目录概述函数重载运算符重载c++ 的运算符重载运算符的规则成员函数实现 Complex 加法运算符重载的方法多种实现方法实现 operator+=三种运算符重载函数成员函数实现友元函
运算符重载 (Operator Overloading)
重载: 将同一名字重新赋予新的含义.
函数重载: 对一个函数赋予新的含义, 使之实现新功能. 例如:
int max(int x, int y);
double max(double a, double b, double c);
运算符也有重载: 赋予运算符新的含义, 使之一名多用. 例如
int main() {
int i = 2, j = 3;
int k = i + j;
string s1 = "Good ", s2 = "morning";
string s3 = s1 + s2;
cout << k << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
5
good morning
通过运算符重载, 扩大了 C++ 已有运算符的作用, 使运算符能用于类对象. 使用运算符重载, 能使程序易于编写, 阅读和维护. 运算符被重载后, 其原有的功能仍然保留, 没有丧失过改变.
运算符重载实质上是函数的重载:
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT2_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT2_COMPLEX_H
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double r, double i);
Complex add(Complex &c2);
void display();
};
#endif //PROJECT2_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iOStream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) : real(r), imag(i) {}
Complex Complex::add(Complex &c2) {
Complex c;
c.real = real + c2.real;
c.imag = imag + c2.imag;
return c;
}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
main:
int main() {
Complex c1(3, 4), c2(5, -10), c3;
cout << "c1 =";
c1.display();
cout << "c2 =";
c2.display();
c3 = c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 + c2 = ";
c3.display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
c1 =(3, 4i)
c2 =(5, -10i)
c1 + c2 = (8, -6i)
运算符重载格式:
函数类型 operator 运算符名称 (形参流标) {对运算符的重载处理}
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double, double);
void display();
Complex operator+(Complex &c2);
};
#endif //PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) :real(r), imag(i) {}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c2) {
Complex c;
c.real = real + c2.real;
c.imag = imag + c2.imag;
return c;
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Complex c1(3, 4), c2(5, -10), c3;
cout << "c1 =";
c1.display();
cout << "c2 =";
c2.display();
c3 = c1 + c2;
cout << "c1 + c2 = ";
c3.display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
c1 =(3, 4i)
c2 =(5, -10i)
c3= (8, -6i)
成员函数实现:
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c2) {
Complex c;
c.real = real + c2.real;
c.imag = imag + c2.imag;
return c;
}
简化:
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c2){
return Complex(real +c2.real, imag + c2.image);
}
友元函数实现:
Complex operator+(Complex &c1, Complex &c2){
......
}
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double, double);
void display();
Complex operator+=(const Complex &c);
};
#endif //PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) :real(r), imag(i) {}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
Complex Complex::operator+=(const Complex &c) {
real += c.real; // this->real += c.real;
imag += c.imag; // this->imag += c.imag;
return *this;
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Complex c1(3, 4), c2(5, -10), c3;
cout << "c1 =";
c1.display();
cout << "c2 =";
c2.display();
c1 += c2;
cout << "c1= ";
c1.display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
c1 =(3, 4i)
c2 =(5, -10i)
c1= (8, -6i)
运算符重载函数可以是类的成员函数:
运算符重载函数可以是类的友元函数:
运算符重载函数还可以是普通函数:
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double, double);
void display();
Complex operator+(double d); // 成员函数实现
};
#endif //PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) :real(r), imag(i) {}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
Complex Complex::operator+(double d) {
return Complex(real + d, imag);
}
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double, double);
void display();
friend Complex operator+(Complex &c, double d); // 友元函数
};
#endif //PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) :real(r), imag(i) {}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
Complex operator+(Complex &c, double d) {
return Complex(c.real + d, c.imag);
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Complex c1(3, 4), c2(5, -10), c3, c4;
cout << "c1 =";
c1.display();
cout << "c2 =";
c2.display();
c3 = c1 + 3.14;
cout << "c3= ";
c3.display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
c1 =(3, 4i)
c2 =(5, -10i)
c3= (6.14, 4i)
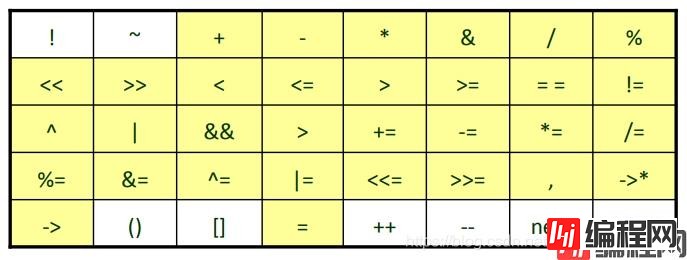
单元运算符 (unary operation), 即只有一个运算量. 如: !a, -b, &c, *p, ++i, i-- 等.
