Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
1.在下面的案例中,执行两次查询控制台只会输出一次 sql 查询: mybatis-config.xml <?xml version="1.0" encodi
1.在下面的案例中,执行两次查询控制台只会输出一次 sql 查询:
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"Http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.Mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xxx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&autoReconnect=true"/>
<property name="username" value="xxx"/>
<property name="passWord" value="xxx"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/hrh/mapper/PersonMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
PersonMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.hrh.mapper.PersonMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.hrh.bean.Person">
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="age" property="age" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id, name, age
</sql>
<select id="list" resultType="com.hrh.bean.Person">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
from tab_person
</select>
</mapper>
public interface PersonMapper {
List<Person> list();
}
String resource = "mybatis-config2.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();//开启会话
PersonMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(PersonMapper.class);
mapper.list();
mapper.list();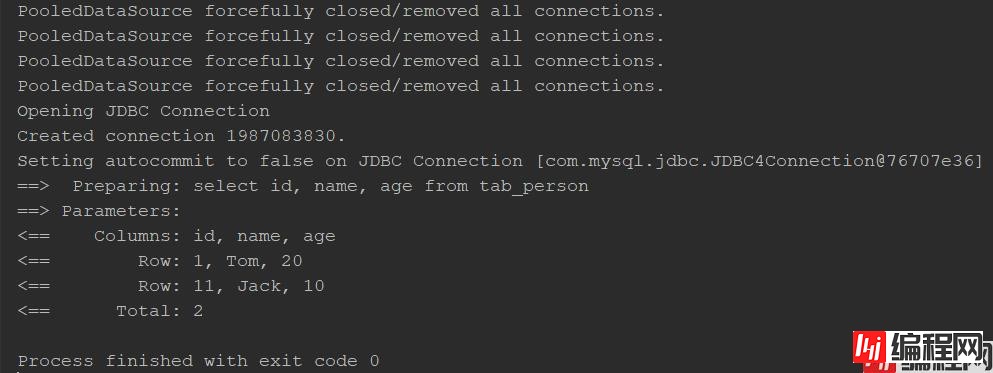
之所以会出现这种情况,是因为 Mybatis 存在一级缓存导致的,下面 debug 探究下内部流程:
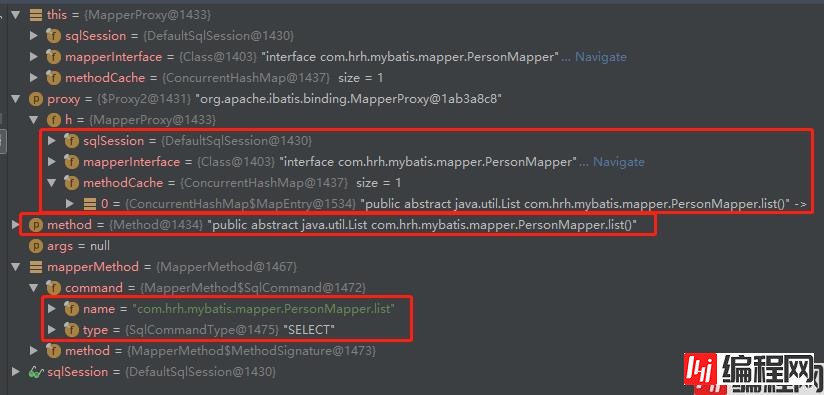
(1)mapper.list() 会进入 MapperProxy#invoke():参数proxy是一个代理对象(每个 Mapper 接口都会被转换成一个代理对象),里面包含会话 sqlSession、接口信息、方法信息;method是目标方法(当前执行的方法),它里面包含了所属的哪个类(接口)、方法名、返回类型(List、Map、void 或其他)、参数类型等;args是参数;
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclarinGClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//从方法缓存methodCache中获取到方法的信息:比如方法名、类型(select、update等)、返回类型
//如果获取中没有MapperMethod,则创建一个并放入methodCache中
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//执行查询SQL并返回结果
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
} 
cacheMapperMethod:MapperMethod 包含方法名、类型(select、update等)、返回类型等信息
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
//缓存中获取
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
//没有则创建一个对象并放入缓存中供下次方便取用
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}(2)MapperMethod#execute()根据 SQL 类型进入不同的查询方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
//返回结果
Object result;
//判断语句类型
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {//插入语句
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {//更新语句
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {//删除语句
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT://查询语句
//返回空的查询
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
//返回List的查询
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeFORMany(sqlSession, args);
//返回Map的查询
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
//返回游标的查询
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}(3)上面的案例是 select 语句,返回结果是List集合,所以进入 MapperMethod#executeForMany():
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
//获取参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//是否有分页查询
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
//如果list中的泛型跟结果类型不一致,进行转换
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}(4)selectList执行了DefaultSqlSession#selectList():
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//SQL执行的信息:resource(xxMapper.xml)、id、sql、返回类型等
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//执行查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
(5)接下来调用缓存执行器的方法:CachingExecutor#query()
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//获取到执行SQL
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
//将SQL包装成一个缓存对对象,该对象和结果集组成键值对存储到缓存中,方便下次直接从缓存中拿而不需要再次查询
//createCacheKey:调用BaseExecutor#createCacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//获取缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
//没有缓存连接查询
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}(6)接下来执行 BaseExecutor#query():从下面可以看到将结果缓存到localCache 中了
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//如果不是嵌套查询(默认为0),且 <select> 的 flushCache=true 时清空缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
