目录前言TopK问题解题方法代码实现与讲解运行结果函数解读PrintTopK 解读TestTopK 解读前言 本篇将详细讲解如何利用小根堆的方法解决TopK问题,这么多数据要处理,
本篇将详细讲解如何利用小根堆的方法解决TopK问题,这么多数据要处理,
该算法时间复度居然只需
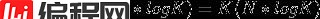
TopK问题介绍:在N个数中找出最大的前K个 (比如在1000个数中找出最大的前10个)
方法1:先排降序,前N个就是最大的。
时间复杂度:

方法2:N个数依次插入大堆,HeapPop K次,每次取堆顶的数据,即为前K个。
时间复杂度:

假设N非常大,N是10亿,内存中存不下这些数,它们存在文件中的。K是100,方法1 和 方法2 就都不能用了……
话说 10 亿个整数,大概占用多少空间?
1G = 1024MB
1G = 1024*1024KB
1G = 1024*1024*1024Byte
要占用10亿字节!所以我们来看看方法3。
方法3:
① 用前个K数建立一个K个数的小堆。
② 剩下的N-K个数,依次跟堆顶的数据进行比较。如果比堆顶的数据大,就替换堆顶的数据,再向下调整。
③ 最后堆里面的K个数就是最大的K个数。
时间复杂度:
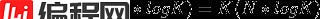
这里为什么使用小堆而不使用大堆?
最大的前K个数一定会比其他数要大,只要进来的数比堆顶数据大,就替代它。因为是小堆(小的在上大的在下),最大的数进去后一定会沉到下面,所以不可能存在大的数堵在堆顶导致某个数进不去的情况,数越大沉得越深。对应地,如果使用大堆就会出现一个大数堵在堆顶,剩下的数都比这个大数小,导致其他数进不来,最后只能选出最大的那一个。
由于还没开始讲 c++ ,这里我们没法用优先级队列,我们得手动自己写一个堆来使用。当然,如果自己懒得写,以下是 C语言 实现堆的代码。
Heap.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap {
HPDataType* array; //指向动态开辟的数组
int size; //有效数据的个数
int capacity; //容量空间的大小
} HP;
void Heapinit(HP* PHP);
void HeapDestroy(HP* php);
void HeapPrint(HP* php);
bool HeapIfEmpty(HP* hp);
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
void HeapCheckCapacity(HP* php);
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py);
void BigAdjustUp(int* arr, int child);
void SmallAdjustUp(int* arr, int child);
void HeapPop(HP* php);
void SmallAdjustDown(int* arr, int n, int parent);
void BigAdjustDown(int* arr, int n, int parent);
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php);
int HeapSize(HP* php);Heap.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Heap.h"
void HeapInit(HP* php) {
assert(php);
php->array = NULL;
php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}
void HeapDestroy(HP* php) {
assert(php);
free(php->array);
php->capacity = php->size = 0;
}
void HeapPrint(HP* php) {
for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++) {
printf("%d ", php->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
bool HeapIfEmpty(HP* php) {
assert(php);
return php->size == 0; // 如果为size为0则表示堆为空
}
void HeapCheckCapacity(HP* php) {
if (php->size == php->capacity) {
int newCapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : (php->capacity * 2); //第一次给4,其他情况扩2倍
HPDataType* tmpArray = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->array, sizeof(HPDataType) * newCapacity); // 数组扩容
if (tmpArray == NULL) { //检查realloc
printf("realloc failed!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//更新他们的大小
php->array = tmpArray;
php->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py) {
HPDataType tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
void BigAdjustUp(int* arr, int child) {
assert(arr);
