Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录1. FilterSecurityInterceptor 源码阅读2. 自定义基于url的授权1. FilterSecurityInterceptor 源码阅读 org.spri
org.springframework.security.WEB.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor
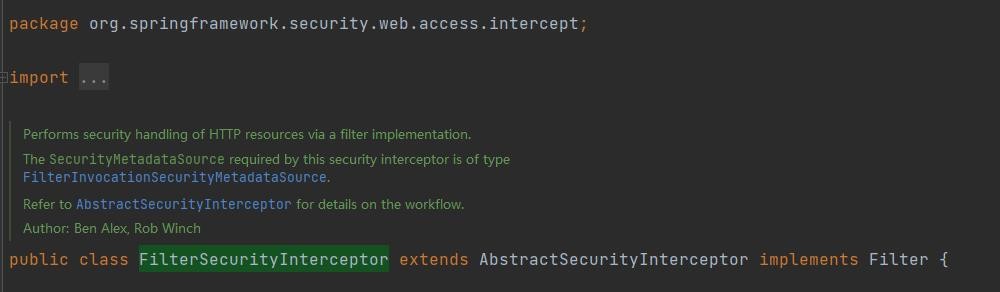
该安全拦截器所需的 SecurityMetadataSource 类型为 FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource。

doFilter方法中直接调用invoke方法

基本都是调用父类的方法,那下面就重点看下父类 AbstractSecurityInterceptor中相关方法
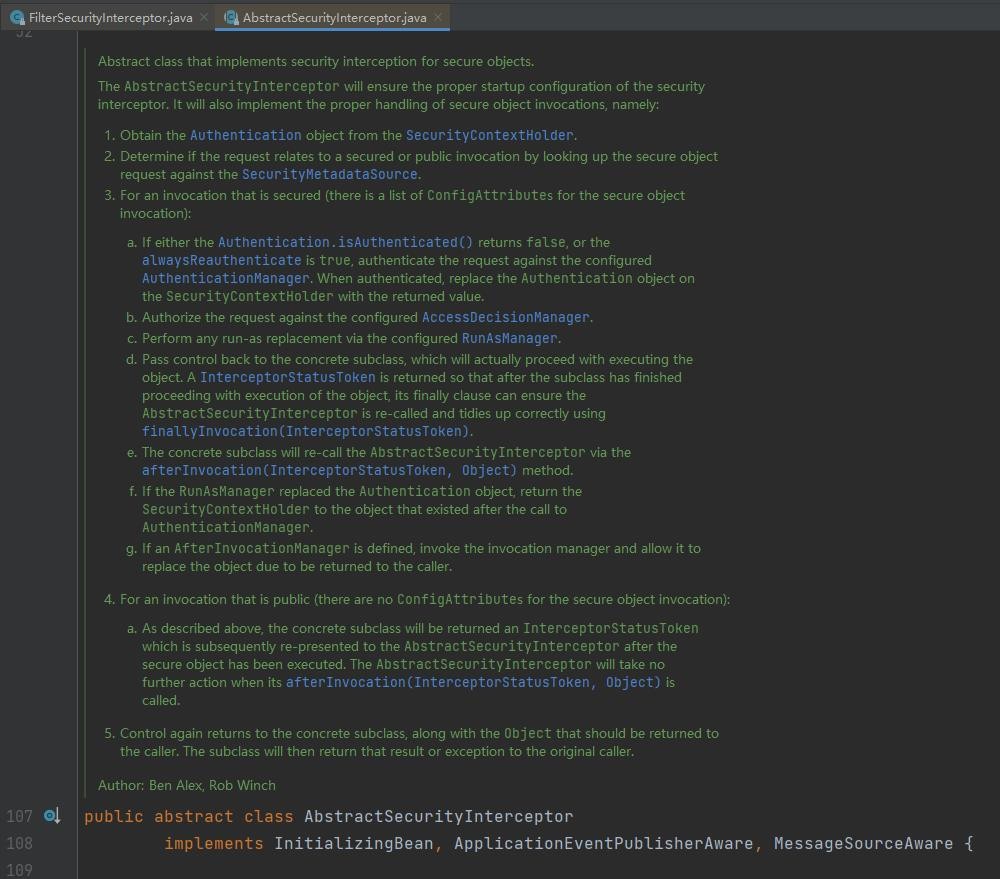
为安全对象实现安全拦截的抽象类。
AbstractSecurityInterceptor 将确保安全拦截器的正确启动配置。 它还将实现对安全对象调用的正确处理,即:
1.从 SecurityContextHolder 获取 Authentication 对象。
2.通过在SecurityMetadataSource中查找安全对象请求,确定请求是与安全调用还是公共调用相关(PS:简单地来讲,就是看一下请求的资源是不是受保护的,受保护的就是安全调用,就要权限,不受保护的就不需要权限就可以访问)。
3.对于受保护的调用(有一个用于安全对象调用的 ConfigAttributes 列表):
4.对于公开的调用(安全对象调用没有 ConfigAttributes):
如上所述,具体的子类将返回一个 InterceptorStatusToken,在执行完安全对象后,该 InterceptorStatusToken 随后被重新呈现给 AbstractSecurityInterceptor。 AbstractSecurityInterceptor 在它的 afterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken, Object) 被调用时不会采取进一步的行动。
5.控制再次返回到具体的子类,以及应该返回给调用者的对象。然后子类会将该结果或异常返回给原始调用者。

