目录前言1.类的定义2.类的构造函数3.类的实例方法4.类的访问器方法5.类的静态方法6.类的继承6.1.extends关键字6.2.super关键字6.3.继承内置类7.类的混入8
在前面一篇中主要介绍了javascript中使用构造函数+原型链实现继承,从实现的步骤来说还是比较繁琐的。在es6中推出的class的关键字可以直接用来定义类,写法类似与其它的面向对象语言,但是使用class来定义的类其本质上依然是构造函数+原型链的语法糖而已,下面就一起来全面的了解一下class吧。
class关键字定义类可使用两种方式来定义:
class Person {} // 类声明
const Person = class {} // 类表达式
从上面class定义类可以发现是没有()让我们来传递参数的,当希望在实例化对象的给类传递一些参数,这个时候就可以使用到类的构造函数constructor了。
每个类都可以有一个自己的constructor方法,注意只能有一个,如果有多个会抛出异常;
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
constructor() {}
}

当通过new操作符来操作类时,就会去调用这个类的constructor方法,并返回一个对象(具体new操作符调用函数时的默认操作步骤在上一篇中有说明);
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
}
const p = new Person('curry', 30)
console.log(p) // Person { name: 'curry', age: 30 }
在构造函数中实现方法继承是将其放到构造函数的原型上,而在class定义的类中,可直接在类中定义方法,最终class还是会帮我们放到其原型上,供多个实例来使用。
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
eating() {
console.log(this.name + 'is eating.')
}
running() {
console.log(this.name + 'is running.')
}
}
在使用Object.defineProperty()方法来控制对象的属性时,在其数据属性描述符中可以使用setter和getter函数,在class定义的类中,也是可以使用这两个访问器方法的。
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this._age = 30 // 使用_定义的属性表示为私有属性,不可直接访问
}
get age() {
console.log('age被访问')
return this._age
}
set age(newValue) {
console.log('age被设置')
this._age = newValue
}
}
const p = new Person('curry', 30)
console.log(p) // Person { name: 'curry', _age: 30 }
p.age // age被访问
p.age = 24 // age被设置
console.log(p) // Person { name: 'curry', _age: 24 }
什么叫类的静态方法呢?该方法不是供实例对象来使用的,而是直接加在类本身的方法,可以使用类名点出来的方法,可以使用static关键字来定义静态方法。
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
static foo() {
console.log('我是Person类的方法')
}
}
Person.foo() // 我是Person类的方法
在ES6之前实现继承是不方便的,ES6中增加了extends关键字,可以方便的帮助我们实现类的继承。
实现Student子类继承自Person父类:
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
eating() {
console.log(this.name + ' is eating.')
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(sno) {
this.sno = sno
}
studying() {
console.log(this.name + ' is studying.')
}
}
那么子类如何使用父类的属性和方法呢?
使用super关键字可以在子类构造函数中调用父类的构造函数,但是必须在子类构造函数中使用this或者返回默认对象之前使用super。
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
eating() {
console.log(this.name + ' is eating.')
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, sno) {
super(name, age)
this.sno = sno
}
studying() {
console.log(this.name + ' is studying.')
}
}
const stu = new Student('curry', 30, 101111)
console.log(stu) // Student { name: 'curry', age: 30, sno: 101111 }
// 父类的方法可直接调用
stu.eating() // curry is eating.
stu.studying() // curry is studying.
但是super关键字的用途并不仅仅只有这个,super关键字一般可以在三个地方使用:
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
eating() {
console.log(this.name + ' is eating.')
}
parentMethod() {
console.log('父类逻辑代码1')
console.log('父类逻辑代码2')
console.log('父类逻辑代码3')
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, sno) {
super(name, age)
this.sno = sno
}
// 直接重写父类eating方法
eating() {
console.log('Student is eating.')
}
// 重写父类的parentMethod方法,并且复用逻辑代码
parentMethod() {
// 通过super调用父类方法,实现复用
super.parentMethod()
console.log('子类逻辑代码4')
console.log('子类逻辑代码5')
console.log('子类逻辑代码6')
}
}

静态方法中:用法就和实例方法的方式一样了;
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
static parentMethod() {
console.log('父类逻辑代码1')
console.log('父类逻辑代码2')
console.log('父类逻辑代码3')
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, sno) {
super(name, age)
this.sno = sno
}
// 重写父类的parentMethod静态方法,并且复用逻辑代码
static parentMethod() {
// 通过super调用父类静态方法,实现复用
super.parentMethod()
console.log('子类逻辑代码4')
console.log('子类逻辑代码5')
console.log('子类逻辑代码6')
}
}
Student.parentMethod()

