Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录前言参考地址前端下载模板下载Easyexcel动态表头解析EasyExcel动态表头导出总结前言 excel文件导入及导出,是日常开发中经常遇到的需求。本次笔者以EasyExce
excel文件导入及导出,是日常开发中经常遇到的需求。本次笔者以EasyExcel为例,针对在项目中遇到的动态表头解析及导出的场景,详细介绍具体的代码实现过程。
https://GitHub.com/alibaba/easyexcel
const download = () => {
axiOS({
method: 'GET',
url: config.Http.baseUrl + '/templateDownload',
responseType: 'blob',
})
.then(function (res) {
const content = res.data
const blob = new Blob([content], { type: "application/application/vnd.openxmlfORMats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet" })
const downloadElement = document.createElement("a");
const href = window.URL.createObjectURL(blob);
downloadElement.href = href;
downloadElement.download = decodeURI(res.headers['filename']);
document.body.appendChild(downloadElement);
downloadElement.click();
document.body.removeChild(downloadElement); // 下载完成移除元素
window.URL.revokeObjectURL(href); // 释放掉blob对象
})
}
excel文件导入功能,常常需要进行模板下载,在SpringBoot项目中,程序是以jar包的形式运行的,所以有很多小伙伴常常
遇到在本地开发中能够实现下载功能,但部署到服务器的时候,找不到模板文件的问题。
@Override
public void templateDownload(HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request) {
//获取要下载的模板名称
String fileName = "批量导入模板.xlsx";
//获取文件下载路径
String filePath = "/template/template.xlsx";
TemplateDownloadUtil.download(response, request, fileName, filePath);
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
@Slf4j
public class TemplateDownloadUtil {
public static void download(HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request,String fileName,String filePath){
try {
response.setContentType("application/application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 这里URLEncoder.encode可以防止中文乱码 当然和easyexcel没有关系
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
response.setHeader("filename", URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Expose-Headers", "filename,Content-Disposition");
//获取文件的路径,此方式本地开发可以运行,服务器无法获取文件
// String filePath = getClass().getResource("/template/template.xlsx").getPath();
// FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//在服务器中能够读取到模板文件
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(filePath);
InputStream input = resource.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[2048];
int len;
while ((len = input.read(b)) != -1) {
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
//修正 Excel在“xxx.xlsx”中发现不可读取的内容。是否恢复此工作薄的内容?如果信任此工作簿的来源,请点击"是"
// response.setHeader("Content-Length", String.valueOf(input.getChannel().size()));
input.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("下载模板失败 :", e);
}
}
}EasyExcel简单的读文件,官网中已经有详细的说明,本文不再赘述。
本文主要针对笔者遇到的复杂表头及动态表头进行讲解。
模板示例
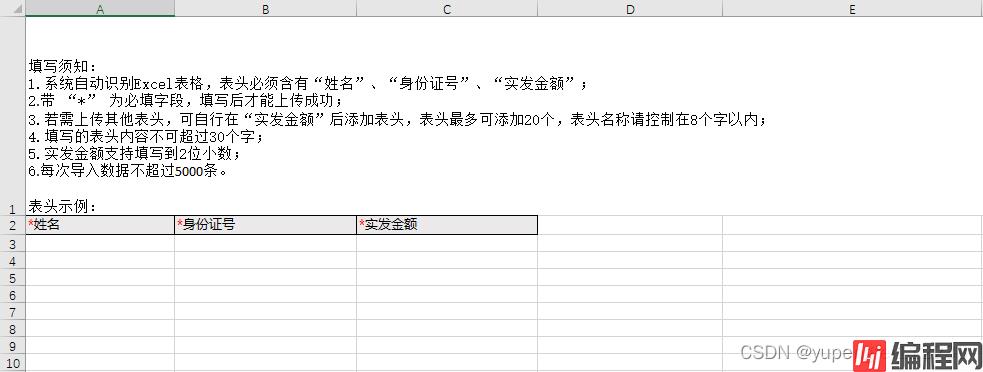
解析
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.fastJSON.jsON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Slf4j
@Data
public class BatchReadListener extends AnalysisEventListener<Map<Integer, String>> {
private static final int BATCH_COUNT = 500;
//Excel数据缓存结构
private List<Map<Integer, Map<Integer, String>>> list = new ArrayList<>();
//Excel表头(列名)数据缓存结构
private Map<Integer, String> headTitleMap = new HashMap<>();
private DbFileBatchService dbFileBatchService;
private DbFileContentService dbFileContentService;
private FileBatch fileBatch;
private int total = 0;
public BatchReadListener(DbFileBatchService dbFileBatchService, DbFileContentService dbFileContentService, FileBatch fileBatch) {
this.dbFileBatchService = dbFileBatchService;
this.dbFileContentService = dbFileContentService;
this.fileBatch = fileBatch;
}
@Override
public void invoke(Map<Integer, String> data, AnalysisContext context) {
log.info("解析到一条数据:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data));