下面具体来看
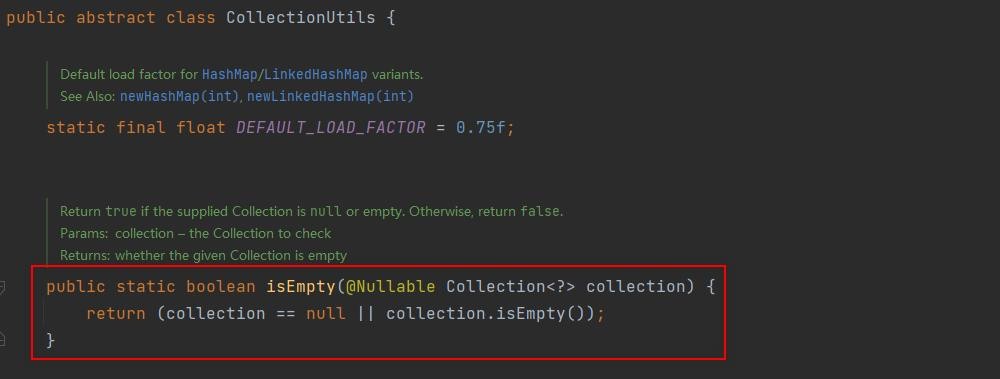
从这里我们可以知道返回null和空集合是一样的。

接下来看授权

这是我们要重点关注的,可以看到,授权靠的是accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes)
因此,我们想要实现自己的基于请求Url的授权只需自定义一个 AccessDecisionManager即可
接下来,我们来具体实现一下
先把Spring Security授权的大致流程流程摆在这儿:

自定义FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource
package com.example.security.core;
import com.example.security.service.SysPermissionService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute;
import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig;
import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class MyFilterSecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
@Autowired
private SysPermissionService sysPermissionService;
private final AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException {
FilterInvocation fi = (FilterInvocation) object;
String url = fi.getRequestUrl();
String httpMethod = fi.getRequest().getMethod();
List<ConfigAttribute> attributes = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, String> urlRoleMap = sysPermissionService.getAllUrlRole();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : urlRoleMap.entrySet()) {
if (antPathMatcher.match(entry.geTKEy(), url)) {
return SecurityConfig.createList(entry.getValue());
}
}
// 返回null和空列表是一样的,都表示当前访问的资源不需要权限,所有人都可以访问
return attributes;
// return null;
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return FilterInvocation.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
}这里需要说明一下,其实Spring Security里面说的role不一定表示的是我们自己建的那个角色表,我们可以这样理解,就是它这里的所谓role只是一个权限标识。我们在建表的时候,通常最基本的是5张表(用户表、角色表、权限表、用户角色关系表、角色权限关系表),我们可以把受保护的资源(通常是一个url)与角色关联起来,建立哪些角色可以访问哪些资源,也可以直接判断资源的权限(通常是权限编码/标识)。

