Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录1 - Java面向对象学习的三条主线2 - 面向过程与面向对象3 - 面向对象的三大特征4 - 面向对象分析方法分析问题的思路和步骤5 - 面向对象的思想概述6 - 类和对象的
①Java类即类的成员:属性 方法 构造器 (代码块 内部类)
②面向对象的三大特征:封装性 继承性 多态性 (抽象性)
③其他关键字:this supper static final abstract interface 等
二者都是一种思想,面向对象是相对于面向过程而言的
1-面向过程:强调的是功能行为,以函数为最小单位,考虑怎么做
2-面向对象:将功能封装进对象,强调具备了功能的对象,以类/对象为最小单位,考虑谁来做
面向对象更加强调运用人类在日常的思维逻辑中采用的思想方法与原则,如抽象,分类,继承,聚合,多态等
封装(Encapsulation)
继承(Inheritance)
多态(Polymorphism)
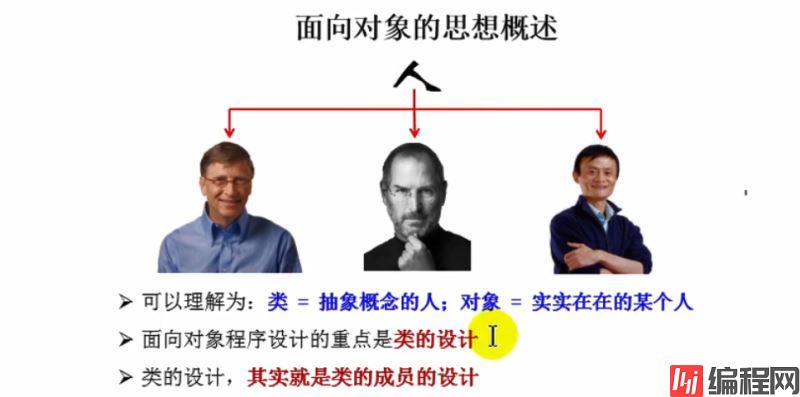
1-类(Class)和对象(Object)是面向对象的核心概念:
①类是对一类事物的描述,是抽象的,概念上的定义
②对象是实际存在的该类事物的每个个体,因而也称其为实例(instance)
③Java世界里,"万物皆对象"

2-代码示例
// 测试类
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 创建Person类的对象
Person p1 = new Person();
// Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 调用对象属性:对象.属性
System.out.println(p1.age); // 22
p1.name = "howie";
p1.isMale = true;
// 调用对象方法:对象.方法
p1.eat();
p1.sleep();
p1.talk("chinese");
// *******************
Person p2 = new Person();
System.out.println(p2.name); // null 说明类的初始化默认值为 null
Person p3 = p1; // 将p1变量保存的对象空间地址值赋值给p3,导致p1和p3都指向了堆空间的同一个对象实体
System.out.println(p3.name); // howie
}
}
// 创建类,设计类的成员
class Person{
// 属性
String name;
int age = 22;
boolean isMale;
// 方法
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人正在吃饭!");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人可以睡觉!");
}