// 首先根据公式计算算出父亲的下标
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// 最坏情况:调到根,child=parent 当child为根节点时结束(根节点永远是0)
while (child > 0) {
if (arr[child] > arr[parent]) { // 如果孩子大于父亲(不符合堆的性质)
// 交换他们的值
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
// 往上走
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
} else { // 如果孩子小于父亲(符合堆的性质)
// 跳出循环
break;
}
}
}
void SmallAdjustUp(int* arr, int child) {
assert(arr);
// 首先根据公式计算算出父亲的下标
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// 最坏情况:调到根,child=parent 当child为根节点时结束(根节点永远是0)
while (child > 0) {
if (arr[child] < arr[parent]) { // 如果孩子大于父亲(不符合堆的性质)
// 交换他们的值
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
// 往上走
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
} else { // 如果孩子小于父亲(符合堆的性质)
// 跳出循环
break;
}
}
}
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x) {
assert(php);
// 检查是否需要扩容
HeapCheckCapacity(php);
// 插入数据
php->array[php->size] = x;
php->size++;
// 向上调整 [目标数组,调整位置的起始位置(刚插入的数据)]
SmallAdjustUp(php->array, php->size - 1);
}
void SmallAdjustDown(int* arr, int n, int parent) {
int child = parent * 2 + 1; // 默认为左孩子
while (child < n) { // 叶子内
// 选出左右孩子中小的那一个
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child + 1] < arr[child]) {
child++;
}
if (arr[child] < arr[parent]) { // 如果孩子小于父亲(不符合小堆的性质)
// 交换它们的值
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
// 往下走
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
} else { // 如果孩子大于父亲(符合小堆的性质)
// 跳出循环
break;
}
}
}
void BigAdjustDown(int* arr, int n, int parent) {
int child = parent * 2 + 1; // 默认为左孩子
while (child < n) { // 叶子内
// 选出左右孩子中大的那一个
if (child + 1 < n && arr[child + 1] > arr[child]) {
child++;
}
if (arr[child] > arr[parent]) { // 如果孩子大于父亲(不符合大堆的性质)
// 交换它们的值
Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
// 往下走
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
} else { // 如果孩子小于父亲(符合大堆的性质)
// 跳出循环
break;
}
}
}
void HeapPop(HP* php) {
assert(php);
assert(!HeapIfEmpty(php));
// 删除数据
Swap(&php->array[0], &php->array[php->size - 1]);
php->size--;
// 向下调整 [目标数组,数组的大小,调整位置的起始位置]
SmallAdjustDown(php->array, php->size, 0);
}
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php) {
assert(php);
assert(!HeapIfEmpty(php));
return php->array[0];
}
int HeapSize(HP* php) {
assert(php);
return php->size;
}
第三种方法的参考代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Heap.h"
void PrintTopK(int* arr, int N, int K) {
HP hp; // 创建堆
HeapInit(&hp); // 初始化堆
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) { // Step1: 创建一个K个数的小堆
HeapPush(&hp, arr[i]);
}
for (int i = K; i < N; i++) { // Step2: 剩下的N-K个数跟堆顶的数据比较
if (arr[i] > HeapTop(&hp)) { // 如果比堆顶的数据大就替换进堆