只要有这个关系,剩下的就是写法不同而已。如果你把role理解成资源的权限标识的话,那么返回的Collection<ConfigAttribute>中就最多有一个元素,如果理解成角色的话,那么可能有多个元素。就这么点儿东西,写法不同而已,本质是一样的。
自定义AccessDecisionManager
package com.example.security.core;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionManager;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.InsufficientAuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Collection;
@Component
public class MyAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager {
@Override
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException {
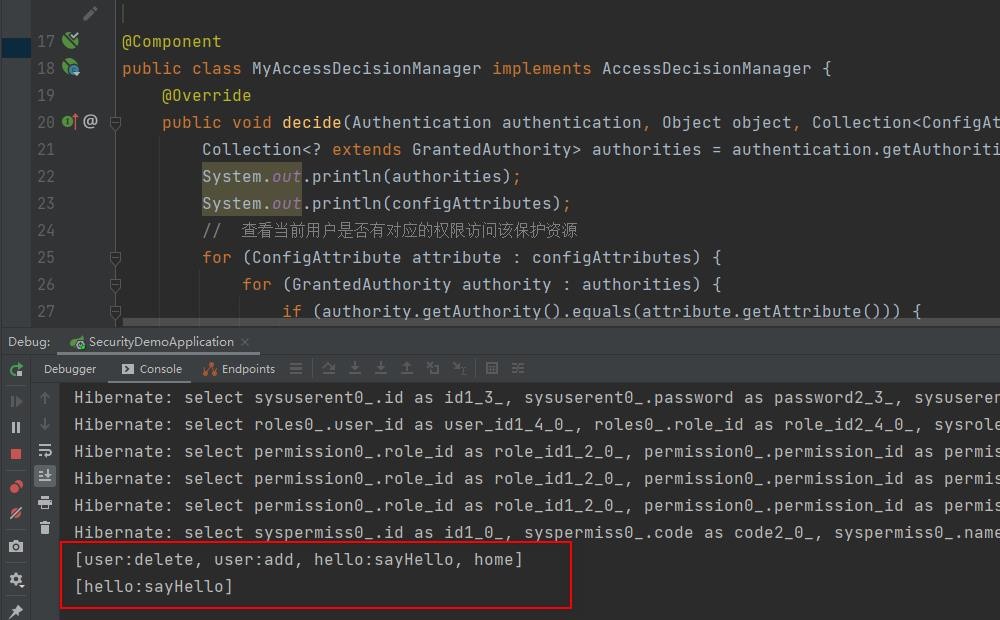
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
System.out.println(authorities);
System.out.println(configAttributes);
// 查看当前用户是否有对应的权限访问该保护资源
for (ConfigAttribute attribute : configAttributes) {
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
if (authority.getAuthority().equals(attribute.getAttribute())) {
return;
}
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("Access is denied");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return true;
}
}decide方法的三个参数,依次表示:
配置WebSecurityConfig
package com.example.security.config;
import com.example.security.core.MyAccessDecisionManager;
import com.example.security.core.MyFilterSecurityMetadataSource;
import com.example.security.core.MyUserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.ObjectPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.httpsecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPassWordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor;
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyUserDetailsService myUserDetailsService;
@Autowired
private MyAccessDecisionManager myAccessDecisionManager;
@Autowired
private MyFilterSecurityMetadataSource myFilterSecurityMetadataSource;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(myUserDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.fORMLogin()
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(O object) {
object.setSecurityMetadataSource(myFilterSecurityMetadataSource);
object.setAccessDecisionManager(myAccessDecisionManager);
return object;
}
})
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}其它不重要的就直接贴出来了
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://Maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>security-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>security-demo</name>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>Mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>application.yml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo126?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 123456
jpa:
database: mysql
show-sql: trueSysPermissionEntity.java
package com.example.security.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
@Table(name = "sys_permission")
public class SysPermissionEntity implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String code;
private String name;
private String url;
}SysRoleEntity.java
package com.example.security.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Set;
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
@Table(name = "sys_role")
public class SysRoleEntity implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String code;
private String name;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name = "sys_role_permission", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "role_id")}, inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "permission_id")})
private Set<SysPermissionEntity> permissions;
}SysUserEntity.java
package com.example.security.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Set;
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
@Table(name = "sys_user")
public class SysUserEntity implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name = "sys_user_role",
joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "role_id")})
private Set<SysRoleEntity> roles;
}SysUserRepository.java
package com.example.security.repository;
import com.example.security.entity.SysUserEntity;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
public interface SysUserRepository extends JpaRepository<SysUserEntity, Integer>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<SysUserEntity> {
SysUserEntity findByUsername(String username);
}SysPermissionServiceImpl.java
package com.example.security.service.impl;
import com.example.security.entity.SysPermissionEntity;
import com.example.security.repository.SysPermissionRepository;
import com.example.security.service.SysPermissionService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
public class SysPermissionServiceImpl implements SysPermissionService {
@Resource
private SysPermissionRepository sysPermissionRepository;
@Override
public Map<String, String> getAllUrlRole() {
List<SysPermissionEntity> list = sysPermissionRepository.findAll();
return list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(SysPermissionEntity::getUrl, SysPermissionEntity::getCode));
}
}MyUserDetails.java
package com.example.security.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Set;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class MyUserDetails implements UserDetails {
private String username;
private String password;
private boolean enabled;
private Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities;
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return authorities;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
