目录前言指令注册全局注册组件内注册指令搜寻指令搜寻的时机指令搜寻的逻辑指令绑定Vnode指令调用关于指令的思考组件上使用指令组件上的一些使用场景总结前言 Vue 指令 是指 对普通D
Vue 指令 是指 对普通DOM元素进行底层操作的js对象, 它们会被挂在Element VNode对象上,在Element VNode的一些生命周期中会被调用,从而可以操作Element VNode的底层DOM元素。
指令注册 是指将指令对应的JS代码放置在某些地方,需要使用的时候可以在这些地方进行查找。
app.directive('pin', (el, binding) => {
el.style.position = 'fixed'
const s = binding.arg || 'top'
el.style[s] = binding.value + 'px'
})<!-- apiCreateApp.js -->
directive(name: string, directive?: Directive) {
// 挂载在全局的`context`的`directives`对象上
context.directives[name] = directive
return app
},directives: {
pin: (el, binding) => {
el.style.position = 'fixed'
const s = binding.arg || 'top'
el.style[s] = binding.value + 'px'
}
}<!-- component.ts -->
export function applyOptions(instance: ComponentInternalInstance) {
// 挂载在组件实例对象的`directives`上
instance.directives = directives
}开发者是在模板中使用指令,所以应该是在模板渲染的时候需要先搜寻到对应的指令。
不使用指令的模板<h4>指令演示</h4>渲染函数如下:
function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { openBlock: _openBlock, createElementBlock: _createElementBlock } = _Vue
return (_openBlock(), _createElementBlock("h4", null, "指令演示"))
}
}使用指令的模板<h4 v-pin:[right]="20">指令演示</h4>渲染函数如下:
function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { createTextVNode: _createTextVNode, resolveDirective: _resolveDirective, withDirectives: _withDirectives, openBlock: _openBlock, createElementBlock: _createElementBlock } = _Vue
const _directive_pin = _resolveDirective("pin")
return _withDirectives((_openBlock(), _createElementBlock("h4", null, _hoisted_2, 512 )), [
[_directive_pin, pinPadding, direction]
])
}
}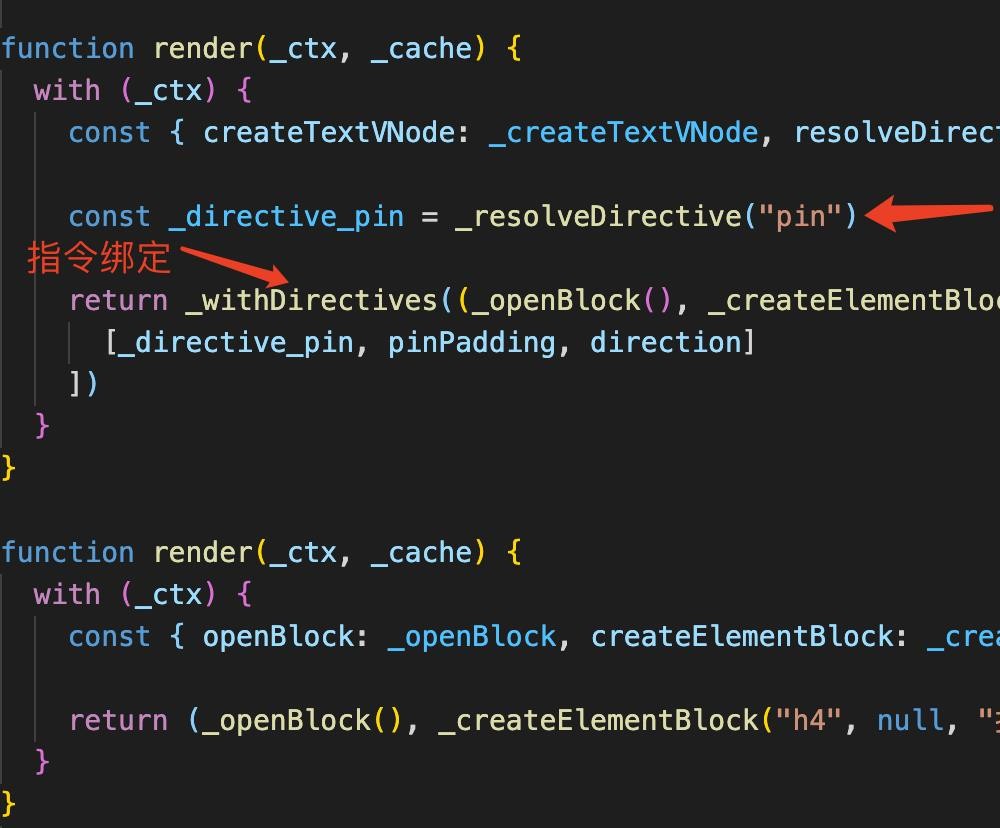
使用指令的模板需要先搜寻对应的指令,然后绑定指令到VNode
export function resolveDirective(name: string): Directive | undefined {
return resolveAsset(DIRECTIVES, name)
}
function resolveAsset(
type: AssetTypes,
name: string,
warnMissing = true,
maybeSelfReference = false
) {
const res =
// local reGIStration
// check instance[type] first which is resolved for options API
resolve(instance[type] || (Component as ComponentOptions)[type], name) ||
// global registration
resolve(instance.appContext[type], name)
return res
}export function withDirectives<T extends VNode>(
vnode: T,
directives: DirectiveArguments
): T {
const bindings: DirectiveBinding[] = vnode.dirs || (vnode.dirs = [])
for (let i = 0; i < directives.length; i++) {
let [dir, value, arg, modifiers = EMPTY_OBJ] = directives[i]
if (isFunction(dir)) {
dir = {
mounted: dir,
updated: dir
} as ObjectDirective
}
bindings.push({
dir,
instance,
value,
oldValue: void 0,
arg,
modifiers
})
}
return vnode
}将每个指令dir和其他一些参数 挂载在 VNode的dirs上。 其他参数是: instance组件实例, value指令的新值(本例为20),oldValue指令的旧值(本例为0),arg指令的参数(本例为right)
指令调用是指 指令的代码什么时候被执行的? 我们最开始提到指令是对普通DOM元素进行底层操作的JS对象,所以指令的逻辑应该是在 Element VNode中进行处理的。
const mountElement = (
vnode: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
// 1
if (dirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'created')
}
// 2
if (dirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'beforeMount')
}
// 3
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
