn't get an action from the chosen form that's invalid
# POST data, so by deleting action it'll fail the validation check
# below. So no need to do anything here
pass
action_form = self.action_form(data, auto_id=None)
action_form.fields['action'].choices = self.get_action_choices(request)
# If the form's valid we can handle the action.
if action_form.is_valid():
action = action_form.cleaned_data['action']
select_across = action_form.cleaned_data['select_across']
func = self.get_actions(request)[action][0]
# Get the list of selected PKs. If nothing's selected, we can't
# perform an action on it, so bail. Except we want to perform
# the action explicitly on all objects.
selected = request.POST.getlist(helpers.ACTION_CHECKBOX_NAME)
if not selected and not select_across:
# Reminder that something needs to be selected or nothing will happen
msg = _("Items must be selected in order to perform "
"actions on them. No items have been changed.")
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.WARNING)
return None
if not select_across:
# Perform the action only on the selected objects
queryset = queryset.filter(pk__in=selected)
response = func(self, request, queryset)
# Actions may return an HttpResponse-like object, which will be
# used as the response from the POST. If not, we'll be a good
# little HTTP citizen and redirect back to the changelist page.
if isinstance(response, HttpResponseBase):
return response
else:
return HttpResponseRedirect(request.get_full_path())
else:
msg = _("No action selected.")
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.WARNING)
return None
def response_delete(self, request, obj_display, obj_id):
"""
Determines the HttpResponse for the delete_view stage.
"""
opts = self.model._meta
if IS_POPUP_VAR in request.POST:
popup_response_data = json.dumps({
'action': 'delete',
'value': str(obj_id),
})
return TemplateResponse(request, self.popup_response_template or [
'admin/%s/%s/popup_response.html' % (opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
'admin/%s/popup_response.html' % opts.app_label,
'admin/popup_response.html',
], {
'popup_response_data': popup_response_data,
})
self.message_user(
request,
_('The %(name)s "%(obj)s" was deleted successfully.') % {
'name': force_text(opts.verbose_name),
'obj': force_text(obj_display),
},
messages.SUCCESS,
)
if self.has_change_permission(request, None):
post_url = reverse(
'admin:%s_%s_changelist' % (opts.app_label, opts.model_name),
current_app=self.admin_site.name,
)
preserved_filters = self.get_preserved_filters(request)
post_url = add_preserved_filters(
{'preserved_filters': preserved_filters, 'opts': opts}, post_url
)
else:
post_url = reverse('admin:index', current_app=self.admin_site.name)
return HttpResponseRedirect(post_url)
def render_delete_form(self, request, context):
opts = self.model._meta
app_label = opts.app_label
request.current_app = self.admin_site.name
context.update(
to_field_var=TO_FIELD_VAR,
is_popup_var=IS_POPUP_VAR,
media=self.media,
)
return TemplateResponse(
request,
self.delete_confirmation_template or [
"admin/{}/{}/delete_confirmation.html".format(app_label, opts.model_name),
"admin/{}/delete_confirmation.html".format(app_label),
"admin/delete_confirmation.html",
],
context,
)
def get_inline_formsets(self, request, formsets, inline_instances, obj=None):
inline_admin_formsets = []
for inline, formset in zip(inline_instances, formsets):
fieldsets = list(inline.get_fieldsets(request, obj))
readonly = list(inline.get_readonly_fields(request, obj))
prepopulated = dict(inline.get_prepopulated_fields(request, obj))
inline_admin_formset = helpers.InlineAdminFormSet(
inline, formset, fieldsets, prepopulated, readonly,
model_admin=self,
)
inline_admin_formsets.append(inline_admin_formset)
return inline_admin_formsets
def get_changeform_initial_data(self, request):
"""
Get the initial form data.
Unless overridden, this populates from the GET params.
"""
initial = dict(request.GET.items())
for k in initial:
try:
f = self.model._meta.get_field(k)
except FieldDoesNotExist:
continue
# We have to special-case M2Ms as a list of comma-separated PKs.
if isinstance(f, models.ManyToManyField):
initial[k] = initial[k].split(",")
return initial
def _get_obj_does_not_exist_redirect(self, request, opts, object_id):
"""
Create a message informing the user that the object doesn't exist
and return a redirect to the admin index page.
"""
msg = _("""%(name)s with ID "%(key)s" doesn't exist. Perhaps it was deleted?""") % {
'name': force_text(opts.verbose_name),
'key': unquote(object_id),
}
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.WARNING)
url = reverse('admin:index', current_app=self.admin_site.name)
return HttpResponseRedirect(url)