total++;
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, String>> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(context.readRowHolder().getRowIndex(), data);
list.add(map);
// 达到BATCH_COUNT了,需要去存储一次数据库,防止数据几万条数据在内存,容易OOM
if (list.size() >= BATCH_COUNT) {
saveData();
// 存储完成清理 list
list.clear();
}
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
// 这里也要保存数据,确保最后遗留的数据也存储到数据库
saveData();
log.info("所有数据解析完成!");
}
@Override
public void invokeHeadMap(Map<Integer, String> headMap, AnalysisContext context) {
log.info("表头数据:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(headMap));
headTitleMap = headMap;
}
private void saveData() {
log.info("{}条数据,开始存储数据库!", list.size());
FileContent fileContent = null;
List<FileContent> fileContentList = list.stream().flatMap(
integerMap -> integerMap.entrySet().stream().map(entrySet -> {
//entrySet.geTKEy()获取的是内容的RowIndex,实际的行数需要根据表头数进行处理
Integer rowIndex = entrySet.getKey();
Map<Integer, String> value = entrySet.getValue();
log.info(JSONObject.toJSONString(value));
fileContent = new FileContent();
fileContent.setBatchId(fileBatch.getId());
fileContent.setBatchNo(fileBatch.getBatchNo());
//固定字段入库
fileContent.setName(value.get(0) != null ? value.get(0).trim() : "");
fileContent.setCertNo(value.get(1) != null ? value.get(1).trim() : "");
fileContent.setRealAmount(value.get(2) != null ? value.get(2).trim() : "");
//所有动态表头数据转为JSON串入库
fileContent.setFieldsValue(JSONObject.toJSONString(value));
//取实际的内容rowIndex
fileContent.setRowNum(rowIndex + 1);
fileContent.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
return xcSalaryFileContent;
}
)).collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info(JSONObject.toJSONString(fileContentList));
dbFileContentService.saveBatch(fileContentList);
log.info("存储数据库成功!");
}
} BatchReadListener listener = new BatchReadListener(dbFileBatchService, dbFileContentService, fileBatch);
try {
//注:headRowNumber默认为1,现赋值为2,即从第三行开始读取内容
EasyExcel.read(fileInputStream, listener).headRowNumber(2).sheet().doRead();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("EasyExcel解析文件失败,{}", e);
throw new CustomException("文件解析失败,请重新上传");
}
//获取表头信息进行处理
Map<Integer, String> headTitleMap = listener.getHeadTitleMap();
//获取动态表头信息
List<String> headList = headTitleMap.keySet().stream().map(key -> {
String head = headTitleMap.get(key);
log.info(head);
return head == null ? "" : head.replace("*", "");
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//可以对表头进行入库保存,方便后续导出
综上,动态表头即可完成解析。
导出示例
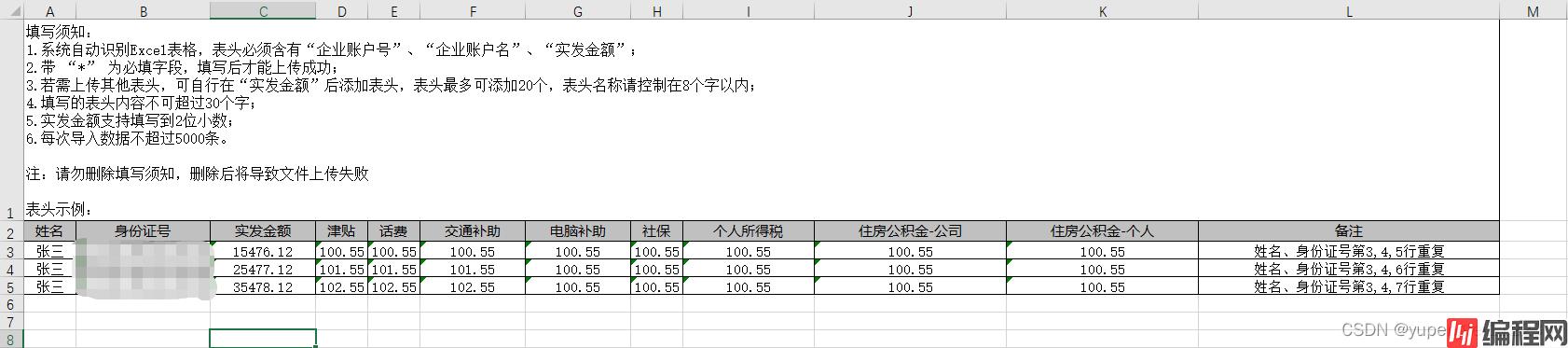
获取动态头
private List<List<String>> getFileHeadList( FileBatch fileBatch) {
String head = fileBatch.getFileHead();
List<String> headList = Arrays.asList(head.split(","));
List<List<String>> fileHead = headList.stream().map(item -> concatHead(Lists.newArrayList(item))).collect(Collectors.toList());
fileHead.add(concatHead(Lists.newArrayList("备注")));
return fileHead;
}
private List<String> concatHead(List<String> headContent) {
String remake = "填写须知: \n" +
"1.系统自动识别Excel表格,表头必须含有“企业账户号”、“企业账户名”、“实发金额”;\n" +
"2.带 “*” 为必填字段,填写后才能上传成功;\n" +
"3.若需上传其他表头,可自行在“实发金额”后添加表头,表头最多可添加20个,表头名称请控制在8个字以内;\n" +
"4.填写的表头内容不可超过30个字;\n" +
"5.实发金额支持填写到2位小数;\n" +
"6.每次导入数据不超过5000条。\n" +
"\n" +
"注:请勿删除填写须知,删除后将导致文件上传失败\n" +
"\n" +
"表头示例:";
headContent.add(0, remake);
return headContent;
}
获取数据
List<FileContent> fileContentList = dbFileContentService.list(
Wrappers.<FileContent>lambdaQuery()
.eq(FileContent::getBatchId, fileBatch.getId())
.orderByAsc(FileContent::getRowNum)
);
List<List<Object>> contentList = fileContentList.stream().map(fileContent -> {
List<Object> rowList = new ArrayList<>();
