目录需求目标原理与思路实现引入Identity组件添加认证服务使用Jwt认证和定义授权方式引入认证授权中间件添加JWT配置增加认证用户Model实现认证服务CreateToken方法
在.net WEB API开发中还有一个很重要的需求是关于身份认证和授权的,这个主题非常大,所以本文不打算面面俱到地介绍整个主题,而仅使用.NET框架自带的认证和授权中间件去实现基于JWT的身份认证和授权功能。一些关于这个主题的基本概念也不会花很多的篇幅去讲解,我们还是专注在实现上。
为TodoList项目增加身份认证和授权功能。
为了实现身份认证和授权功能,我们需要使用.NET自带的Authentication和Authorization组件。在本文中我们不会涉及Identity Server的相关内容,这是另一个比较大的主题,因为许可证的变更,Identity Server 4将不再能够免费应用于盈利超过一定限额的商业应用中,详情见官网IdentityServer。微软同时也在将广泛使用的IdentityServer的相关功能逐步集成到框架中:ASP.net core 6 and Authentication Servers,在本文中同样暂不会涉及。
我们在Infrastructure项目中添加以下Nuget包:
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Aspnetcore.Authentication.JwtBearer" Version="6.0.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="6.0.1" />
并新建Identity目录用于存放有关认证和授权的具体功能,首先添加用户类ApplicationUser:
ApplicationUser.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
namespace TodoList.Infrastructure.Identity;
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser
{
// 不做定制化实现,仅使用原生功能
}
由于我们希望使用现有的SQL Server数据库来存储认证相关的信息,所以还需要修改DbContext:
TodoListDbContext.cs
public class TodoListDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser>
{
private readonly IDomainEventService _domainEventService;
public TodoListDbContext(
DbContextOptions<TodoListDbContext> options,
IDomainEventService domainEventService) : base(options)
{
_domainEventService = domainEventService;
}
// 省略其他...
}
为了后面演示的方便,我们还可以在添加种子数据的逻辑里增加内置用户数据:
TodoListDbContextSeed.cs
// 省略其他...
public static async Task SeedDefaultUserAsync(UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager, RoleManager<IdentityRole> roleManager)
{
var administratorRole = new IdentityRole("Administrator");
if (roleManager.Roles.All(r => r.Name != administratorRole.Name))
{
await roleManager.CreateAsync(administratorRole);
}
var administrator = new ApplicationUser { UserName = "admin@localhost", Email = "admin@localhost" };
if (userManager.Users.All(u => u.UserName != administrator.UserName))
{
// 创建的用户名为admin@localhost,密码是admin123,角色是Administrator
await userManager.CreateAsync(administrator, "admin123");
await userManager.AddToRolesAsync(administrator, new[] { administratorRole.Name });
}
}
并在ApplicationStartupExtensions中修改:
ApplicationStartupExtensions.cs
public static class ApplicationStartupExtensions
{
public static async Task MigrateDatabase(this WebApplication app)
{
using var scope = app.Services.CreateScope();
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
try
{
var context = services.GetRequiredService<TodoListDbContext>();
context.Database.Migrate();
var userManager = services.GetRequiredService<UserManager<ApplicationUser>>();
var roleManager = services.GetRequiredService<RoleManager<IdentityRole>>();
// 生成内置用户
await TodoListDbContextSeed.SeedDefaultUserAsync(userManager, roleManager);
// 省略其他...
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"An error occurred migrating the DB: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
最后我们需要来修改DependencyInjection部分,以引入身份认证和授权服务:
DependencyInjection.cs
// 省略其他....
// 配置认证服务
// 配置认证服务
services
.ADDDefaultIdentity<ApplicationUser>(o =>
{
o.PassWord.RequireDigit = true;
o.Password.RequiredLength = 6;
o.Password.RequireLowercase = true;
o.Password.RequireUppercase = false;