@csrf_protect_m
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
with transaction.atomic(using=router.db_for_write(self.model)):
return self._changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
def _changeform_view(self, request, object_id, form_url, extra_context):
to_field = request.POST.get(TO_FIELD_VAR, request.GET.get(TO_FIELD_VAR))
if to_field and not self.to_field_allowed(request, to_field):
raise DisallowedModelAdminToField("The field %s cannot be referenced." % to_field)
model = self.model
opts = model._meta
if request.method == 'POST' and '_saveasnew' in request.POST:
object_id = None
add = object_id is None
if add:
if not self.has_add_permission(request):
raise PermissionDenied
obj = None
else:
obj = self.get_object(request, unquote(object_id), to_field)
if not self.has_change_permission(request, obj):
raise PermissionDenied
if obj is None:
return self._get_obj_does_not_exist_redirect(request, opts, object_id)
ModelForm = self.get_form(request, obj)
if request.method == 'POST':
form = ModelForm(request.POST, request.FILES, instance=obj)
if form.is_valid():
form_validated = True
new_object = self.save_form(request, form, change=not add)
else:
form_validated = False
new_object = form.instance
formsets, inline_instances = self._create_formsets(request, new_object, change=not add)
if all_valid(formsets) and form_validated:
self.save_model(request, new_object, form, not add)
self.save_related(request, form, formsets, not add)
change_message = self.construct_change_message(request, form, formsets, add)
if add:
self.log_addition(request, new_object, change_message)
return self.response_add(request, new_object)
else:
self.log_change(request, new_object, change_message)
return self.response_change(request, new_object)
else:
form_validated = False
else:
if add:
initial = self.get_changeform_initial_data(request)
form = ModelForm(initial=initial)
formsets, inline_instances = self._create_formsets(request, form.instance, change=False)
else:
form = ModelForm(instance=obj)
formsets, inline_instances = self._create_formsets(request, obj, change=True)
adminForm = helpers.AdminForm(
form,
list(self.get_fieldsets(request, obj)),
self.get_prepopulated_fields(request, obj),
self.get_readonly_fields(request, obj),
model_admin=self)
media = self.media + adminForm.media
inline_formsets = self.get_inline_formsets(request, formsets, inline_instances, obj)
for inline_formset in inline_formsets:
media = media + inline_formset.media
context = dict(
self.admin_site.each_context(request),
title=(_('Add %s') if add else _('Change %s')) % force_text(opts.verbose_name),
adminform=adminForm,
object_id=object_id,
original=obj,
is_popup=(IS_POPUP_VAR in request.POST or
IS_POPUP_VAR in request.GET),
to_field=to_field,
media=media,
inline_admin_formsets=inline_formsets,
errors=helpers.AdminErrorList(form, formsets),
preserved_filters=self.get_preserved_filters(request),
)
# Hide the "Save" and "Save and continue" buttons if "Save as New" was
# previously chosen to prevent the interface from getting confusing.
if request.method == 'POST' and not form_validated and "_saveasnew" in request.POST:
context['show_save'] = False
context['show_save_and_continue'] = False
# Use the change template instead of the add template.
add = False
context.update(extra_context or {})
return self.render_change_form(request, context, add=add, change=not add, obj=obj, form_url=form_url)
def add_view(self, request, form_url='', extra_context=None):
return self.changeform_view(request, None, form_url, extra_context)
def change_view(self, request, object_id, form_url='', extra_context=None):
return self.changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
@csrf_protect_m
def changelist_view(self, request, extra_context=None):
"""
The 'change list' admin view for this model.
"""
from django.contrib.admin.views.main import ERROR_FLAG
opts = self.model._meta
app_label = opts.app_label
if not self.has_change_permission(request, None):
raise PermissionDenied
list_display = self.get_list_display(request)
list_display_links = self.get_list_display_links(request, list_display)
list_filter = self.get_list_filter(request)
search_fields = self.get_search_fields(request)
list_select_related = self.get_list_select_related(request)
# Check actions to see if any are available on this changelist
actions = self.get_actions(request)
if actions:
# Add the action checkboxes if there are any actions available.
list_display = ['action_checkbox'] + list(list_display)
ChangeList = self.get_changelist(request)
try:
cl = ChangeList(
request, self.model, list_display,
list_display_links, list_filter, self.date_hierarchy,
search_fields, list_select_related, self.list_per_page,
