Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟JSON差不多,但json使用起来更简单,不过,古时候,在json还没诞生的黑暗年代,大家只能选择用xml呀,至今很多传统公司如金融行业的很多系统的接口还主要是xml。xml的格式如下,就
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟JSON差不多,但json使用起来更简单,不过,古时候,在json还没诞生的黑暗年代,大家只能选择用xml呀,至今很多传统公司如金融行业的很多系统的接口还主要是xml。
xml的格式如下,就是通过<>节点来区别数据结构的:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank updated="yes">2</rank>
<year>2008</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/>
<neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/>
</country>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank updated="yes">5</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/>
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank updated="yes">69</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/>
<neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/>
</country>
</data>xml协议在各个语言里的都 是支持的,在python中可以用以下模块操作xml
#!/usr/bin/env Python
# coding: utf-8
__author__ = 'www.py3study.com'
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
#读取并解析xml文件
tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml")
#获得root节点
root = tree.getroot()
#节点标签名
print(root.tag)
# 遍历xml文档
for child in root:
#child.tag就是country,child.attrib就是country的属性,就是name值
print(child.tag, child.attrib)
for i in child:
#i.tag就是country里面的之列表,比如rank
#i.text就是子列表显示的值,比如2
print(i.tag, i.text)
# 只遍历year 节点
for node in root.iter('year'):
print(node.tag, node.text)执行输出
data
country {'name': 'Liechtenstein'}
rank 2
....
修改和删除xml文档内容
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
__author__ = 'www.py3study.com'
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml")
root = tree.getroot()
# 修改
for node in root.iter('year'):
#获取每一个年,加1
new_year = int(node.text) + 1
node.text = str(new_year)
#增加属性updated
node.set("updated", "yes")
tree.write("xmltest.xml")
# 删除node
for country in root.findall('country'):
#获取country下的rank值
rank = int(country.find('rank').text)
#当大于50,就删除
if rank > 50:
root.remove(country)
tree.write('output.xml')执行程序,查看output.xml文件内容
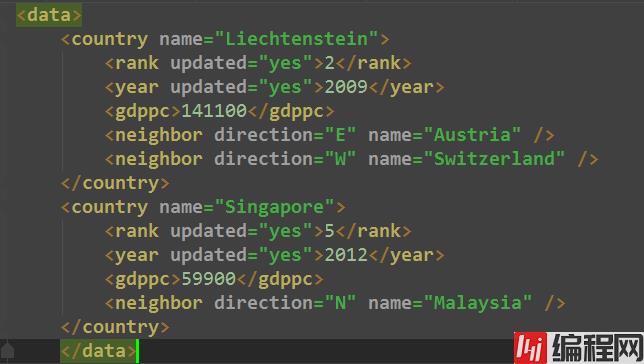
自己创建xml文档
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
__author__ = 'www.py3study.com'
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET,re
#根节点
new_xml = ET.Element("personinfolist")
#SubElement子节点,new_xml节点名,attrib属性
personinfo = ET.SubElement(new_xml, "personinfo", attrib={"enrolled": "yes"})
name = ET.SubElement(personinfo, "name")
name.text = "Zhang Shao Han"
age = ET.SubElement(personinfo, "age", attrib={"checked": "no"})
sex = ET.SubElement(personinfo, "sex")
#设置属性值
age.text = '23'
personinfo2 = ET.SubElement(new_xml, "personinfo", attrib={"enrolled": "no"})
name = ET.SubElement(personinfo2, "name")
name.text = "Liu Yi Fei"
age = ET.SubElement(personinfo2, "age")
age.text = '19'
et = ET.ElementTree(new_xml) # 生成文档对象
#xml_declaration表示头部信息
et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8", xml_declaration=True)
ET.dump(new_xml) # 打印生成的格式执行程序,查看test.xml文件
由于默认的write方法,写入文件,代码都挤到一块了。
使用网页工具,进行展示
Http://tool.oschina.net/codefORMat/xml/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<personinfolist>
<personinfo enrolled="yes">
<name>Zhang Shao Han</name>
<age checked="no">23</age>
<sex/>
</personinfo>
<personinfo enrolled="no">
<name>Liu Yi Fei</name>
<age>19</age>
</personinfo>
</personinfolist>--结束END--
本文标题: python xml模块
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/179014.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0