Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录使用效果优点如何装配特殊需求使用注解的形式,装配在id字段,自动调用fegin赋值给目标字段。 使用效果 1.先给vo类中字段添加注解 2.调用feignDataS
使用注解的形式,装配在id字段,自动调用fegin赋值给目标字段。
1.先给vo类中字段添加注解

2.调用feignDataSetUtils.setData 方法 将vo类放入 比如我的
feignDataSetUtils.setData(Stream.of(vo).collect(Collectors.toList()));调用前

调用后 产生赋值。

利用类字段注解的形式配置好对应的fegin关系,达到自动调用fegin的效果。
1.省略大部分代码,只需配置注解,和编写fegin所需方法。
2.无其他重依赖,适应性强。
3.随意装配,不需要vo类或者fegin类继承任何接口。
加入所有工具类后,只需两步。
先加入 以下类
ApplicationContextProvider:
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ApplicationContextProvider implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContextSpring;
@Override
public synchronized void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
applicationContextSpring = applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContextSpring.getBean(clazz);
}
}FeignColum:
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FeignColum {
String targetFieldName();
String split() default "";
FeignType feignType();
}FeignDataSetUtils:
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Component
public class FeignDataSetUtils {
// @Value("${appId}")
private String appId;
public List setData(List voList) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(voList)) {
return voList;
}
Object object = voList.get(0);
Class objectClass = object.getClass();
// 获得feign的class为key Field集合为value的map
Map<FeignType, List<Field>> feignFieldsMap = getFieldsAnnotationMap(objectClass);
// 获得数据dataMap 后面用来发送给feign
Map<FeignType, List<Object>> idDataMap = buildDataMap(feignFieldsMap.keySet());
// 遍历所有注解
// 遍历所有携带注解的字段-获得id集合
putIdDataMap(feignFieldsMap, voList, idDataMap);
// Feign返回结果集合
Map<FeignType, Map<Object, Object>> feignResultMap = getFeignResultMap(idDataMap);
// 遍历所有
// 遍历所有携带注解的字段-添加集合
putDataMap(feignFieldsMap, objectClass, voList, feignResultMap);
return voList;
}
private Map<FeignType, Map<Object, Object>> getFeignResultMap(Map<FeignType, List<Object>> idDataMap) {
// 初始化Feign返回结果集合
Map<FeignType, Map<Object, Object>> feignResultMap = new HashMap();
Map<FeignType, IFeignFunction> feignFunctionMap = FeignFunctionMap.getFeignFunctionMap();
idDataMap.keySet().forEach(feignType -> {
IFeignFunction feignFunction = feignFunctionMap.get(feignType);
Optional.ofNullable(feignFunction).ifPresent(m -> {
m.setAppId(appId);
m.setFeign(ApplicationContextProvider.getBean(feignType.getFeignClass()));
Optional.ofNullable(idDataMap.get(feignType)).ifPresent(idList ->
feignResultMap.put(feignType, m.getBatch(idList))
);
});
});
// // 获得用户集合
// Map<String, Object> userVoMap= Optional.ofNullable(idDataMap.get(FeignType.UserInfoFeign.getFeignClass())).map(m->userInfoFeign.getBatch(m,appId).stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(UserVo::getId, my->(Object)my))).orElse(null) ;
// Optional.ofNullable(userVoMap).ifPresent(p->
// feignResultMap.put(FeignType.UserInfoFeign.getFeignClass(),p)
// );
return feignResultMap;
}
private void putIdDataMap(Map<FeignType, List<Field>> feignFieldsMap, List voList, Map<FeignType, List<Object>> idDataMap) {
