去阿里面试,三面的时候被问到了这个问题,当时思路虽然正确,可惜表述的不够清晰后来花了一些时间整理了下思路,那么如何实现给所有的async函数添加try/catch呢?async如果不加 try/catch 会发生什么事?// 示例 asyn
去阿里面试,三面的时候被问到了这个问题,当时思路虽然正确,可惜表述的不够清晰
后来花了一些时间整理了下思路,那么如何实现给所有的async函数添加try/catch呢?
// 示例
async function fn() {
let value = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('failure');
});
console.log('do something...');
}
fn()
导致浏览器报错:一个未捕获的错误
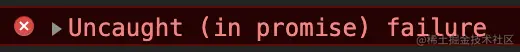
在开发过程中,为了保证系统健壮性,或者是为了捕获异步的错误,需要频繁的在 async 函数中添加 try/catch,避免出现上述示例的情况
可是我很懒,不想一个个加,懒惰使我们进步?
下面,通过手写一个babel 插件,来给所有的async函数添加try/catch
原始代码:
async function fn() {
await new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject('报错'));
await new Promise((resolve) => resolve(1));
console.log('do something...');
}
fn();
使用插件转化后的代码:
async function fn() {
try {
await new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject('报错'));
await new Promise(resolve => resolve(1));
console.log('do something...');
} catch (e) {
console.log("\nfilePath: E:\\myapp\\src\\main.js\nfuncName: fn\nError:", e);
}
}
fn();
打印的报错信息:
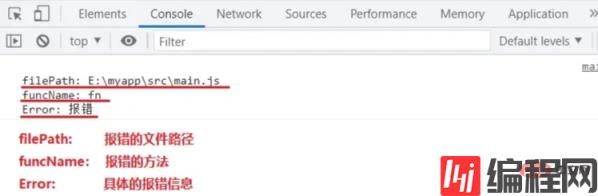
通过详细的报错信息,帮助我们快速找到目标文件和具体的报错方法,方便去定位问题
1)借助AST抽象语法树,遍历查找代码中的await关键字
2)找到await节点后,从父路径中查找声明的async函数,获取该函数的body(函数中包含的代码)
3)创建try/catch语句,将原来async的body放入其中
4)最后将async的body替换成创建的try/catch语句
先聊聊 AST 这个帅小伙?,不然后面的开发流程走不下去
AST是代码的树形结构,生成 AST 分为两个阶段:词法分析和 语法分析
词法分析
词法分析阶段把字符串形式的代码转换为令牌(tokens) ,可以把tokens看作是一个扁平的语法片段数组,描述了代码片段在整个代码中的位置和记录当前值的一些信息
比如let a = 1,对应的AST是这样的

语法分析
语法分析阶段会把token转换成 AST 的形式,这个阶段会使用token中的信息把它们转换成一个 AST 的表述结构,使用type属性记录当前的类型
例如 let 代表着一个变量声明的关键字,所以它的 type 为 VariableDeclaration,而 a = 1 会作为 let 的声明描述,它的 type 为 VariableDeclarator
AST在线查看工具:AST explorer
再举个?,加深对AST的理解
function demo(n) {
return n * n;
}
转化成AST的结构
{
"type": "Program", // 整段代码的主体
"body": [
{
"type": "FunctionDeclaration", // function 的类型叫函数声明;
"id": { // id 为函数声明的 id
"type": "Identifier", // 标识符 类型
"name": "demo" // 标识符 具有名字
},
"expression": false,
"generator": false,
"async": false, // 代表是否 是 async function
"params": [ // 同级 函数的参数
{
"type": "Identifier",// 参数类型也是 Identifier
"name": "n"
}
],
"body": { // 函数体内容 整个格式呈现一种树的格式
"type": "BlockStatement", // 整个函数体内容 为一个块状代码块类型
"body": [
{
"type": "ReturnStatement", // return 类型
"argument": {
"type": "BinaryExpression",// BinaryExpression 二进制表达式类型
"start": 30,
"end": 35,
"left": { // 分左 右 中 结构
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "n"
},
"operator": "*", // 属于操作符
"right": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "n"
}
}
}
]
}
}
],
"sourceType": "module"
}
| 类型原名称 | 中文名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Program | 程序主体 | 整段代码的主体 |
| VariableDeclaration | 变量声明 | 声明一个变量,例如 var let const |
FunctionDeclaration | 函数声明 | 声明一个函数,例如 function |
| ExpressionStatement | 表达式语句 | 通常是调用一个函数,例如 console.log() |
| BlockStatement | 块语句 | 包裹在 {} 块内的代码,例如 if (condition){var a = 1;} |
| BreakStatement | 中断语句 | 通常指 break |
| ContinueStatement | 持续语句 | 通常指 continue |
| ReturnStatement | 返回语句 | 通常指 return |
| SwitchStatement | Switch 语句 | 通常指 Switch Case 语句中的 Switch |
| IfStatement | If 控制流语句 | 控制流语句,通常指 if(condition){}else{} |
| Identifier | 标识符 | 标识,例如声明变量时 var identi = 5 中的 identi |
| CallExpression | 调用表达式 | 通常指调用一个函数,例如 console.log() |
