目录一、sqlSession简单介绍二、获得sqlSession对象源码分析三、SQL执行流程,以查询为例一、sqlSession简单介绍 拿到SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory对象后,会调用SqlSessionFactory的openSesison方法,这个方法会创建一个Sql执行器(Executor),这个Sql执行器会代理你配置的拦截器方法。SqlSession(默认使用DefaultSqlSession),这个SqlSession中也包含了Configration对象,所以通过SqlSession也能拿到全局配置;SqlSession对象后就能执行各种CRUD方法了。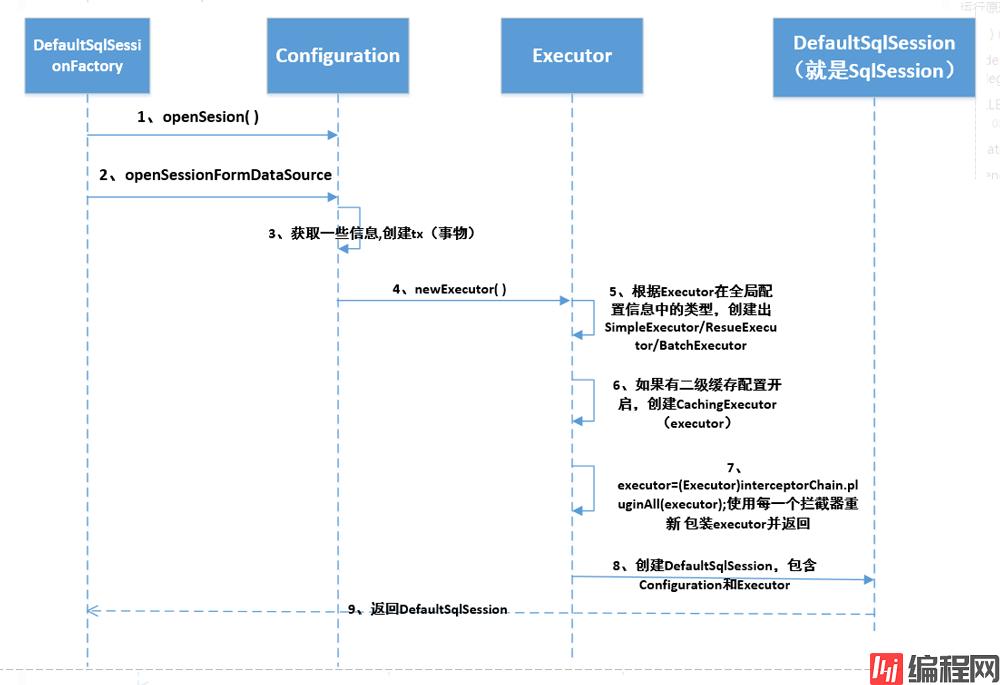
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level,
boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 获取环境变量
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 获取一个事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 获取执行器,这边获得的执行器已经代理拦截器的功能
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 根据获取的执行器创建SqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
// 默认使用SIMPLE的执行器
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
// 批量的执行器
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
// 可重复使用的执行器
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 简单的sql执行器
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 判断mybatis的全局配置文件是否开启二级缓存
if (cacheEnabled) {
// 开启缓存,吧executor包装为CachingExecutor
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 插件的调用:责任链模式
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}

public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
// 查询数据
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
// 长度为1,拿第一个
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
// 长度大于一,抛异常
throw new TooManyResultsException(
"Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
// 没有拿到返回null
return null;
}
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 通过statement去全局配置文件中获取MappedStatement(得到mapper中增删改查的节点)
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 通过执行器去执行SQL
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 通过参数进行sql解析
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 判断sql是否开启了缓存 <cache></cache>
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 有缓存
if (cache != null) {
// 判断是否需要刷新缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 去二级缓存中获取(装饰者模式)
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
// 二级缓存没有找到
if (list == null) {
// 查询数据,并放入缓存
list = delegate.<E>query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 查询数据
return delegate.<E>query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
// 已经关闭了,抛异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清空本地缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
// 从一级缓存中获取数据
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// 缓存里面有,进行处理
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 缓存没有,进行查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 去数据库查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 一级缓存进行缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,
BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 得到整体的配置对象
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 内部封装了ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 得到要执行的sql
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 执行sql
statement.execute(sql);
// 处理结果集
return resultSetHandler.<E>handleResultSets(statement);
}到此这篇关于SQL语句解析执行的过程及原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SQL语句解析原理内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: SQL语句解析执行的过程及原理
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/144309.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0