o.Password.RequireNonAlphanumeric = false;
o.User.RequireUniqueEmail = true;
})
.AddRoles<IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<TodoListDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
在Applicaiton/Common/Interfaces中添加认证服务接口IIdentityService:
IIdentityService.cs
namespace TodoList.Application.Common.Interfaces;
public interface IIdentityService
{
// 出于演示的目的,只定义以下方法,实际使用的认证服务会提供更多的方法
Task<string> CreateUserAsync(string userName, string password);
Task<bool> ValidateUserAsync(UserForAuthentication userForAuthentication);
Task<string> CreateTokenAsync();
}
然后在Infrastructure/Identity中实现IIdentityService接口:
IdentityService.cs
namespace TodoList.Infrastructure.Identity;
public class IdentityService : IIdentityService
{
private readonly ILogger<IdentityService> _logger;
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager;
private ApplicationUser? User;
public IdentityService(
ILogger<IdentityService> logger,
IConfiguration configuration,
UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager)
{
_logger = logger;
_configuration = configuration;
_userManager = userManager;
}
public async Task<string> CreateUserAsync(string userName, string password)
{
var user = new ApplicationUser
{
UserName = userName,
Email = userName
};
await _userManager.CreateAsync(user, password);
return user.Id;
}
public async Task<bool> ValidateUserAsync(UserForAuthentication userForAuthentication)
{
User = await _userManager.FindByNameAsync(userForAuthentication.UserName);
var result = User != null && await _userManager.CheckPasswordAsync(User, userForAuthentication.Password);
if (!result)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"{nameof(ValidateUserAsync)}: Authentication failed. Wrong username or password.");
}
return result;
}
public async Task<string> CreateTokenAsync()
{
// 暂时还不来实现这个方法
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
并在DependencyInjection中进行依赖注入:
DependencyInjection.cs
// 省略其他...
// 注入认证服务
services.AddTransient<IIdentityService, IdentityService>();
现在我们来回顾一下已经完成的部分:我们配置了应用程序使用内建的Identity服务并使其使用已有的数据库存储;我们生成了种子用户数据;还实现了认证服务的功能。
在继续下一步之前,我们需要对数据库做一次Migration,使认证鉴权相关的数据表生效:
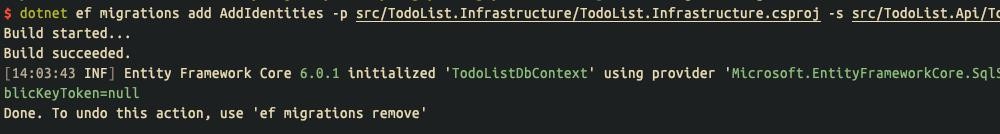
$ dotnet ef database update -p src/TodoList.Infrastructure/TodoList.Infrastructure.csproj -s src/TodoList.Api/TodoList.Api.csproj
Build started...
Build succeeded.
[14:04:02 INF] Entity Framework Core 6.0.1 initialized 'TodoListDbContext' using provider 'Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.sqlServer:6.0.1' with options: MigrationsAssembly=TodoList.Infrastructure, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null
# 创建相关数据表...
[14:04:03 INF] Executed DbCommand (43ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
CREATE TABLE [AspNetRoles] (
[Id] nvarchar(450) NOT NULL,
[Name] nvarchar(256) NULL,
[NORMalizedName] nvarchar(256) NULL,
[ConcurrencyStamp] nvarchar(max) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_AspNetRoles] PRIMARY KEY ([Id])
);
# 省略中间的部分..
[14:04:03 INF] Executed DbCommand (18ms) [Parameters=[], CommandType='Text', CommandTimeout='30']
INSERT INTO [__EFMigrationsHistory] ([MigrationId], [ProductVersion])
VALUES (N'20220108060343_AddIdentities', N'6.0.1');
Done.
运行Api程序,然后去数据库确认一下生成的数据表:

种子用户:

以及角色:

到目前为止,我已经集成了Identity框架,接下来我们开始实现基于JWT的认证和API的授权功能:
在Infrastructure项目的DependencyInjection中添加JWT认证配置:
DependencyInjection.cs
// 省略其他...
// 添加认证方法为JWT Token认证
services
.AddAuthentication(opt =>
{
opt.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
opt.DefaultChallengeScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
})
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
ValidIssuer = configuration.GetSection("JwtSettings")["validIssuer"],
ValidAudience = configuration.GetSection("JwtSettings")["validAudience"],
// 出于演示的目的,我将SECRET值在这里fallback成了硬编码的字符串,实际环境中,最好是需要从环境变量中进行获取,而不应该写在代码中
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("SECRET") ?? "TodoListApiSecreTKEy"))
};
});
// 添加授权Policy是基于角色的,策略名称为OnlyAdmin,策略要求具有Administrator角色
services.AddAuthorization(options =>
options.AddPolicy("OnlyAdmin", policy => policy.RequireRole("Administrator")));
在Api项目的Program中,MapControllers上面引入:
Program.cs
// 省略其他...
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
appsettings.Development.JSON
"JwtSettings": {
"validIssuer": "TodoListApi",
"validAudience": "Http://localhost:5050",
"expires": 5
}
在Application/Common/Models中添加用于用户认证的类型:
UserForAuthentication.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace TodoList.Application.Common.Models;
public record UserForAuthentication
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "username is required")]
public string? UserName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "password is required")]
public string? Password { get; set; }
}
因为本篇文章我们没有使用集成的IdentityServer组件,而是应用程序自己去发放Token,那就需要我们去实现CreateTokenAsync方法:
IdentityService.cs
// 省略其他...
public async Task<string> CreateTokenAsync()
{
var signinGCredentials = GetSigningCredentials();
var claims = await GetClaims();
var tokenOptions = GenerateTokenOptions(signingCredentials, claims);
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(tokenOptions);
}
private SigningCredentials GetSigningCredentials()
{
// 出于演示的目的,我将SECRET值在这里fallback成了硬编码的字符串,实际环境中,最好是需要从环境变量中进行获取,而不应该写在代码中
var key = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("SECRET") ?? "TodoListApiSecretKey");
var secret = new SymmetricSecurityKey(key);
return new SigningCredentials(secret, SecurityAlGorithms.HMacSha256);
}
private async Task<List<Claim>> GetClaims()
{
// 演示了返回用户名和Role两类Claims
var claims = new List<Claim>
{
new(ClaimTypes.Name, User!.UserName)
};
var roles = await _userManager.GetRolesAsync(User);
claims.AddRange(roles.Select(role => new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, role)));
return claims;
}
private JwtSecurityToken GenerateTokenOptions(SigningCredentials signingCredentials, List<Claim> claims)
{
// 配置JWT选项
var jwtSettings = _configuration.GetSection("JwtSettings");
var tokenOptions = new JwtSecurityToken
(
jwtSettings["validIssuer"],
jwtSettings["validAudience"],
claims,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(Convert.ToDouble(jwtSettings["expires"])),
signingCredentials: signingCredentials
);
return tokenOptions;
}
在Api项目中新建一个Controller用于实现获取Token的接口:
AuthenticationController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.mvc;
using TodoList.Application.Common.Interfaces;
using TodoList.Application.Common.Models;
namespace TodoList.Api.Controllers;
[ApiController]
public class AuthenticationController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IIdentityService _identityService;
private readonly ILogger<AuthenticationController> _logger;
public AuthenticationController(IIdentityService identityService, ILogger<AuthenticationController> logger)
{
_identityService = identityService;
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpPost("login")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Authenticate([FromBody] UserForAuthentication userForAuthentication)
{
if (!await _identityService.ValidateUserAsync(userForAuthentication))
{
return Unauthorized();
}
return Ok(new { Token = await _identityService.CreateTokenAsync() });
}
}
我们准备使用创建TodoList接口来演示认证和授权功能,所以添加属性如下:
// 省略其他...
[HttpPost]
// 演示使用Policy的授权
[Authorize(Policy = "OnlyAdmin")]
[ServiceFilter(typeof(LogFilterAttribute))]
public async Task<ApiResponse<Domain.Entities.TodoList>> Create([FromBody] CreateTodoListCommand command)
{
return ApiResponse<Domain.Entities.TodoList>.Success(await _mediator.Send(command));
}
启动Api项目,直接执行创建TodoList的请求:

得到了401 Unauthorized结果。
请求获取Token的接口:

可以看到我们已经拿到了JWT Token,把这个Token放到JWT解析一下可以看到:

主要在payload中可以看到两个Claims和其他配置的信息。
选择Bearer Token验证方式并填入获取到的Token,再次请求创建TodoList:

修改Infrastructure/DependencyInjection.cs
// 省略其他...
// 添加授权Policy是基于角色的,策略名称为OnlyAdmin,策略要求具有Administrator角色
services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("OnlyAdmin", policy => policy.RequireRole("Administrator"));
options.AddPolicy("OnlySuper", policy => policy.RequireRole("SuperAdmin"));
});
并修改创建TodoList接口的授权Policy:
// 省略其他...
[Authorize(Policy = "OnlySuper")]
还是使用admin@locahost用户的用户名和密码获取最新的Token后,携带Token请求创建新的TodoList:
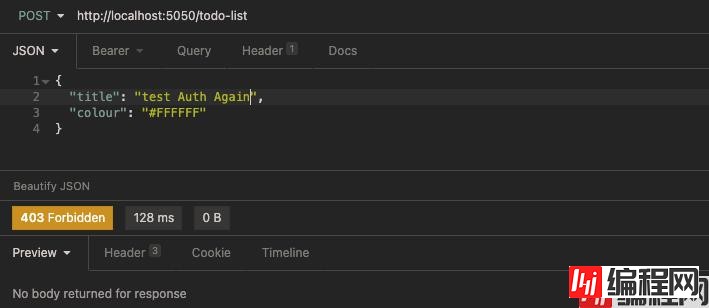
得到了403 Forbidden返回,并且从日志中我们可以看到:

告诉我们需要一个具有SuperAdmin角色的用户的合法Token才会被授权。
那么到此为止,我们已经实现了基于.NET自带的Identity框架,发放Token,完成认证和授权的功能。
关于在.NET Web API项目中进行认证和授权的主题非常庞大,首先是认证的方式可以有很多种,除了我们在本文中演示的基于JWT Token的认证方式以外,还有OpenId认证,基于Azure Active Directory的认证,基于OAuth协议的认证等等;其次是关于授权的方式也有很多种,可以是基于角色的授权,可以是基于Claims的授权,可以是基于Policy的授权,也可以自定义更多的授权方式。然后是具体的授权服务器的实现,有基于Identity Server 4的实现,当然在其更改过协议后,我们可以转而使用.NET中移植进来的IdentityServer组件实现,配置的方式也有很多。
由于IdentityServer涉及的知识点过于庞杂,所以本文并没有试图全部讲到,考虑后面单独出一个系列来讲关于IdentityServer在.NET 6 Web API开发中的应用。
在本文中,我们实现了基于JWT Token的认证和授权。下一篇文章我们来看看为什么需要以及如何实现Refresh Token机制。
IdentityServer
ASP.net core 6 and Authentication Servers
以上就是.NET 6实现基于JWT的Identity功能方法详解的详细内容,更多关于.NET 6基于JWT的Identity功能的资料请关注编程网其它相关文章!
--结束END--
本文标题: .NET6实现基于JWT的Identity功能方法详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/162126.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2023-05-21
2023-05-21
2023-05-21
2023-05-21
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0