| BinaryExpression | 二进制表达式 | 通常指运算,例如 1+2 |
| MemberExpression | 成员表达式 | 通常指调用对象的成员,例如 console 对象的 log 成员 |
| ArrayExpression | 数组表达式 | 通常指一个数组,例如 [1, 3, 5] |
FunctionExpression | 函数表达式 | 例如const func = function () {} |
ArrowFunctionExpression | 箭头函数表达式 | 例如const func = ()=> {} |
AwaitExpression | await表达式 | 例如let val = await f() |
ObjectMethod | 对象中定义的方法 | 例如 let obj = { fn () {} } |
| NewExpression | New 表达式 | 通常指使用 New 关键词 |
| AssignmentExpression | 赋值表达式 | 通常指将函数的返回值赋值给变量 |
| UpdateExpression | 更新表达式 | 通常指更新成员值,例如 i++ |
| Literal | 字面量 | 字面量 |
| BooleanLiteral | 布尔型字面量 | 布尔值,例如 true false |
| NumericLiteral | 数字型字面量 | 数字,例如 100 |
| StringLiteral | 字符型字面量 | 字符串,例如 vansenb |
| SwitchCase | Case 语句 | 通常指 Switch 语句中的 Case |
1)原始代码
async function fn() {
await f()
}
对应的AST结构

2)增加try catch后的代码
async function fn() {
try {
await f()
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
}
}
对应的AST结构

通过AST结构对比,插件的核心就是将原始函数的body放到try语句中
我曾在之前的文章中聊过如何开发一个babel插件
这里简单回顾一下
module.exports = function (babel) {
let t = babel.type
return {
visitor: {
// 设置需要范围的节点类型
CallExression: (path, state) => {
do soming ……
}
}
}
}
1)通过 babel 拿到 types 对象,操作 AST 节点,比如创建、校验、转变等
2)visitor:定义了一个访问者,可以设置需要访问的节点类型,当访问到目标节点后,做相应的处理来实现插件的功能
回到业务需求,现在需要找到await节点,可以通过AwaitExpression表达式获取
module.exports = function (babel) {
let t = babel.type
return {
visitor: {
// 设置AwaitExpression
AwaitExpression(path) {
// 获取当前的await节点
let node = path.node;
}
}
}
}
通过findParent方法,在父节点中搜寻 async 节点
// async节点的属性为true
const asyncPath = path.findParent(p => p.node.async)
async 节点的AST结构

这里要注意,async 函数分为4种情况:函数声明 、箭头函数 、函数表达式 、函数为对象的方法
// 1️⃣:函数声明
async function fn() {
await f()
}
// 2️⃣:函数表达式
const fn = async function () {
await f()
};
// 3️⃣:箭头函数
const fn = async () => {
await f()
};
// 4️⃣:async函数定义在对象中
const obj = {
async fn() {
await f()
}
}
需要对这几种情况进行分别判断
module.exports = function (babel) {
let t = babel.type
return {
visitor: {
// 设置AwaitExpression
AwaitExpression(path) {
// 获取当前的await节点
let node = path.node;
// 查找async函数的节点
const asyncPath = path.findParent((p) => p.node.async && (p.isFunctionDeclaration() || p.isArrowFunctionExpression() || p.isFunctionExpression() || p.isObjectMethod()));
}
}
}
}
babel-template可以用以字符串形式的代码来构建AST树节点,快速优雅开发插件
// 引入babel-template
const template = require('babel-template');
// 定义try/catch语句模板
let tryTemplate = `
try {
} catch (e) {
console.log(CatchError:e)
}`;
// 创建模板
const temp = template(tryTemplate);
// 给模版增加key,添加console.log打印信息
let tempArgumentObj = {
// 通过types.stringLiteral创建字符串字面量
CatchError: types.stringLiteral('Error')
};
// 通过temp创建try语句的AST节点
let tryNode = temp(tempArgumentObj);
module.exports = function (babel) {
let t = babel.type
return {
visitor: {
AwaitExpression(path) {
let node = path.node;
const asyncPath = path.findParent((p) => p.node.async && (p.isFunctionDeclaration() || p.isArrowFunctionExpression() || p.isFunctionExpression() || p.isObjectMethod()));
let tryNode = temp(tempArgumentObj);
// 获取父节点的函数体body
let info = asyncPath.node.body;
// 将函数体放到try语句的body中
tryNode.block.body.push(...info.body);
// 将父节点的body替换成新创建的try语句
info.body = [tryNode];
}
}
}
}
到这里,插件的基本结构已经成型,但还有点问题,如果函数已存在try/catch,该怎么处理判断呢?