self.list_max_show_all, self.list_editable, self,
)
except IncorrectLookupParameters:
# Wacky lookup parameters were given, so redirect to the main
# changelist page, without parameters, and pass an 'invalid=1'
# parameter via the query string. If wacky parameters were given
# and the 'invalid=1' parameter was already in the query string,
# something is screwed up with the database, so display an error
# page.
if ERROR_FLAG in request.GET.keys():
return SimpleTemplateResponse('admin/invalid_setup.html', {
'title': _('Database error'),
})
return HttpResponseRedirect(request.path + '?' + ERROR_FLAG + '=1')
# If the request was POSTed, this might be a bulk action or a bulk
# edit. Try to look up an action or confirmation first, but if this
# isn't an action the POST will fall through to the bulk edit check,
# below.
action_failed = False
selected = request.POST.getlist(helpers.ACTION_CHECKBOX_NAME)
# Actions with no confirmation
if (actions and request.method == 'POST' and
'index' in request.POST and '_save' not in request.POST):
if selected:
response = self.response_action(request, queryset=cl.get_queryset(request))
if response:
return response
else:
action_failed = True
else:
msg = _("Items must be selected in order to perform "
"actions on them. No items have been changed.")
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.WARNING)
action_failed = True
# Actions with confirmation
if (actions and request.method == 'POST' and
helpers.ACTION_CHECKBOX_NAME in request.POST and
'index' not in request.POST and '_save' not in request.POST):
if selected:
response = self.response_action(request, queryset=cl.get_queryset(request))
if response:
return response
else:
action_failed = True
if action_failed:
# Redirect back to the changelist page to avoid resubmitting the
# form if the user refreshes the browser or uses the "No, take
# me back" button on the action confirmation page.
return HttpResponseRedirect(request.get_full_path())
# If we're allowing changelist editing, we need to construct a formset
# for the changelist given all the fields to be edited. Then we'll
# use the formset to validate/process POSTed data.
formset = cl.formset = None
# Handle POSTed bulk-edit data.
if request.method == 'POST' and cl.list_editable and '_save' in request.POST:
FormSet = self.get_changelist_formset(request)
formset = cl.formset = FormSet(request.POST, request.FILES, queryset=self.get_queryset(request))
if formset.is_valid():
changecount = 0
for form in formset.forms:
if form.has_changed():
obj = self.save_form(request, form, change=True)
self.save_model(request, obj, form, change=True)
self.save_related(request, form, formsets=[], change=True)
change_msg = self.construct_change_message(request, form, None)
self.log_change(request, obj, change_msg)
changecount += 1
if changecount:
if changecount == 1:
name = force_text(opts.verbose_name)
else:
name = force_text(opts.verbose_name_plural)
msg = ungettext(
"%(count)s %(name)s was changed successfully.",
"%(count)s %(name)s were changed successfully.",
changecount
) % {
'count': changecount,
'name': name,
'obj': force_text(obj),
}
self.message_user(request, msg, messages.SUCCESS)
return HttpResponseRedirect(request.get_full_path())
# Handle GET -- construct a formset for display.
elif cl.list_editable:
FormSet = self.get_changelist_formset(request)
formset = cl.formset = FormSet(queryset=cl.result_list)
# Build the list of media to be used by the formset.
if formset:
media = self.media + formset.media
else:
media = self.media
# Build the action form and populate it with available actions.
if actions:
action_form = self.action_form(auto_id=None)
action_form.fields['action'].choices = self.get_action_choices(request)
media += action_form.media
else:
action_form = None
selection_note_all = ungettext(
'%(total_count)s selected',
'All %(total_count)s selected',
cl.result_count
)
context = dict(
self.admin_site.each_context(request),
module_name=force_text(opts.verbose_name_plural),
selection_note=_('0 of %(cnt)s selected') % {'cnt': len(cl.result_list)},
selection_note_all=selection_note_all % {'total_count': cl.result_count},
title=cl.title,
is_popup=cl.is_popup,
to_field=cl.to_field,
cl=cl,
media=media,
has_add_permission=self.has_add_permission(request),
opts=cl.opts,
action_form=action_form,
actions_on_top=self.actions_on_top,
actions_on_bottom=self.actions_on_bottom,
actions_selection_counter=self.actions_selection_counter,
preserved_filters=self.get_preserved_filters(request),
)
context.update(extra_context or {})
request.current_app = self.admin_site.name
return TemplateResponse(request, self.change_list_template or [
'admin/%s/%s/change_list.html' % (app_label, opts.model_name),