//遍历所有数据
voList.stream().forEach(entry -> {
feignFieldsMap.keySet().stream().forEach(feignClass -> {
feignFieldsMap.get(feignClass).stream().forEach(field -> {
FeignColum colum = field.getAnnotation(FeignColum.class);
field.setAccessible(true);
// 开始添加id数据
try {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(colum.split())) {
Optional.ofNullable(field.get(entry)).filter(f -> !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(f)).ifPresent(
fieldValue -> idDataMap.get(colum.feignType()).add(fieldValue));
} else {
Optional.ofNullable(field.get(entry)).map(m -> (String) m).filter(f -> StringUtils.isNotEmpty(f)).ifPresent(
fieldValue -> idDataMap.get(colum.feignType()).addAll(Arrays.stream(fieldValue.split(colum.split())).collect(Collectors.toList())));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
});
});
// 删除没有的数据
idDataMap.values().removeIf(value -> CollectionUtils.isEmpty(value));
}
private void putDataMap(Map<FeignType, List<Field>> feignFieldsMap, Class objectClass, List voList, Map<FeignType, Map<Object, Object>> resultMap) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(feignFieldsMap) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(resultMap)) {
return;
}
voList.stream().forEach(entry -> {
feignFieldsMap.keySet().stream().forEach(feignType -> {
Map<Object, Object> voMap = resultMap.get(feignType);
feignFieldsMap.get(feignType).stream().forEach(field -> {
try {
FeignColum colum = field.getAnnotation(FeignColum.class);
String targetFieldName = colum.targetFieldName();
// 目标字段
Field targetField = objectClass.getDeclaredField(targetFieldName);
targetField.setAccessible(true);
// 开始添加用户数据
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(colum.split())) {
Optional.ofNullable(field.get(entry)).filter(f -> !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(f)).ifPresent(
fieldValue -> {
Object object = voMap.get(fieldValue);
try {
targetField.set(entry, object);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} else {
Optional.ofNullable(field.get(entry)).map(m -> (String) m).filter(f -> StringUtils.isNotEmpty(f)).ifPresent(
fieldValue -> {
try {
Object object = Arrays.stream(fieldValue.split(colum.split())).map(m -> {
return voMap.get(m);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
targetField.set(entry, object);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
});
});
}
private Map<FeignType, List<Field>> getFieldsAnnotationMap(Class cls) {
// 注解集合对象
Map<FeignType, List<Field>> feignMap = buildAnnotationMap();
// 字段遍历
Arrays.stream(cls.getDeclaredFields()).forEach(field -> {
feignMap.keySet().stream().forEach(feignClass -> {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(FeignColum.class)) {
FeignColum colum = field.getAnnotation(FeignColum.class);
if(colum.feignType()!=feignClass){
return;
}
feignMap.get(colum.feignType()).add(field);
}
});
});
// 删除没有的字段注解
feignMap.values().removeIf(value -> CollectionUtils.isEmpty(value));