// 示例代码,不再添加try/catch
async function fn() {
try {
await f()
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
}
}
通过isTryStatement判断是否已存在try语句
module.exports = function (babel) {
let t = babel.type
return {
visitor: {
AwaitExpression(path) {
// 判断父路径中是否已存在try语句,若存在直接返回
if (path.findParent((p) => p.isTryStatement())) {
return false;
}
let node = path.node;
const asyncPath = path.findParent((p) => p.node.async && (p.isFunctionDeclaration() || p.isArrowFunctionExpression() || p.isFunctionExpression() || p.isObjectMethod()));
let tryNode = temp(tempArgumentObj);
let info = asyncPath.node.body;
tryNode.block.body.push(...info.body);
info.body = [tryNode];
}
}
}
}
获取报错时的文件路径 filePath 和方法名称 funcName,方便快速定位问题
获取文件路径
// 获取编译目标文件的路径,如:E:\myapp\src\App.Vue
const filePath = this.filename || this.file.opts.filename || 'unknown';
获取报错的方法名称
// 定义方法名
let asyncName = '';
// 获取async节点的type类型
let type = asyncPath.node.type;
switch (type) {
// 1️⃣函数表达式
// 情况1:普通函数,如const func = async function () {}
// 情况2:箭头函数,如const func = async () => {}
case 'FunctionExpression':
case 'ArrowFunctionExpression':
// 使用path.getSibling(index)来获得同级的id路径
let identifier = asyncPath.getSibling('id');
// 获取func方法名
asyncName = identifier && identifier.node ? identifier.node.name : '';
break;
// 2️⃣函数声明,如async function fn2() {}
case 'FunctionDeclaration':
asyncName = (asyncPath.node.id && asyncPath.node.id.name) || '';
break;
// 3️⃣async函数作为对象的方法,如vue项目中,在methods中定义的方法: methods: { async func() {} }
case 'ObjectMethod':
asyncName = asyncPath.node.key.name || '';
break;
}
// 若asyncName不存在,通过argument.callee获取当前执行函数的name
let funcName = asyncName || (node.argument.callee && node.argument.callee.name) || '';
用户引入插件时,可以设置exclude、include、 customLog选项
exclude: 设置需要排除的文件,不对该文件进行处理
include: 设置需要处理的文件,只对该文件进行处理
customLog: 用户自定义的打印信息
入口文件index.js
// babel-template 用于将字符串形式的代码来构建AST树节点
const template = require('babel-template');
const { tryTemplate, catchConsole, mergeOptions, matchesFile } = require('./util');
module.exports = function (babel) {
// 通过babel 拿到 types 对象,操作 AST 节点,比如创建、校验、转变等
let types = babel.types;
// visitor:插件核心对象,定义了插件的工作流程,属于访问者模式
const visitor = {
AwaitExpression(path) {
// 通过this.opts 获取用户的配置
if (this.opts && !typeof this.opts === 'object') {
return console.error('[babel-plugin-await-add-trycatch]: options need to be an object.');
}
// 判断父路径中是否已存在try语句,若存在直接返回
if (path.findParent((p) => p.isTryStatement())) {
return false;
}
// 合并插件的选项
const options = mergeOptions(this.opts);
// 获取编译目标文件的路径,如:E:\myapp\src\App.vue
const filePath = this.filename || this.file.opts.filename || 'unknown';
// 在排除列表的文件不编译
if (matchesFile(options.exclude, filePath)) {
return;
}
// 如果设置了include,只编译include中的文件
if (options.include.length && !matchesFile(options.include, filePath)) {
return;
}
// 获取当前的await节点
let node = path.node;
// 在父路径节点中查找声明 async 函数的节点
// async 函数分为4种情况:函数声明 || 箭头函数 || 函数表达式 || 对象的方法
