Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录前言示例注意事项总结前言 Apache POI是一种流行的api,允许程序员使用Java程序创建,修改和显示MS Office文件。 它是由Apache Software Fou
Apache POI是一种流行的api,允许程序员使用Java程序创建,修改和显示MS Office文件。 它是由Apache Software Foundation开发和分发的开源库,用于使用Java程序设计或修改Microsoft Office文件。 它包含将用户输入数据或文件解码为MS Office文档的类和方法。
HSSF - 用于读取和写入MS-excel文件的xls格式
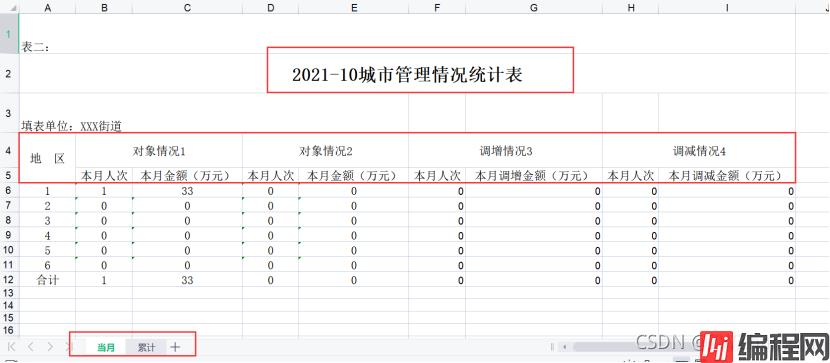
类似上面的需要合并表头的报表在日常的开发中也是经常遇到,这里总结下关于类似的报表开发整理。
对于这种的报表看起来很麻烦,但其实掌握了技巧开发起来也是很简单的。下面的代码仅供参考,有些字段为了脱敏都以数字显示了,见谅。
// 创建sheet
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("当月");
//表头字体
Font headerFont = wb.createFont();
headerFont.setFontName("宋体");
headerFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 18);
headerFont.setBold(true);
headerFont.setColor(Font.COLOR_NORMAL);
//正文字体
Font contextFont = wb.createFont();
contextFont.setFontName("宋体");
contextFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
headerFont.setBold(true);
//表头样式,左右上下居中
CellStyle headerStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
headerStyle.setFont(headerFont);
// 左右居中
headerStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
// 上下居中
headerStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
headerStyle.setLocked(true);
// 自动换行
headerStyle.setWrapText(false);
//单元格样式,左右上下居中 边框
CellStyle commonStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
commonStyle.setFont(contextFont);
// 左右居中
commonStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
// 上下居中
commonStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
commonStyle.setLocked(true);
// 自动换行
commonStyle.setWrapText(false);
//单元格样式,左右上下居中 边框
CellStyle commonWrapStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
commonWrapStyle.setFont(contextFont);
//单元格样式,竖向 边框
CellStyle verticalStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
verticalStyle.setFont(contextFont);
CellStyle commonStyleNoBorder = wb.createCellStyle();
commonStyleNoBorder.setFont(contextFont);
commonStyleNoBorder.setLocked(true);
// 自动换行
commonStyleNoBorder.setWrapText(false);
CellStyle alignLeftStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
alignLeftStyle.setFont(contextFont);
alignLeftStyle.setLocked(true);
// 自动换行
alignLeftStyle.setWrapText(false);
//单元格样式,左对齐 无边框
CellStyle alignLeftNoBorderStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
alignLeftNoBorderStyle.setFont(contextFont);
alignLeftNoBorderStyle.setLocked(true);
// 自动换行
alignLeftNoBorderStyle.setWrapText(false);
//单元格样式,右对齐
CellStyle alignRightStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
alignRightStyle.setFont(contextFont);
alignRightStyle.setLocked(true);
// 自动换行
alignRightStyle.setWrapText(false);
// 行号
int rowNum = 0;
//设置列宽
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
sheet.setColumnWidth(i, 3000);
}
//第一行
Row r0 = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
r0.setHeight((short) 800);
Cell c00 = r0.createCell(0);
c00.setCellValue("表二:");
c00.setCellStyle(alignLeftNoBorderStyle);
//合并单元格
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0, 8));
//第二行城市对象综合统计表
Row r1= sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