vnodeHook && invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, vnode)
needCallTransitionHooks && transition!.enter(el)
dirs && invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'mounted')
}, parentSuspense)
}const patchElement = (
n1: VNode,
n2: VNode,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
const el = (n2.el = n1.el!)
// 1
if (dirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(n2, n1, parentComponent, 'beforeUpdate')
}
// 2
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
vnodeHook && invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, n2, n1)
dirs && invokeDirectiveHook(n2, n1, parentComponent, 'updated')
}, parentSuspense)
}const unmount: UnmountFn = (
vnode,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
doRemove = false,
optimized = false
) => {
const {
type,
props,
ref,
children,
dynamicChildren,
shapeFlag,
patchFlag,
dirs
} = vnode
// unset ref
if (ref != null) {
setRef(ref, null, parentSuspense, vnode, true)
}
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE) {
;(parentComponent!.ctx as KeepAliveContext).deactivate(vnode)
return
}
const shouldInvokeDirs = shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT && dirs
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | undefined | null
if ((vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeBeforeUnmount)) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, vnode)
}
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
unmountComponent(vnode.component!, parentSuspense, doRemove)
} else {
if (shouldInvokeDirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'beforeUnmount')
}
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
vnodeHook && invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, vnode)
shouldInvokeDirs &&
invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'unmounted')
}, parentSuspense)
}在挂载元素VNode的时候,会调用指令的created, beforeMount和mounted钩子函数;
在更新元素VNode的时候,会调用指令的beforeUpdate, updated钩子函数;
在卸载元素VNode的时候,会调用指令的beforeUnmount, unmounted钩子函数;
我们上面提到了指令是作用在元素VNode上的,那组件使用指令(例如<son v-pin:[right]="20"></son>)是什么效果呢?结果是组件上使用的指令会作用在组件内部的根节点的元素VNode上。
export function renderComponentRoot(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance
): VNode {
const {
type: Component,
vnode,
proxy,
withProxy,
props,
propsOptions: [propsOptions],
slots,
attrs,
emit,
render,
renderCache,
data,
setupState,
ctx,
inheritAttrs
} = instance
// inherit directives
if (vnode.dirs) {
if (__DEV__ && !isElementRoot(root)) {
warn(
`Runtime directive used on component with non-element root node. ` +
`The directives will not function as intended.`
)
}
root.dirs = root.dirs ? root.dirs.concat(vnode.dirs) : vnode.dirs
}
}在组件渲染子树VNode的根VNode时候,会将组件的指令dirs添加在根元素VNode的dirs中。所以作用于组件的指令 等同于 作用于 根节点的元素VNode上。
我觉得一些比较使用的指令的使用场景有:
到此这篇关于vue3指令是如何实现的的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Vue3指令实现内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: 一篇文章告诉你Vue3指令是如何实现的
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/164025.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-12
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0