extends关键字不仅可以实现继承我们自定义的父类,还可以继承JavaScript提供的内置类,可对内置类的功能进行扩展。
比如,在Array类上扩展两个方法,一个方法获取指定数组的第一个元素,一个方法数组的最后一个元素:
class myArray extends Array {
firstItem() {
return this[0]
}
lastItem() {
return this[this.length - 1]
}
}
const arr = new myArray(1, 2, 3)
console.log(arr) // myArray(3) [ 1, 2, 3 ]
console.log(arr.firstItem()) // 1
console.log(arr.lastItem()) // 3
何为类的混入?在上面的演示代码中,都只实现了子类继承自一个父类,因为JavaScript的类只支持单继承,不能继承自多个类。如果非要实现继承自多个类呢?那么就可以引入混入(Mixin)的概念了。
看看JavaScript中通过代码如何实现混入效果:
// 封装混入Animal类的函数
function mixinClass(BaseClass) {
// 返回一个匿名类
return class extends BaseClass {
running() {
console.log('running...')
}
}
}
class Person {
eating() {
console.log('eating...')
}
}
class Student extends Person {
studying() {
console.log('studying...')
}
}
const NewStudent = mixinClass(Student)
const stu = new NewStudent
stu.running() // running...
stu.eating() // eating...
stu.studying() // studying...
混入的实现一般不常用,因为参数不太好传递,过于局限,在JavaScript中单继承已经足够用了。
上面介绍ES6中类的各种使用方法,极大的方便了我们对类的使用。我们在日常开发中编写的ES6代码都是会被babel解析成ES5代码,为了对低版本浏览器做适配。那么使用ES6编写的类被编译成ES5语法会是什么样呢?通过babel官网的试一试可以清楚的看到ES6语法转成ES5后的样子。
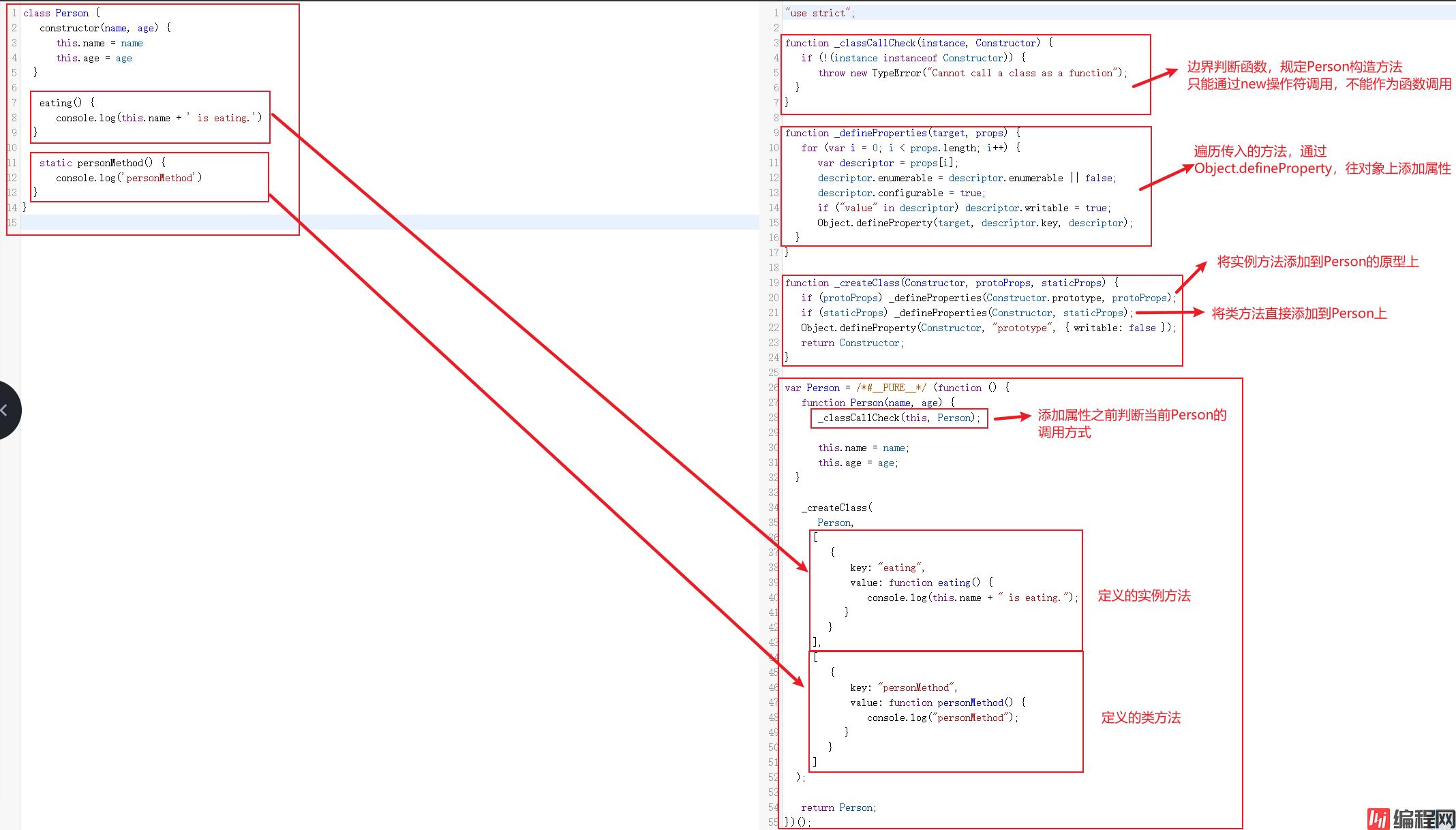
这里可以提出一个小问题:定义在constructor外的属性最终会被添加到哪里呢?还是会被添加到类的实例化对象上,因为ES6对这样定义的属性进行了单独的处理。
class Person {
message = 'hello world'
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
eating() {
console.log(this.name + ' is eating.')
}
static personMethod() {
console.log('personMethod')
}
}
const p = new Person('curry', 30)
console.log(p) // Person { message: 'hello world', name: 'curry', age: 30 }

扩展:在上图中通过通过babel转换后的代码中,定义的Person函数前有一个,那么这个有什么作用呢?
tree-shaking,没有使用到的纯函数会直接在打包的时候被压缩掉,达到减小包体积效果;到此这篇关于JavaScript面向对象之深入了解ES6的class的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关了解ES6的class内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: JavaScript面向对象之深入了解ES6的class
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/142993.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-01-12
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
2023-05-20
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0