return feignMap;
}
private Map<FeignType, List<Field>> buildAnnotationMap() {
return Arrays.stream(FeignType.values()).collect(Collectors.toMap(my -> my, my -> new ArrayList()));
}
private Map<FeignType, List<Object>> buildDataMap(Collection<FeignType> collection) {
return collection.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(my -> my, my -> new ArrayList()));
}
}IFeignFunction:
import lombok.Data;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Data
public abstract class IFeignFunction<T,E> {
Class<T> clazz;
T feign;
String appId;
public IFeignFunction(){
doGetClass();
}
public abstract Map<E, Object> getBatch(List<E> idList);
public void doGetClass() {
Type genType = this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
Type[] params = ((ParameterizedType) genType).getActualTypeArguments();
this.clazz = (Class<T>) params[0];
}
}剩下的两块代码需要自己加东西
FeignType:这个是用来给注解配置Feign的枚举选项,也就是你想要什么Feign就需要在FeignType中添加一次。
例如我的:
public enum FeignType {
UserInfoFeign(),
UserInfoFeign2();
}FeignFunctionMap:它的作用是用来绑定FeignType和IFeignFunction(Feign的方法)的关系。
import com.xxx.xxx.sdk.feign.UserInfoFeign;
import com.xxx.xxx.sdk.vo.UserVo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class FeignFunctionMap {
private static Map<FeignType, IFeignFunction> feignFunctionMap = new HashMap();
static {
// 用户Feign
put(FeignType.UserInfoFeign,new IFeignFunction<UserInfoFeign,String>() {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getBatch(List<String> idList) {
// feign对象相当于UserInfoFeign的实例化对象,appid你们可以不用管,这个是我的feign必须要携带的一个常量。
// 为什么要返回一个Map<String, Object> ? 因为这将要用来做成字典,key是id,value是这个feign根据这个id调用来的值
return feign.getBatch(idList, appId).stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(UserVo::getId, my -> (Object) my));
}
});
put(FeignType.UserInfoFeign2,new IFeignFunction<UserInfoFeign,Long>() {
@Override
public Map<Long, Object> getBatch(List<Long> idList) {
return feign.getBatch(idList.stream().map(m->String.valueOf(m)).collect(Collectors.toList()), appId).stream().collect(Collectors.toMap( my ->Long.valueOf(my.getId()), my -> (Object) my));
}
});
}
public static void put(FeignType feignType,IFeignFunction iFeignFunction){
feignFunctionMap.put(feignType,iFeignFunction);
}
public static Map<FeignType, IFeignFunction> getFeignFunctionMap() {
return feignFunctionMap;
}
}如果把自己的FeignType和FeignFunctionMap配置完成后就可以在自己的类中加入注解了。
比如下面是我的vo类。
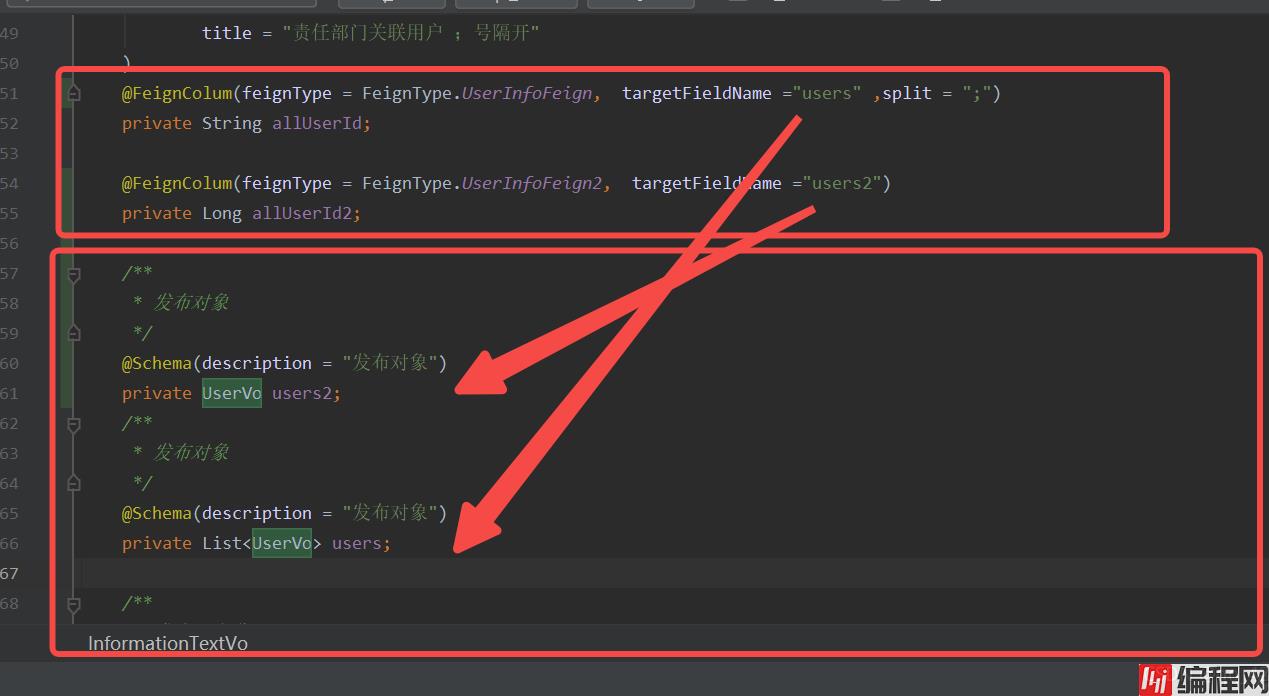
之后放入feignDataSetUtils.setData(Stream.of(vo).collect(Collectors.toList()))当中就能够赋值了。

上面的代码没有必要放出来所以我就已图片的形式展示出来了。
FeignColum注解类的三个属性用意:
targetFieldName:用来记录目标赋值的字段名称 split:用来切割字符串的分割符号,比如我的 字段是allUserId的值是 "1;2" 那我就需要配置 split = ";",且目标字段也必须是List接收。feignType:用来绑定使用的feginType的枚举类型。1.假如我的feign的方法每次请求除了携带id还需要携带一个常量参数访问该怎么办?
这个可以是用全局搜索参看 appId的使用方式。

以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程网。
--结束END--
本文标题: 使用Feign调用注解组件(实现字段赋值功能)
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/142418.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0