}MyUserDetailsService.java
package com.example.security.core;
import com.example.security.domain.MyUserDetails;
import com.example.security.entity.SysPermissionEntity;
import com.example.security.entity.SysUserEntity;
import com.example.security.repository.SysUserRepository;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.transaction.Transactional;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Transactional
@Service
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Resource
private SysUserRepository sysUserRepository;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
SysUserEntity sysUserEntity = sysUserRepository.findByUsername(username);
if (null == sysUserEntity) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在");
}
Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities = sysUserEntity.getRoles().stream()
.flatMap(roleId->roleId.getPermissions().stream())
.map(SysPermissionEntity::getCode)
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
return new MyUserDetails(sysUserEntity.getUsername(), sysUserEntity.getPassword(), true, authorities);
}
}HelloController.java
package com.example.security.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/sayHello")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello";
}
@GetMapping("/sayHi")
public String sayHi() {
return "Hi";
}
}
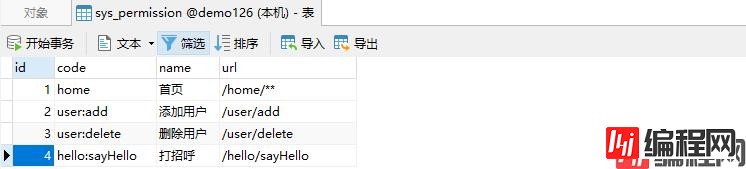
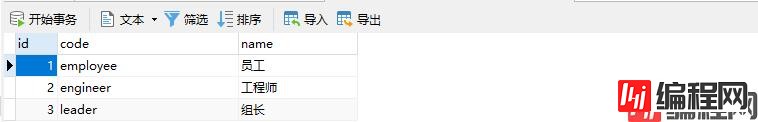
数据库脚本如下
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for sys_permission
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sys_permission`;
CREATE TABLE `sys_permission` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`code` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '权限编码(标识)',
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '权限名称',
`url` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '权限URL',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 5 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sys_permission
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sys_permission` VALUES (1, 'home', '首页', '/home/**');
INSERT INTO `sys_permission` VALUES (2, 'user:add', '添加用户', '/user/add');
INSERT INTO `sys_permission` VALUES (3, 'user:delete', '删除用户', '/user/delete');
INSERT INTO `sys_permission` VALUES (4, 'hello:sayHello', '打招呼', '/hello/sayHello');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for sys_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sys_role`;
CREATE TABLE `sys_role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`code` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '角色编码',
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '角色名称',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sys_role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sys_role` VALUES (1, 'employee', '员工');
INSERT INTO `sys_role` VALUES (2, 'engineer', '工程师');
INSERT INTO `sys_role` VALUES (3, 'leader', '组长');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for sys_role_permission
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sys_role_permission`;
CREATE TABLE `sys_role_permission` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色ID',
`permission_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '权限ID',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 8 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sys_role_permission
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (2, 2, 1);
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (3, 2, 2);
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (4, 3, 1);
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (5, 3, 2);
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (6, 3, 3);
INSERT INTO `sys_role_permission` VALUES (7, 3, 4);
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for sys_user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sys_user`;
CREATE TABLE `sys_user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`password` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '密码',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 2 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sys_user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sys_user` VALUES (1, 'zhangsan', '$2a$10$e4wFsFHQCNjPe5tTJMPkRuKGwmMGC45pfjMupY9nwbTuoKQ0bKc/u');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for sys_user_role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sys_user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `sys_user_role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`role_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色ID',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sys_user_role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sys_user_role` VALUES (1, 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `sys_user_role` VALUES (2, 1, 2);
INSERT INTO `sys_user_role` VALUES (3, 1, 3);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/hello/sayHi 正常返回,不用登录,因为没有在sys_permission表中配置该资源,也就是说它不是一个受保护的资源(公开资源)
访问http://localhost:8080/hello/sayHello则需要先登录,用zhangsan登录成功以后正确返回

项目结构如下
到此这篇关于Spring Security 基于URL的权限判断的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Security权限判断内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Spring Security 基于URL的权限判断源码解析
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/159278.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0