String fieldsValue = fileContent.getFieldsValue();
JSONObject contentObj = JSONObject.parseObject(fieldsValue);
for (int columnIndex = 0 , length = headList.size(); columnIndex < length; columnIndex++) {
Object content = contentObj.get(columnIndex);
rowList.add(content == null ? "" : content);
}
rowList.add(fileContent.getCheckMessage());
return rowList;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
单元格格式设置
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.DataFormatData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.WriteCellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.handler.context.CellWriteHandlerContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.style.WriteCellStyle;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.style.WriteFont;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.HorizontalCellStyleStrategy;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.BorderStyle;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.HorizontalAlignment;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.IndexedColors;
import java.util.List;
public class CellStyleStrategy extends HorizontalCellStyleStrategy {
private final WriteCellStyle headWriteCellStyle;
private final WriteCellStyle contentWriteCellStyle;
private final List<Integer> columnIndexes;
public CellStyleStrategy(List<Integer> columnIndexes,WriteCellStyle headWriteCellStyle, WriteCellStyle contentWriteCellStyle) {
this.columnIndexes = columnIndexes;
this.headWriteCellStyle = headWriteCellStyle;
this.contentWriteCellStyle = contentWriteCellStyle;
}
//设置头样式
@Override
protected void setHeadCellStyle( CellWriteHandlerContext context) {
// 获取字体实例
WriteFont headWriteFont = new WriteFont();
headWriteFont.setFontName("宋体");
//表头不同处理
if (columnIndexes.get(0).equals(context.getRowIndex())) {
headWriteCellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.WHITE.getIndex());
headWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.LEFT);
headWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
headWriteFont.setBold(false);
headWriteFont.setFontName("宋体");
}else{
headWriteCellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.GREY_25_PERCENT.getIndex());
headWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
headWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 11);
headWriteFont.setBold(false);
headWriteFont.setFontName("微软雅黑");
}
headWriteCellStyle.setWriteFont(headWriteFont);
DataFormatData dataFormatData = new DataFormatData();
dataFormatData.setIndex((short)49);
headWriteCellStyle.setDataFormatData(dataFormatData);
if (stopProcessing(context)) {
return;
}
WriteCellData<?> cellData = context.getFirstCellData();
WriteCellStyle.merge(headWriteCellStyle, cellData.getOrCreateStyle());
}
//设置填充数据样式
@Override
protected void setContentCellStyle(CellWriteHandlerContext context) {
WriteFont contentWriteFont = new WriteFont();
contentWriteFont.setFontName("宋体");
contentWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 11);
//设置数据填充后的实线边框
contentWriteCellStyle.setWriteFont(contentWriteFont);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
DataFormatData dataFormatData = new DataFormatData();
dataFormatData.setIndex((short)49);
contentWriteCellStyle.setDataFormatData(dataFormatData);
contentWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
WriteCellData<?> cellData = context.getFirstCellData();
WriteCellStyle.merge(contentWriteCellStyle, cellData.getOrCreateStyle());
}
}行高设置
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.row.AbstractRowHeightStyleStrategy;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
public class CellRowHeightStyleStrategy extends AbstractRowHeightStyleStrategy {
@Override