'admin/%s/change_list.html' % app_label,
'admin/change_list.html'
], context)
@csrf_protect_m
def delete_view(self, request, object_id, extra_context=None):
with transaction.atomic(using=router.db_for_write(self.model)):
return self._delete_view(request, object_id, extra_context)
def _delete_view(self, request, object_id, extra_context):
"The 'delete' admin view for this model."
opts = self.model._meta
app_label = opts.app_label
to_field = request.POST.get(TO_FIELD_VAR, request.GET.get(TO_FIELD_VAR))
if to_field and not self.to_field_allowed(request, to_field):
raise DisallowedModelAdminToField("The field %s cannot be referenced." % to_field)
obj = self.get_object(request, unquote(object_id), to_field)
if not self.has_delete_permission(request, obj):
raise PermissionDenied
if obj is None:
return self._get_obj_does_not_exist_redirect(request, opts, object_id)
using = router.db_for_write(self.model)
# Populate deleted_objects, a data structure of all related objects that
# will also be deleted.
(deleted_objects, model_count, perms_needed, protected) = get_deleted_objects(
[obj], opts, request.user, self.admin_site, using)
if request.POST and not protected: # The user has confirmed the deletion.
if perms_needed:
raise PermissionDenied
obj_display = force_text(obj)
attr = str(to_field) if to_field else opts.pk.attname
obj_id = obj.serializable_value(attr)
self.log_deletion(request, obj, obj_display)
self.delete_model(request, obj)
return self.response_delete(request, obj_display, obj_id)
object_name = force_text(opts.verbose_name)
if perms_needed or protected:
title = _("Cannot delete %(name)s") % {"name": object_name}
else:
title = _("Are you sure?")
context = dict(
self.admin_site.each_context(request),
title=title,
object_name=object_name,
object=obj,
deleted_objects=deleted_objects,
model_count=dict(model_count).items(),
perms_lacking=perms_needed,
protected=protected,
opts=opts,
app_label=app_label,
preserved_filters=self.get_preserved_filters(request),
is_popup=(IS_POPUP_VAR in request.POST or
IS_POPUP_VAR in request.GET),
to_field=to_field,
)
context.update(extra_context or {})
return self.render_delete_form(request, context)
def history_view(self, request, object_id, extra_context=None):
"The 'history' admin view for this model."
from django.contrib.admin.models import LogEntry
# First check if the user can see this history.
model = self.model
obj = self.get_object(request, unquote(object_id))
if obj is None:
return self._get_obj_does_not_exist_redirect(request, model._meta, object_id)
if not self.has_change_permission(request, obj):
raise PermissionDenied
# Then get the history for this object.
opts = model._meta
app_label = opts.app_label
action_list = LogEntry.objects.filter(
object_id=unquote(object_id),
content_type=get_content_type_for_model(model)
).select_related().order_by('action_time')
context = dict(
self.admin_site.each_context(request),
title=_('Change history: %s') % force_text(obj),
action_list=action_list,
module_name=capfirst(force_text(opts.verbose_name_plural)),
object=obj,
opts=opts,
preserved_filters=self.get_preserved_filters(request),
)
context.update(extra_context or {})
request.current_app = self.admin_site.name
return TemplateResponse(request, self.object_history_template or [
"admin/%s/%s/object_history.html" % (app_label, opts.model_name),
"admin/%s/object_history.html" % app_label,
"admin/object_history.html"
], context)
def _create_formsets(self, request, obj, change):
"Helper function to generate formsets for add/change_view."
formsets = []
inline_instances = []
prefixes = {}
get_formsets_args = [request]
if change:
get_formsets_args.append(obj)
for FormSet, inline in self.get_formsets_with_inlines(*get_formsets_args):
prefix = FormSet.get_default_prefix()
prefixes[prefix] = prefixes.get(prefix, 0) + 1
if prefixes[prefix] != 1 or not prefix:
prefix = "%s-%s" % (prefix, prefixes[prefix])
formset_params = {
'instance': obj,
'prefix': prefix,
'queryset': inline.get_queryset(request),
}
if request.method == 'POST':
formset_params.update({
'data': request.POST.copy(),
'files': request.FILES,
'save_as_new': '_saveasnew' in request.POST
})
formsets.append(FormSet(**formset_params))
inline_instances.append(inline)
return formsets, inline_instances当然不用看上面那么多,我们暂时只需要关注两点即可
class ModelAdmin(BaseModelAdmin):
list_display = ('__str__',)
list_display_links = ()
list_filter = ()
list_select_related = False
search_fields = ()
# Actions
actions = []
action_form = helpers.ActionForm
actions_on_top = True
actions_on_bottom = False
actions_selection_counter = True
checks_class = ModelAdminChecks
#__init__也进行了简化,不是原版
def __init__(self, model:
self.model = model
这就是文章开头说的提供的五种接口,当时我们继承的就是这个类,并对list_display属性进行了修改,这点等会再说