HeapPop(&hp); // 此数确实比堆顶大,删除堆顶
HeapPush(&hp, arr[i]); // 将此数推进堆中,数越大下沉越深
}
}
HeapPrint(&hp); // 打印K个数的堆
HeapDestroy(&hp); // 销毁堆
}
void TestTopK() {
int N = 1000000;
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
srand(time(0)); // 置随机数种子
for(size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// 产生随机数,每次产生的随机数都mod100w,这样产生的数一定是小于100w的
arr[i] = rand() % 1000000;
}
// 再去设置10个比100w大的数
arr[5] = 1000000 + 1;
arr[1231] = 1000000 + 2;
arr[5355] = 1000000 + 3;
arr[51] = 1000000 + 4;
arr[15] = 1000000 + 5;
arr[2335] = 1000000 + 6;
arr[9999] = 1000000 + 7;
arr[76] = 1000000 + 8;
arr[423] = 1000000 + 9;
arr[3144] = 1000000 + 10;
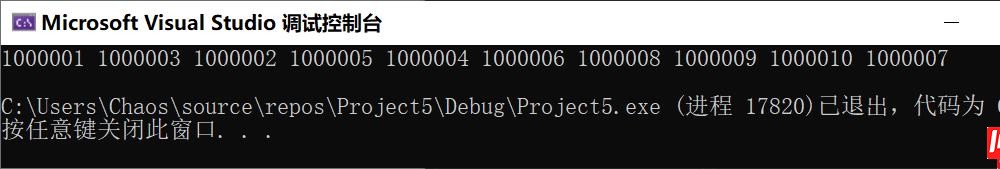
PrintTopK(arr, N, 10); //测试用,所以给10个
}
int main(void) {
TestTopK();
return 0;
}
① 准备好我们实现好的堆之后,我们就可以写TopK的算法了。我们创建一个 PrintTopK 函数,函数需要接收存放数据的数组、数组的大小(N)和要找前多少个(K)。
② 首先创建一个堆,用来存放K 。按照规矩我们先把 HeapInit(初始化)和 HeapDestroy(销毁)先写好,防止自己不小心忘记销毁。
③ 核心步骤1:创建一个K个数的小堆,我们直接用 for 循环将数组中前K个值先逐个 HeapPush (堆的插入)进去。
这里不代表最后的结果,我们只是相当于 "默认" 认为这前K个数是最大的,方便我们后续进行比较替代。经过 HeapPush (堆的插入)后,这些数据会通过 SmallAdjustDown (小堆下调接口) 对数据进行相应的调整:
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) { // Step1: 创建一个K个数的小堆
HeapPush(&hp, arr[i]);
}④ 核心步骤2:除去K,将剩下的N-K个数据进行比较。我们再利用 for 循环将数组中剩下的N-K个数据进行遍历。
这里逐个进行判断,如果该数堆顶的数据 i<K(max),我们就进行替换操作。调用 HeapPop(堆的删除)删除堆顶的数据,给 让位。之后将其 HeapPush (堆的插入)推到堆中,就完成了替换的工作。值得一提的是,我们还可以不调用 Pop 和 Push 这两个操作,手动进行替换。hp.array [ 0 ] 就表示栈顶,我们将 赋值给它,随后再手动进行 SmallAdjustDown (小堆下调操作),传入相应的值即可:
for (int i = K; i < N; i++) { // Step2: 剩下的N-K个数跟堆顶的数据比较
if (arr[i] > HeapTop(&hp)) { // 如果比堆顶的数据大就替换进堆
HeapPop(&hp); // 此数确实比堆顶大,删除堆顶
HeapPush(&hp, arr[i]); // 将此数推进堆中,数越大下沉越深
}
}⑤ 当 for 遍历完所有数据之后,小堆中就保留了N个数据中最大的前K个数了。此时我们调用堆打印接口将小堆里的数据打印出来就大功告成了。
① 这是用来测试我们写的TopK算法的函数。设置 N 的大小为 100w,动态内存开辟一块可以存下这么多数据的空间:
int N = 1000000;
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);② 随后根据时间来置随机数种子,将每个元素都进行随机数的填充,每次产生的随机数都模上100w,这样可以保证产生的随机数一定是小于100w的。
srand(time(0));
for(size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = rand() % 1000000;
}③ 随便写几个大于100w的数,便于测试:
// 再去设置10个比100w大的数
arr[5] = 1000000 + 1;
arr[1231] = 1000000 + 2;
arr[5355] = 1000000 + 3;
arr[51] = 1000000 + 4;
arr[15] = 1000000 + 5;
arr[2335] = 1000000 + 6;
arr[9999] = 1000000 + 7;
arr[76] = 1000000 + 8;
arr[423] = 1000000 + 9;
arr[3144] = 1000000 + 10;④ 调用我们刚才实现好的 PrintTopK 函数,递交对应的参数后就可以进行测试了。这里为了方便测试,我们的K设置为10:
PrintTopK(arr, N, 10);到此这篇关于C语言 如何用堆解决Topk问题的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Topk问题内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: C语言 如何用堆解决Topk问题
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/158979.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0