protected void setHeadColumnHeight(Row row, int relativeRowIndex) {
//设置主标题行高为17.7
if(relativeRowIndex == 0){
//如果excel需要显示行高为15,那这里就要设置为15*20=300
row.setHeight((short) 3240);
}
}
@Override
protected void setContentColumnHeight(Row row, int relativeRowIndex) {
}
}
列宽度自适应
如果是简单表头,可以使用EasyExcel中的LongestMatchColumnWidthStyleStrategy()来实现。
EasyExcel.write(fileName, LongestMatchColumnWidthData.class)
.reGISterWriteHandler(new LongestMatchColumnWidthStyleStrategy()).sheet("模板").doWrite(dataLong());
如果是复杂表头,就需要自己来实现,代码如下:
import com.alibaba.excel.enums.CellDataTypeEnum;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Head;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.CellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.WriteCellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.holder.WriteSheetHolder;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.column.AbstractColumnWidthStyleStrategy;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
public class CellWidthStyleStrategy extends AbstractColumnWidthStyleStrategy {
private Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> CACHE = new HashMap<>();
@Override
protected void setColumnWidth(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, List<WriteCellData<?>> cellDataList, Cell cell, Head head, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
Map<Integer, Integer> maxColumnWidthMap = CACHE.get(writeSheetHolder.getSheetNo());
if (maxColumnWidthMap == null) {
maxColumnWidthMap = new HashMap<>();
CACHE.put(writeSheetHolder.getSheetNo(), maxColumnWidthMap);
}
if (isHead) {
if(relativeRowIndex.intValue() == 1){
Integer length = cell.getStrinGCellValue().getBytes().length;
Integer maxColumnWidth = maxColumnWidthMap.get(cell.getColumnIndex());
if (maxColumnWidth == null || length > maxColumnWidth) {
maxColumnWidthMap.put(cell.getColumnIndex(), length);
writeSheetHolder.getSheet().setColumnWidth(cell.getColumnIndex(), length * 300);
}
}
}else{
Integer columnWidth = this.dataLength(cellDataList, cell, isHead);
if (columnWidth >= 0) {
if (columnWidth > 255) {
columnWidth = 255;
}
Integer maxColumnWidth = maxColumnWidthMap.get(cell.getColumnIndex());
if (maxColumnWidth == null || columnWidth > maxColumnWidth) {
maxColumnWidthMap.put(cell.getColumnIndex(), columnWidth);
writeSheetHolder.getSheet().setColumnWidth(cell.getColumnIndex(), columnWidth * 256);
}
}
}
}
private Integer dataLength(List<WriteCellData<?>> cellDataList, Cell cell, Boolean isHead) {
if (isHead) {
return cell.getStringCellValue().getBytes().length;
} else {
CellData cellData = cellDataList.get(0);
CellDataTypeEnum type = cellData.getType();
if (type == null) {
return -1;
} else {
switch (type) {
case STRING:
return cellData.getStringValue().getBytes().length;
case BOOLEAN:
return cellData.getBooleanValue().toString().getBytes().length;
case NUMBER:
return cellData.getNumberValue().toString().getBytes().length;
default:
return -1;
}
}
}
}
}写入文件
EasyExcel.write(response.getOutputStream())
.head(head)
.registerWriteHandler(new CellRowHeightStyleStrategy()) //设置行高的策略
.registerWriteHandler(new CellStyleStrategy(Arrays.asList(0,1),new WriteCellStyle(), new WriteCellStyle()))
.registerWriteHandler(new CellWidthStyleStrategy())
.sheet(sheetName)
.doWrite(list);
以上便是EasyExcel解析动态表头及导出的整个过程。
在使用过程中,笔者的感受是,上手难度很低,很适合新手去做简单的表格解析,当然,如果你的需求有复杂的格式,EasyExcel也提供了api,能够很好的满足需要。
到此这篇关于Java利用EasyExcel解析动态表头及导出实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关EasyExcel解析动态表头及导出内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Java利用EasyExcel解析动态表头及导出实现过程
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/174420.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0