public void talk(String language){
System.out.println("人可以说话,使用的是"+language);
}
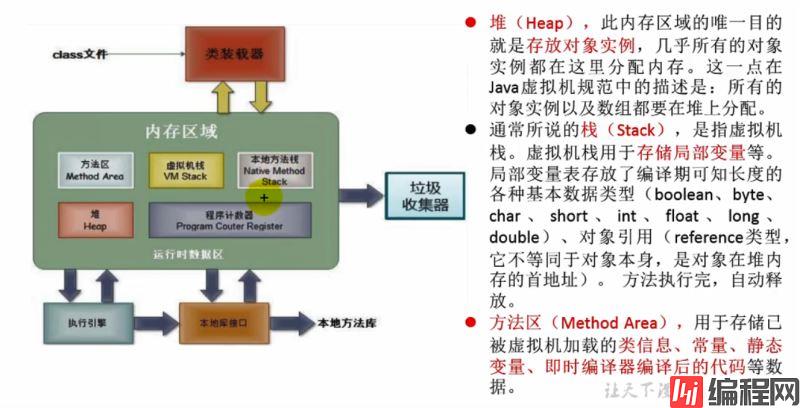
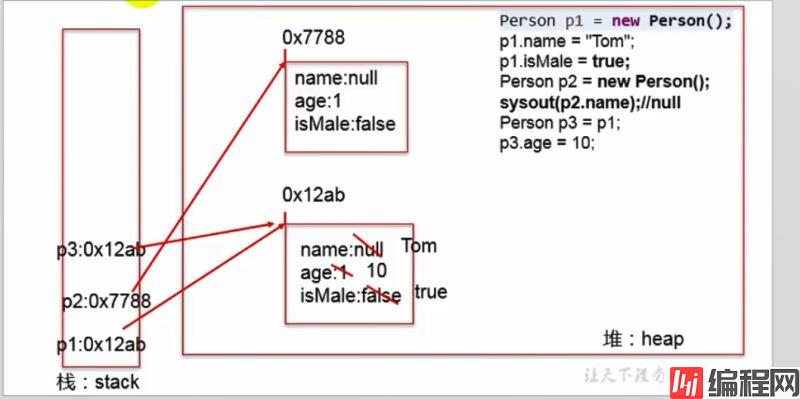
}1-内存解析
2-对象内存解析
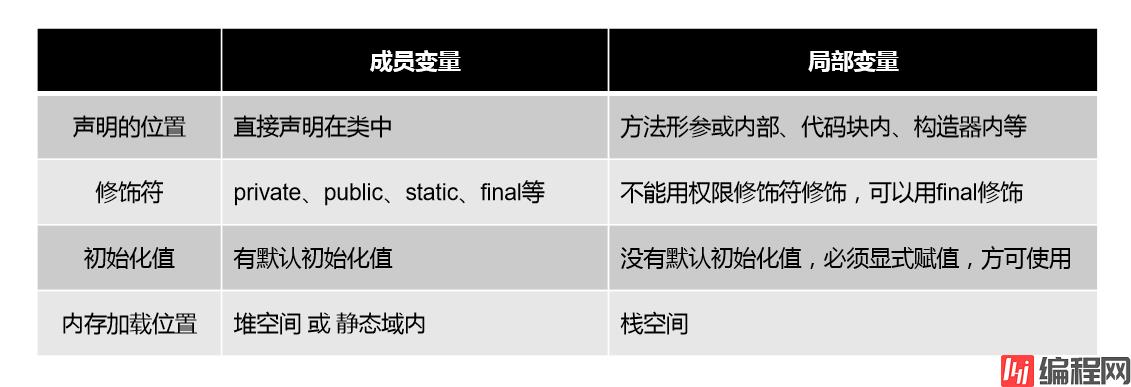
1-属性(成员变量)vs 局部变量
* 1-相同点
* ①定义变量的格式:数据类型 变量名 = 变量值
* ②先声明,后使用
* ③变量都有其对应的作用域
* 2-不同点
* ①在类中声明的位置不同
* 属性:直接定义在类的一对{}内
* 局部变量:声明在方法内,方法形参,代码块,构造器形参,构造器内部的变量
* ②关于权限修饰符的不同
* 属性:可以在声明属性时,指定其权限,使用权限修饰符。常用的权限修饰符:private , public , 缺省 , protected
* 目前,大家声明属性时,都使用缺省就可以(什么都不加)
* 局部变量:不可以使用权限修饰符
* ③默认初始化的值
* 属性:类的属性,根据其类型,都有默认初始值。
* 整型(byte、short、int、long):0
* 浮点型(float、double):0.0
* 字符型(char):0(或'\u00000')
* 布尔(boolean):false
*
* 引用数据类型(类、数组、接口):null
* 局部变量:没有默认初始化值,意味着我们在调用局部变量之前,一定要显示赋值,特别的,形参调用时赋值即可。
* ④在内存中加载的位置
* 属性:堆空间(非static)
* 局部变量:栈
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u1 = new User();
System.out.println(u1.name);
System.out.println(u1.age);
System.out.println(u1.isMale);
// 调用形参
u1.talk("English");
}
}
class User{
// 属性(或成员变量)
String name;
int age;
boolean isMale;
public void talk(String language) {// 形参,也是局部变量
System.out.println("我们使用"+language+"交流");
}
public void eat() {
String foot = "米线"; // 在方法中定义的局部变量
System.out.println("云南人喜欢吃:"+foot);
}
}⑤内存解析需要注意两点
1-内存结构:栈(局部变量)、堆[new 出来的结构:对象(非 static成员变量)、数组]
2-变量:成员变量 vs 局部变量(方法内、方法形参、构造器内、构造器形参、代码块内)
类中方法的申明和使用
方法:描述类应该具备的功能
比如 Math类:aqrt()\random()...
