1. 新增(Create) insert into [表名] (字段1, 字段2,....) value (value1, value2, ...); insert into
insert into [表名] (字段1, 字段2,....) value (value1, value2, ...);
insert into [表名] (字段1, 字段2, ....) values
(value1, ...),
(value2, ...),
(value3, ...);
实例:
创建一个学生成绩表
CREATE TABLE exam_result (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
chinese DECIMAL(3,1),
math DECIMAL(3,1),
english DECIMAL(3,1)
);
1.1 单行数据 + 全列插入
-- 插入两条记录,value_list 数量必须和定义表的列的数量及顺序一致
insert into exam_result value ( 1, 'tom', 68, 98, 56);
insert into exam_result value ( 2, 'jum', 87.5, 78, 77);
每次插入数据, 为一条记录, 包含了若干个列~~
列的数目和数据类型要和表的结构对应~
value 前省略指定列默认为全列插入
1.2 多行数据 + 指定列
- 插入两条记录,value_list 数量必须和指定列数量及顺序一致
INSERT INTO exam_result (id,name, chinese, math, english) VALUES
(1,'tom', 67, 98, 56),
(2,'jum', 87.5, 78, 77),
(3,'lim', 88, 98.5, 90),
(4,'tim', 82, 84, 67),
(5,'huy', 55.5, 85, 45),
(6,'sun', 70, 73, 78.5),
(7,'ming', 75, 65, 30);
2.1 全列查询
select * from [表名];
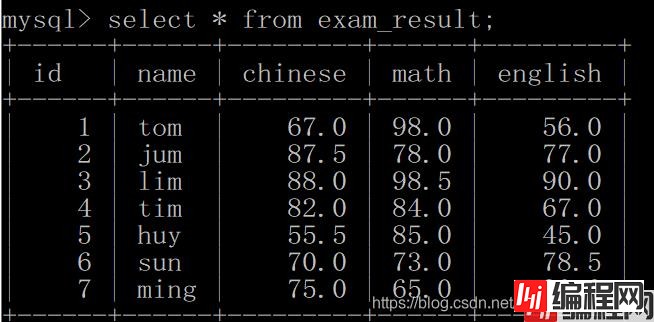
*表示通配符, 意思就是查找所有的列
2.2 指定列查询
select [指定查询列] from [表名];

2.3 查询字段为表达式
select [字段表达式] from [表名];

2.4 别名
select colum [as] [列名] from [表名];