r1.setHeight((short) 800);
Cell r10 = r1.createCell(0);
r10.setCellValue("城市对象管理情况统计表");
r10.setCellStyle(headerStyle);
//合并单元格
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(1, 1, 0, 8));
//第三行
Row r2 = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
r2.setHeight((short) 800);
Cell r20 = r2.createCell(0);
r20.setCellValue("填表单位:XXX街道");
r20.setCellStyle(alignLeftNoBorderStyle);
//合并单元格
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(2, 2, 0, 4));
//第四行
Row r3 = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
r3.setHeight((short) 700);
String[] rowSecond = {"地 区", "对象情况1", "","对象情况2","" ,"调增情况3","","情况4",""};
for (int i = 0; i < rowSecond.length; i++) {
Cell tempCell = r3.createCell(i);
tempCell.setCellValue(rowSecond[i]);
tempCell.setCellStyle(commonStyle);
}
//第5行
Row r4 = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
String[] rowSecond5 = {"1", "2", "3","4","5","6","7","8"};
for (int i = 0; i < rowSecond5.length; i++) {
Cell tempCell = r4.createCell(i+1);
tempCell.setCellValue(rowSecond5[i]);
tempCell.setCellStyle(commonStyle);
}
//合并单元格
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(3, 4, 0, 0));
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(3, 3, 1, 2));
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(3, 3, 3, 4));
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(3, 3, 5, 6));
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(3, 3, 7, 8));
//查询数据
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList = XXX.list(XXX);
//统计合计数据
Map<String,Object> mapTotal = new HashMap<>();
for (Map<String, Object> map : dataList) {
Row tempRow = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
//列表数据
Cell tempCell0 = tempRow.createCell(0);
String sqmc = (String) map.get("XXX");
tempCell0.setCellValue(sqmc);
tempCell0.setCellStyle(commonStyle);
}
//导出
response.setContentType("application/vnd.ms-excel");
// 文件名
String fileName = "报表名称.xls";
response.setHeader("Content-disposition", "attachment;filename=\"" + fileName + "\"");
OutputStream stream = response.getOutputStream();
try {
if (null != wb && null != stream) {
wb.write(stream);
stream.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("excel文档导出错误-异常信息:", e);
}
【1】POI操作的行和列都是从0位置开始的
【2】所有的复杂表头无非是合并单元格,这里都可以通过下面的API实现
int addMergedRegion(CellRangeAddress region)
添加合并的单元格区域
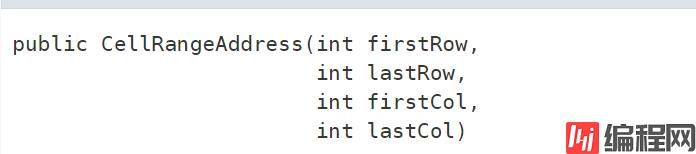
创建新的单元格范围。索引是从零开始的。
参数:
firstRow—第一行的索引
lastRow—最后一行(含)的索引必须等于或大于第一行
firstCol—第一列的索引
lastCol—最后一列(包括)的索引必须等于或大于firstCol
示例
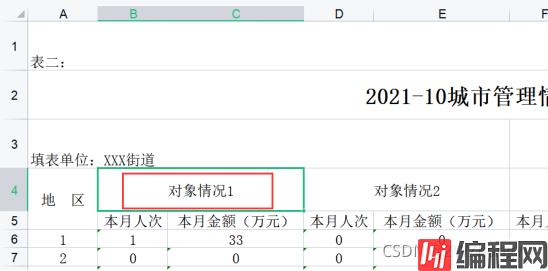
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(3, 3, 1, 2));
合并第四行第1列和第2列
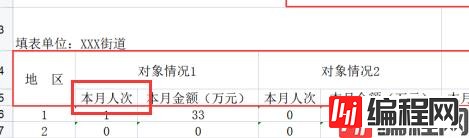
【3】对于空的单元格,直接在数组或者列表中给个空值就可以了。对于下面的图片中第5行的[本月人次]这种如果是数组直接在创建列的时候指定起始位置为1就可以了,注意不要影响合并的位置,而且合并的单元格不要有冲突否则会抛出异常,注意些就可以了.
到此这篇关于Java导出Excel统计报表合并单元格的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java导出Excel统计报表内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Java导出Excel统计报表合并单元格的方法详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/137711.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0