Scanner类:nexInt() ...
Arrays类:sort() \ binarySearch() \ toString() \ equals() \ ...
1-举例
public void eat() {}
public void sleep(int hour) {}
public String getName() {}
public String getNation(String nation) {}2-方法的声明
权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(形参列表) {
方法体
}
注意:static final abstract 来修饰的方法,后面在介绍
3-说明
①权限修饰符:Java规定的4种权限修饰符:private(私有的) , public , 缺省 , protected
默认方法的权限修饰符先都使用public
②返回类型:有返回值 vs 没有返回值
1-如果方法有返回值,则必须在方法声明时,指定返回值的类型。同时,方法中,需要使用时return关键字来返回指定类型的变量或常量
2-如果方法没有返回值,则方法声明时,使用 void来表示。通常没有返回值的方法中,就不需要使用return关键字了
③方法名:属于标识符,遵循标识符的规则和规范,见名知意
④形参列表:方法可以声明0个,1个,或多个形参...格式:数据类型1 形参1,数据类型2 形参2,...
⑤方法体:方法功能的体现
4-return关键字的使用
①使用范围:使用在方法体中
②作用:1.结束方法2.针对于有返回值类型的方法,使用 'return 数据'方法返回所要的数据。
③注意点:return关键字后面不可以声明执行语句
5-方法的使用:可以调用当前类的属性或方法
特殊的:方法A中调用方法A称作 递归方法
方法中不可以再定义方法
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
// 客户类
class Customer{
// 属性
String name;
int age;
boolean isMale;
// 方法
public void eat() {
System.out.println("客户吃饭");
}
public void sleep(int hour) {
System.out.println("客户休息了"+hour+"个小时");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getNation(String nation) {
String info = "我的国籍是"+nation;
return info;
}
}练习题
public class Exer3Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exer3Test test = new Exer3Test();
// 第1题的测试
// test.method();
// 第2题的测试
// double s = test.method();
// System.out.println("面积为"+s);
// 第3题的测试
System.out.println(test.method(12,10));
}
// 第1问
// public void method(){
// for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
// for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++){
// System.out.print("* ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
// }
// 第2问
// public double method(){
// for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){
// for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++){
// System.out.print("* ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
// return 10*8;
// 第3问
public int method(int n,int m){
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
return n * m;
}
}
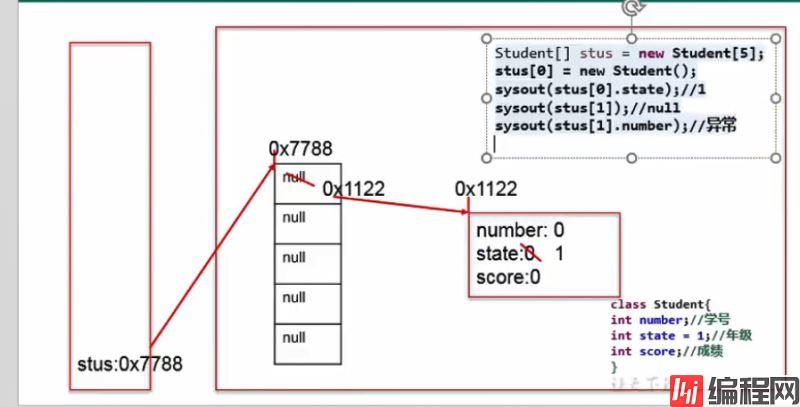
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 声明Student对象数组
Student[] students = new Student[20];
for(int i = 0;i < students.length;i++){
// 给数组元素赋值
students[i] = new Student();
// 给Student对象的属性赋值
students[i].number = i + 1;
double value = Math.random();
students[i].state = (int)(value * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1);
double v = Math.random();
students[i].score = (int)(v * (100 + 1) + 0);
// System.out.print(students[i].score+"\t");
}
// 遍历学生数组
for(int i = 0;i < students.length;i++){
// System.out.println(students[i].number+","+students[i].state+","+students[i].score);
// System.out.println(students[i].showInfo());
// 问题1:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息
if(students[i].state == 3){
// System.out.println(students[i].showInfo());
}
}
// 问题2:使用 [冒泡排序] 按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
for(int i = 0;i < students.length - 1;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < students.length - 1 - i;j++){
if(students[j].score > students[j+1].score){
Student temp = students[j];
students[j] = students[j+1];
students[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
// 遍历 排好序的 学生信息 从最高分打印
for(int i = 0;i < students.length;i++){
System.out.println(students[students.length - i-1].showInfo());
}
}
}
class Student{
int number; // 学号
int state; // 年级
int score; // 成绩
public String showInfo(){
return "学号:"+number+" "+"年级:"+state+" "+"成绩:"+score;
}
}
对象数组使用示例数组对象内存解析
public class PhoneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Phone p = new Phone();