//嵌套查询层数+1
queryStack++;
//从localCache缓存中获取
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//连接查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
//下面是延迟加载逻辑
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//缓存中添加占位符
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//连接查询获取到数据结果
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//删除占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//将结果缓存起来
localCache.putObject(key, list);
//处理存储过程
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}2.但当 spring Framework + Mybatis 时,情况就不一样了,每次查询都会连接数据库查询,控制台都会打印 SQL 出来,如下案例:
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonMapper personMapper;
public List<Person> getList() {
personMapper.list();
personMapper.list();
return personMapper.list();
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.hrh")
@MapperScan("com.hrh.mapper")
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource());
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(resolveMapperLocations());
return factoryBean;
}
public Resource[] resolveMapperLocations() {
ResourcePatternResolver resourceResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
List<String> mapperLocations = new ArrayList<>();
mapperLocations.add("classpath*:com/hrh/mapper/*Mapper*.xml");
List<Resource> resources = new ArrayList();
if (mapperLocations != null) {
for (String mapperLocation : mapperLocations) {
try {
Resource[] mappers = resourceResolver.getResources(mapperLocation);
resources.addAll(Arrays.asList(mappers));
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
return resources.toArray(new Resource[resources.size()]);
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername("xxx");
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword("xxx");
driverManagerDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xxx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&autoReconnect=true");
return driverManagerDataSource;
}
}
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyBatisConfig.class);
PersonService bean = context.getBean(PersonService.class);
bean.getList();
下面debug进入的步骤跟上面的(1)、(2)、(3)是一致的,但第四步却是进入SqlSessionTemplate#selectList()中【SqlSessionTemplate是mybatis-spring-xx.jar的,上文的DefaultSqlSession是属于mybatis-xx.jar的】:
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}接下来的selectList() 会被方法拦截:method.invoke() 会执行到 DefaultSqlSession#selectList(),重新回到上文的第四步并且继续下去,也就是在上文的(1)~(6)中插入了前后文,在其中做了关闭会话的操作;
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//得到会话
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(
SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
//执行方法查询
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);//在关闭会话前提交和回滚
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {//有异常抛出异常并结束会话
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
// release the connection to avoid a deadlock if the translator is no loaded. See issue #22
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
//关闭会话
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}Mybatis 的一级缓存是会话级别的缓存(单线程的,特别鸡肋),Mybatis 每创建一个 SqlSession 会话对象,就表示打开一次数据库会话,在一次会话中,应用程序很可能在短时间内反复执行相同的查询语句,如果不对数据进行缓存,则每查询一次就要执行一次数据库查询,这就造成数据库资源的浪费。又因为通过 SqlSession 执行的操作,实际上由 Executor 来完成数据库操作的,所以在 Executor 中会建立一个简单的缓存,即一级缓存;将每次的查询结果缓存起来,再次执行查询的时候,会先查询一级缓存(默认开启的),如果命中,则直接返回,否则再去查询数据库并放入缓存中。
一级缓存的生命周期与 SqlSession 的生命周期相同,因此当 Mybatis 和Spring Framework 的集成包中扩展了一个 SqlSessionTemplate 类(它是一个代理类,增强了查询方法),所有的查询经过 SqlSessionTemplate 代理拦截后再进入到 DefaultSqlSession#selectList() 中,结束查询后把会话SqlSession 关了,所以导致了缓存失效。
那为什么要这么操作呢?
原始的 Mybatis 有暴露 SqlSession 接口,因此有 close 方法暴露出来供你选择使用,你可以选择关与不关,但在Mybatis 和Spring Framework 的集成包中,SqlSession 是交给了Spring Framework 管理的,没有暴露出来,为了稳妥决定,直接给你关了。
到此这篇关于Mybatis一级缓存和结合Spring Framework后失效的源码探究的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Mybatis一级缓存Spring Framework失效内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: Mybatis一级缓存和结合Spring Framework后失效的源码探究
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/124778.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0