Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
Java中Collection的常用方法 1、add() 向中添加元素 add(100) 自动装箱操作,实际上是放进去的一个对象, Integer n = new Integer(
1、add() 向中添加元素
add(100) 自动装箱操作,实际上是放进去的一个对象, Integer n = new Integer(100),实际上是把n放进了
Collection co = new ArrayList();
co.add(1);2、addAll( Collection c )
将指定集合中的所有元素添加到从集合中
因为ArryList类中重写了equals() 方法,所以两个集合比较相等。
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {
c.add(i);
}
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
c1.addAll(c);
System.out.println(c1.equals(c)); // true
}
}
3、size() 获取集合中元素个数
Collection co = new ArrayList();
int n = co.size();4、clear() 清空集合
Collection co = new ArrayList();
co.clear();5、contains(100) 判断当前集合中是否包含100这个元素 返回 true、false
Collection co = new ArrayList();
co.add(100);
co.add(200);
boolean r = co.contains(100); // true*** 深入探究***
例一:
下边代码,new了两个字符串,s1被添加到集合中去了,但是s2没有添加进去,最后输入s2是否在集合当中?
分析:
按道理来说,s1和s2在栈内存中是两个变量分别指向了在堆内存中存储的也是两个对象,只不过这两个对象同时指向了 "123" 在常量池中的地址而已,怎么地集合中都不能包含s2啊?
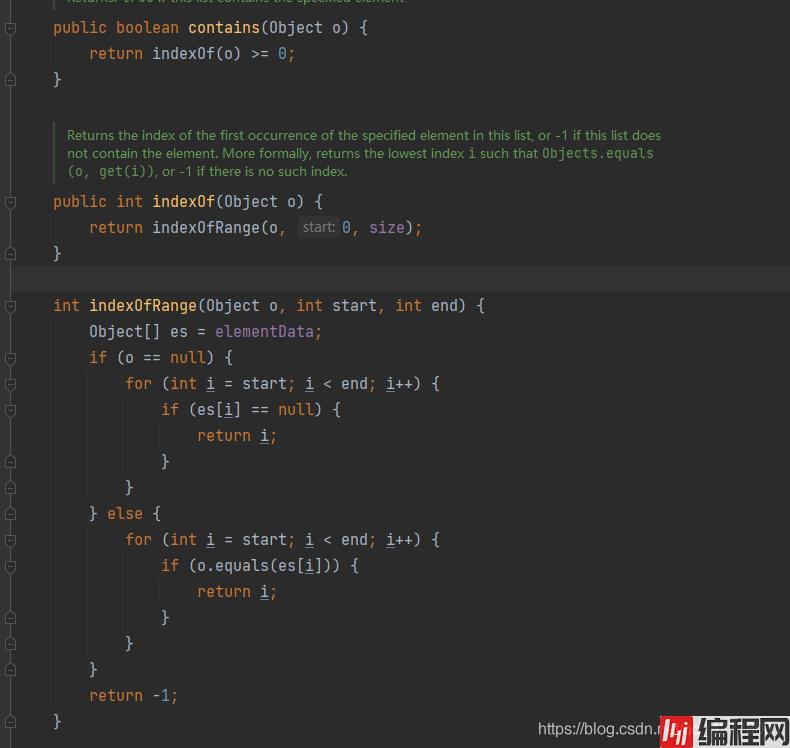
下边我们来看下contains源码:
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection r = new ArrayList();
String s1 = new String("123");
r.add(s1);
String s2 = new String("123");
System.out.println(r.contains(s2)); // true
}
}
contains()源码:
参数o是调用contains()方法传递的参数,内部调用了indexOf(),而indexof方法内部调用了indexOfRange方法,在这个方法中会去获取集合中的每一个元素,然后通过equals() 方法来判断传递的参数与集合中的元素是否相等,我们传的参数是字符串,而字符串的equals()方法在源码中已经被重写了,只要字符串值相等就想等,实际判断的是:s1.equals(s2), 结果相等,返回元素在集合中的索引,而索引一定 >= 0,所以返回true!
其实调用contains() 方法,内部是调用equals()方法来判断的!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
例二:
下边知道为什么返回false了吧,Person类的eqauls() 方法继承的是object对象上的,所以没有重写equals() 方法的两个对象比较自然返回false了。
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection r = new ArrayList();
Person p1 = new Person("lxc", 20);
r.add(p1);
Person p2 = new Person("lxc", 20);
System.out.println(r.contains(p2)); // false
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
我们来重写下Person对象的eqauls() 方法:
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection r = new ArrayList();
Person p1 = new Person("lxc", 20);
r.add(p1);
Person p2 = new Person("lxc", 20);
System.out.println(r.contains(p2)); // true
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(!(obj instanceof Person)) return false;
if(this == obj) return true;
Person o = (Person) obj;
if((this.name == o.name) && (this.age == o.age)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
6、remove() 删除集合中某个元素
Collection co = new ArrayList();
co.remove(100);****深入探究****
其实remove() 方法和contains() 方法类似,内部也是调用了equals() 方法,所以s1和s2相等,删除了s2等同于删除了s1。
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection r = new ArrayList();
String s1 = new String("abc");
r.add(s1);
String s2 = new String("abc");
Boolean res = r.remove(s2);
System.out.println(res); // 删除成功了
System.out.println(r.size()); // 0
}
}
remove源码:
获取集合中的每一个元素,使用equals() 方法判断是否相等,如果相等调用fastRemove方法删除元素。

7、isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空 true、false
co.isEmpty();8、Object r = col.toArray() 把集合转数组
9、iterator 迭代器对象 (重点)
xxx.iterator( ); 获取迭代器。
Collection h = new HashSet();
Iterator r = h.iterator() 获取iterator对象,目的遍历数组 r迭代器对象 - 负责迭代集合当中的元素。
r迭代器对象中的方法:
(1)boolean hasNext()如果仍有元素可迭代,则返回true;
(2)Object next() 返回迭代的下一个元素。
(3)void remove() 没返回,删除集合中的元素
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection h = new HashSet();
h.add(1);
h.add(2);
h.add(new Object());
// 获取迭代器
Iterator r = h.iterator();
while(r.hasNext()) {
Object res = r.next();
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
Iterator i = c.iterator();
c.add(1);
c.add(2);
Iterator i1 = c.iterator();
while(i1.hasNext()) {
Object r = i1.next();
i1.remove();
System.out.println(r);
}
System.out.println(c.size()); // 0
}
}
****重点****
当集合的结构发生改变的时候,迭代器必须重新获取,如果还是以前老的迭代器,会出现异常。
下边集合的结构发生了改变,结果报错:
// 报错:java.base/java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
Iterator i = c.iterator();
c.add(1);
c.add(2);
while(i.hasNext()) {
Object r = i.next();
System.out.println(r);
}
}
}
修改:
public class lxc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
Iterator i = c.iterator();
c.add(1);
c.add(2);
Iterator i1 = c.iterator();
while(i1.hasNext()) {
Object r = i1.next();
System.out.println(r);
}
}
}
到此这篇关于在Java中Collection的一些常用方法总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java Collection常用方法内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: 在Java中Collection的一些常用方法总结
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/128151.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0