// p = null;
System.out.println(p);
p.sendEmail();
p.playGame();
// 匿名对象
// new Phone().sendEmail();
// new Phone().playGame();
new Phone().price = 199;
new Phone().showPrice(); // 0.0
PhoneMall mall = new PhoneMall();
// mall.show(p);
// 匿名对象的使用
mall.show(new Phone());
}
}
class PhoneMall{
public void show(Phone phone) {
phone.sendEmail();
phone.playGame();
}
}
class Phone{
double price; // 价格
public void sendEmail() {
System.out.println("发送邮件");
}
public void playGame() {
System.out.println("打游戏");
}
public void showPrice() {
System.out.println("手机价格为"+price);
}
}
匿名对象的使用注意两个Java文件在同级目录
①在ArrayUtils.java 文件中 创建类并分装方法
public class ArrayUtils {
// 求数组最大值
public int getMax(int[] array){
int max = array[0];
for(int i = 1;i < array.length;i++){
if(array[i] > max){
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
// 求数组最小值
public int getMin(int[] array){
int min = array[0];
for(int i = 1;i < array.length;i++){
if(min > array[i]){
min = array[i];
}
}
return min;
}
// 求数组总和
public int getSum(int[] array){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
sum += array[i];
}
return sum;
}
// 求数组平均值
public double getAvg(int[] array){
return getSum(array) / array.length;
}
// 反转数组
public void reverseArray(int[] array){
for(int i = 0;i < array.length / 2;i++){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[array.length - i - 1];
array[array.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
// 复制数组
public int[] copyArray(int[] array){
int[] newArray = new int[array.length];
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
newArray[i] = array[i];
}
return newArray;
}
// 数组排序
public void sortArray(int[] array){
for(int i = 0;i < array.length - 1;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < array.length - i -1;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 遍历数组
public void print(int[] array){
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
System.out.print(array[i]+"\t");
}
}
// 查找数组指定的元素
public int getIndex(int[] array,int dest){
int head = 0;
int end = array.length - 1; // 初始的末索引
boolean isFlag = false;
int middle = 0;
sortArray(array);
while(head <= end){
middle = (head + end) / 2;
if(dest == array[middle]){
isFlag = true;
break;
}else if(dest > array[middle]){
head = middle + 1;
}else{
end = middle - 1;
}
}
if(isFlag){
return middle;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
ArrayUtils.java②在ArrayUtilsTest.java 文件中测试封装好的方法
public class ArrayUtilsTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayUtils array = new ArrayUtils();
int[] arr = new int[]{1,5,7,9,845,21,30,12,222,56,-30};
// 获取数组最大值
System.out.println(array.getMax(arr));
// 获取数组最小值
System.out.println(array.getMin(arr));
// 数组反转
array.reverseArray(arr);
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
// 数组复制
int[] arr2 = new int[]{1,2,3};
int[] newArray = array.copyArray(arr2);
for(int i = 0;i < newArray.length;i++){
System.out.print(newArray[i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
// 查找元素
int i = array.getIndex(arr2,4);
System.out.println(i); // -1 表示没有找到此元素
// 数组排序
int[] array3 = new int[]{1,5,8,77,98,33,0,2};
ArrayUtils a = new ArrayUtils();
System.out.print("排序前:");
a.print(array3);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("排序后:");
a.sortArray(array3);
a.print(array3);
}
}
ArrayUtilsTest.java到此这篇关于Java面向对象类和对象的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java面向对象类和对象内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Java面向对象类和对象实例详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/142292.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0