重载单元运算符实现分数对象的相反数.
Fraction 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_FRACTION_H
#define PROJECT4_FRACTION_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Fraction {
private:
int nume; // 分子
int deno; // 分母
public:
Fraction();
Fraction(int, int);
Fraction operator-(const Fraction &c); // 分数相减
Fraction operator-(); // 取反一目运算
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &output, const Fraction &f);
};
#endif //PROJECT4_FRACTION_H
Fraction.cpp:
#include "Fraction.h"
Fraction::Fraction() : nume(0), deno(0) {}
Fraction::Fraction(int n , int d) : nume(n), deno(d) {}
Fraction Fraction::operator-(const Fraction &c) {
return Fraction(nume*c.deno - c.nume*deno, deno*c.deno);
}
Fraction Fraction::operator-() {
return Fraction(-nume, deno);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream &output, const Fraction &f) {
double result = (double)f.nume / f.deno;
output << result << endl;
return output;
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Fraction.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Fraction f1(1,3), f2(1,5), f3, f4;
f3 = f1 - f2; // 分数相减
f4 = -f1; // 分数取反
cout << f3;
cout << f4;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
0.133333
-0.333333
二元运算符 (binary operation).
要求:
步骤:
String 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_STRING_H
#define PROJECT4_STRING_H
#include <cstdlib>
class String {
private:
char *p;
public:
String(){p=nullptr;}
String(char *str);
void display();
};
#endif //PROJECT4_STRING_H
String.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
String::String(char *str) {
p = new char[sizeof(str)];
strcpy(p, str);
}
void String::display() {
cout << p;
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
String s1("Hello");
String s2("China");
s1.display( );
cout<<" ";
s2.display( );
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
Hello China
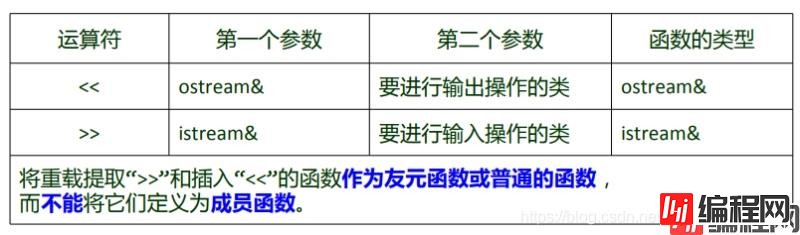
通过重载输入流 (input stream) 和输出流 (output stream), 我们可以用来输出用户自己定义的数据.
格式:
ostream &operator<<(ostream&, const 自定义类&);
istream &operator>>(istream&,自定义类&);
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double, double);
void display();
Complex operator+(Complex &c);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &output, const Complex &c);
};
#endif //PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) :real(r), imag(i) {}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c) {
return Complex(real + c.real, imag + c.imag);
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &output, const Complex &c) {
output<<"("<<c.real<<" + "<<c.imag<<"i)";
return output;
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Complex c1(2, 4),c2(6, 10),c3;
c3 = c1 + c2;
cout << c1 << " + " << c2 << " = " << c3 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
(2 + 4i) + (6 + 10i) = (8 + 14i)
Complex 类:
#ifndef PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#define PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex();
Complex(double, double);
void display();
Complex operator+(Complex &c);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &output, const Complex &c);
friend istream& operator>>(istream &input, Complex &c);
};
#endif //PROJECT4_COMPLEX_H
Complex.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
Complex::Complex() : real(0), imag(0) {}
Complex::Complex(double r, double i) :real(r), imag(i) {}
void Complex::display() {
cout << "(" << real << ", ";
cout << imag << "i)" << endl;
}
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c) {
return Complex(real + c.real, imag + c.imag);
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &output, const Complex &c) {
output<<"("<<c.real<<" + "<<c.imag<<"i)";
return output;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &input, Complex &c) {
cout << "input real part and imaginary part:\n";
input >> c.real >> c.imag;
return input;
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Complex c1, c2;
cin >> c1 >> c2;
cout << "c1=" << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2=" << c2 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
input real part and imaginary part:
2 4
input real part and imaginary part:
6 10
c1=(2 + 4i)
c2=(6 + 10i)
运算符重载使类的设计更加丰富多彩, 扩大了类的功能和使用范围. 运算符重载使得程序易于理解, 易于对对象进行操作. 有了运算符重载, 在声明了类之后, 我们就可以像使用标准类型一样来使用自己声明的类.
类的声明往往是一劳永逸的. 有了好的类, 用户在程序中就不必定义许多成员函数去完成运算和 I/O 的功能, 使主函数更加简单易读. 好的运算符重载能细心啊面向对象程序设计思想.
到此这篇关于C++中运算符重载详解及其作用介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++运算符重载内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: C++中运算符重载详解及其作用介绍
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/134834.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0