注意一下这个类的__init__,它的参数是model,等会会用到这个点
至于self._registry就简单了,它只是AdminSite类的一个字典而已

现在我们再去看看上面的代码:
def register(self, model, admin_class=None, **options):
if not admin_class:
admin_class = ModelAdmin
self._registry[model] = admin_class(model)
当admin_class为空的时候,默认admin_class是ModelAdmin类,注意这里是没有括号的
同时为自己的_registry字典中添加数据,model是表名。 admin_class(model)是实例化对象,admin_class是一个类,它的参数上面说了是一个model类
当admin_class不为空的时候,传进来的admin_class也是继承了ModleAdmin类,只是改了像list_display这样的参数而已
所以register这个函数的作用就是把表传入自己的_registry中
那么我们现在为了路由分发就需要写一个类似ModelAdmin的类和一个register函数


这样就可以实现模型表的注册了

现在实现路由分发:
注册了的表都已经存进了self._registry中
#测试函数
def test(request):
return HttpResponse('测试')
def get_urls(self):
tem=[]
for model_class,conf_obj in self._registery.items():
#获取app名字,不同app之间表可能重名
app_label=model_class._meta.app_label
#获取表的名字
model_name=model_class._meta.model_name
tem.append(
url(r'^%s/%s/'%(app_label, model_name),test)
)
return tem运行Django,

至此我们就实现了路由分发,这个时候只要在stark.py的文件中进行了表的注册,那么就会自动创建路由
3.模型表数据展示:
路由分发实现了,那么怎么展示表中的数据呢,首先在前端数据不能写死,每个表的数据都不一样,先看看admin是怎么实现的吧

admin展示的表头是表名的大写,表体是一个个对象
加了list_display之后:

所以数据展示主要是从list_display入手
在源码中,我们知道了默认的list_display=['__str__',],不加修饰的情况下,就是只展示model的__str__,list_display除了默认的__str__其余就是人为添加的表的字段了,所以我们通过list_display获取表的字段
def list_views(self,request):
head_list=[]#定义一个空列表用于存储表头
for header in self.list_display:
if header=='__str__':#如果是__str__就把表名大写
var=self.model._meta.model_name.upper()
else:
#获取注释名称,没有的注释,获取字段名
var=self.model._meta.get_field(header).verbose_name
head_list.append(var)
queryset=self.model.objects.all()
body_list=[]
for i in queryset:#i相当于表的一行
tem=[]
for k in self.list_display:#k是字段名
var=getattr(i,k)#var是在一行中,通过k字段名获取到ed数据
tem.append(var)
body_list.append(tem)
#结束的时候,body_list的结构应该是[[],[],[],]
return render(request,'list_views.html',locals())编写前端代码
<table class="table table-bordered table-hover table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
{% for foo in head_list %}
<td>{{ foo }}</td>
{% endfor %}
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for body in body_list %}
<tr>
{% for foo in body %}
<td>{{ foo }}</td>
{% endfor %}
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
实现效果:

这样的效果不是最终效果
我们可以在list_display中添加字段,那么我们能不能添加函数?
当然可以,添加函数之后,我们就可以实现各种效果,如下图:

很简单,只需要在循环display_list的时候,判断是否是str类即可
一个简单的编辑函数:
def edit_col(self,is_header=False):
if is_header:
return '编辑'
return mark_safe('<a href="#">编辑</a>')当不是表头的时候,返回一个a标签(通过mark_safe)实现,当是表头的时候,返回一个字符串
循环的时候,加上isinstance判断一下即可if isinstance(header,str):,如果是函数 var=header(self,is_header=True),(这是表头数据)
至此数据展示完成
未完待续...






0