const asyncPath = path.findParent((p) => p.node.async && (p.isFunctionDeclaration() || p.isArrowFunctionExpression() || p.isFunctionExpression() || p.isObjectMethod()));
// 获取async的方法名
let asyncName = '';
let type = asyncPath.node.type;
switch (type) {
// 1️⃣函数表达式
// 情况1:普通函数,如const func = async function () {}
// 情况2:箭头函数,如const func = async () => {}
case 'FunctionExpression':
case 'ArrowFunctionExpression':
// 使用path.getSibling(index)来获得同级的id路径
let identifier = asyncPath.getSibling('id');
// 获取func方法名
asyncName = identifier && identifier.node ? identifier.node.name : '';
break;
// 2️⃣函数声明,如async function fn2() {}
case 'FunctionDeclaration':
asyncName = (asyncPath.node.id && asyncPath.node.id.name) || '';
break;
// 3️⃣async函数作为对象的方法,如vue项目中,在methods中定义的方法: methods: { async func() {} }
case 'ObjectMethod':
asyncName = asyncPath.node.key.name || '';
break;
}
// 若asyncName不存在,通过argument.callee获取当前执行函数的name
let funcName = asyncName || (node.argument.callee && node.argument.callee.name) || '';
const temp = template(tryTemplate);
// 给模版增加key,添加console.log打印信息
let tempArgumentObj = {
// 通过types.stringLiteral创建字符串字面量
CatchError: types.stringLiteral(catchConsole(filePath, funcName, options.customLog))
};
// 通过temp创建try语句
let tryNode = temp(tempArgumentObj);
// 获取async节点(父节点)的函数体
let info = asyncPath.node.body;
// 将父节点原来的函数体放到try语句中
tryNode.block.body.push(...info.body);
// 将父节点的内容替换成新创建的try语句
info.body = [tryNode];
}
};
return {
name: 'babel-plugin-await-add-trycatch',
visitor
};
};
util.js
const merge = require('deepmerge');
// 定义try语句模板
let tryTemplate = `
try {
} catch (e) {
console.log(CatchError,e)
}`;
let catchConsole = (filePath, funcName, customLog) => `
filePath: ${filePath}
funcName: ${funcName}
${customLog}:`;
// 默认配置
const defaultOptions = {
customLog: 'Error',
exclude: ['node_modules'],
include: []
};
// 判断执行的file文件 是否在 exclude/include 选项内
function matchesFile(list, filename) {
return list.find((name) => name && filename.includes(name));
}
// 合并选项
function mergeOptions(options) {
let { exclude, include } = options;
if (exclude) options.exclude = toArray(exclude);
if (include) options.include = toArray(include);
// 使用merge进行合并
return merge.all([defaultOptions, options]);
}
function toArray(value) {
return Array.isArray(value) ? value : [value];
}
module.exports = {
tryTemplate,
catchConsole,
defaultOptions,
mergeOptions,
matchesFile,
toArray
};
GitHub仓库
npm网站搜索babel-plugin-await-add-trycatch
有兴趣的朋友可以下载玩一玩
babel-plugin-await-add-trycatch
通过开发这个babel插件,了解很多 AST 方面的知识,了解 babel 的原理。实际开发中,大家可以结合具体的业务需求开发自己的插件
--结束END--
本文标题: 面试题:如何给所有的async函数添加try/catch?
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/173429.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2023-05-25
2023-05-25
2023-05-25
2023-05-25
2023-05-25
2023-05-24
2023-05-24
2023-05-24
2023-05-24
2023-05-24
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0