2.5 去重: DISTINCT
使用 distinct 关键字对某列数据去重
--98 分重复了
select math from exam_result;
+------+
| math |
+------+
| 98.0 |
| 78.0 |
| 98.0 |
| 84.0 |
| 85.0 |
| 73.0 |
| 65.0 |
+------+
-- 去重结果
select distinct math from exam_result;
+------+
| math |
+------+
| 98.0 |
| 78.0 |
| 84.0 |
| 85.0 |
| 73.0 |
| 65.0 |
+------+
2.6 排序: ORDER BY
select * from [表名] order by [排序字段];
用 order by 指定某一列进行排序, 默认按照升序排序.
显式加上 desc , 就是降序排序. 使用 asc 也是升序
select name, math from exam_result order by math desc;
+------+------+
| name | math |
+------+------+
| tom | 98.0 |
| lim | 98.0 |
| huy | 85.0 |
| tim | 84.0 |
| jum | 78.0 |
| sun | 73.0 |
| ming | 65.0 |
+------+------+
NULL 数据排序,视为比任何值都小,升序出现在最上面,降序出现在最下面
排序也可以指定多个列执行
select * from exam_result order by math desc, chinese desc;
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| 3 | lim | 88.0 | 98.0 | 90.0 |
| 1 | tom | 67.0 | 98.0 | 56.0 |
| 5 | huy | 55.5 | 85.0 | 45.0 |
| 4 | tim | 82.0 | 84.0 | 67.0 |
| 2 | jum | 87.5 | 78.0 | 77.0 |
| 6 | sun | 70.0 | 73.0 | 78.5 |
| 7 | ming | 75.0 | 65.0 | 30.0 |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
多列排序时, 是在第一列区分不出来大小的时候, 再按第二列排序.
2.7 条件查询: WHERE
比较运算符
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| >, >=, <, <= | 大于,大于等于,小于,小于等于 |
| = | 等于,NULL 不安全,例如 NULL = NULL 的结果是 NULL |
| <=> | 等于,NULL 安全,例如 NULL <=> NULL 的结果是 TRUE(1) |
| !=, <> | 不等于 |
| BETWEEN a0 AND a1 | 范围匹配,[a0, a1],如果 a0 <= value <= a1,返回 TRUE(1) |
| IN (option, …) | 如果是 option 中的任意一个,返回 TRUE(1) |
| IS NULL | 是 NULL |
| IS NOT NULL | 不是 NULL |
| LIKE | 模糊匹配。% 表示任意多个(包括 0 个)任意字符;_ 表示任意一个字符 |
逻辑运算符:
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| AND | 多个条件必须都为 TRUE(1),结果才是 TRUE(1) |
| OR | 任意一个条件为 TRUE(1), 结果为 TRUE(1) |
| NOT | 条件为 TRUE(1),结果为 FALSE(0) |
注意:
实例:
基本查询:
-- 查询英语不及格的同学及英语成绩 ( < 60 )
select name, english from exam_result where english < 60;
-- 查询语文成绩好于英语成绩的同学
select name, chinese, english from exam_result where chinese > english;
-- 查询总分在 200 分以下的同学
select name, chinese + math + english as total from exam_result where chinese + math + english < 200;
AND 与 OR:
-- 查询语文成绩大于80分,且英语成绩大于80分的同学
select * from exam_result where chinese > 80 and english > 80;
-- 查询语文成绩大于80分,或英语成绩大于80分的同学
select * from exam_result where chinese > 80 or english > 80;
关于优先级问题, and 比 or 更优先,
范围查询:
1.BETWEEN … AND …
-- 查询语文成绩在 [80, 90] 分的同学及语文成绩
select name, chinese from exam_result where chinese BETWEEN 80 AND 90;
select name, chinese, from exam_result where chinese >= 80 and chinese <= 90;
IN
-- 查询数学成绩是 58 或者 59 或者 98 或者 99 分的同学及数学成绩
select name, math from exam_result where math in (58, 59, 98, 99);
模糊查询: LIKE
select name from exam_result where name like 't%';
+------+
| name |
+------+
| tom |
| tim |
+------+
% 是一个通配符, 可以用来代替任意多个字符
t% 找出以 t 开头的字符串
%t 找出以 t 结尾的字符串
%t% 找出包含 t 的
除了 % 之外, 还有 _ ,(_ 只能代表一个字符~)
select name from exam_result where name like 't__';
+------+
| name |
+------+
| tom |
| tim |
+------+
通配符也能针对数字进行模糊查询
select name, chinese from exam_result where chinese like '%8%';
+------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+------+---------+
| jum | 87.5 |
| lim | 88.0 |
| tim | 82.0 |
+------+---------+
注意:
模糊查询看起来比较好用, 实际执行效率低下
NULL 的查询: IS [NOT] NULL
select name from exam_result where id id not null;
2.8 分页查询: LIMIT
-- 最初数据表
select * from exam_result;
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | tom | 67.0 | 98.0 | 56.0 |
| 2 | jum | 87.5 | 78.0 | 77.0 |
| 3 | lim | 88.0 | 98.0 | 90.0 |
| 4 | tim | 82.0 | 84.0 | 67.0 |
| 5 | huy | 55.5 | 85.0 | 45.0 |
| 6 | sun | 70.0 | 73.0 | 78.5 |
| 7 | ming | 75.0 | 65.0 | 30.0 |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
-- 前三条记录
select * from exam_result limit 3;
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | tom | 67.0 | 98.0 | 56.0 |
| 2 | jum | 87.5 | 78.0 | 77.0 |
| 3 | lim | 88.0 | 98.0 | 90.0 |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
-- 从第三条开始的三条记录
select * from exam_result limit 3 offset 3;
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| 4 | tim | 82.0 | 84.0 | 67.0 |
| 5 | huy | 55.5 | 85.0 | 45.0 |
| 6 | sun | 70.0 | 73.0 | 78.5 |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
offset 表示从第几条开始查找, offset 可以省略
select * from exam_result limit 3 , 4;
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
| 4 | tim | 82.0 | 84.0 | 67.0 |
| 5 | huy | 55.5 | 85.0 | 45.0 |
| 6 | sun | 70.0 | 73.0 | 78.5 |
| 7 | ming | 75.0 | 65.0 | 30.0 |
+------+------+---------+------+---------+
– 将总成绩倒数前三的 3 位同学的数学成绩加上 30 分
update exam_result set math = math + 30 order by chinese + math + english limit 3;
update 不加条件, 就可以针对所有
delete from [表名];
-- 删除 ming 同学的考试成绩
delete from exam_result where name = 'ming';
-- 删除整张表
delete from exam_result;
如果不指定条件, 此时就把整个表删除掉了, (与 drop 删除表还有不同)
delete 删除后表为 null, drop 删除后表就不存在了
-- 单行插入
insert into [表名] (字段1, ..., 字段N) values (value1, ...,value N);
-- 多行插入
insert into [表名](字段1, ..., 字段N) values
(value1, ...),
(value2, ...),
(value3, ...);
查询
--全表查询
select * from [表名];
--指定列查询
select [列名1, 列名2,...] from [表名];
--查询表达式字段
select [表达式1, 表达式2,...] from [表名];
--别名
select
--去重 DISTINCT
select distinct [字段] from [表名];
-- 排序ORDER BY
select * from [表名] order by [排序字段];
-- 条件查询WHERE
-- (1)比较运算符 (2)BETWEEN ... AND ... (3)IN (4)IS NULL (5)LIKE (6)AND (7)OR
(8)NOT
select * from [表名] where [条件];
修改
update [表] set [修改内容1, 修改内容2, ....] where [条件];
删除
delete from [表名] where [条件];
到此这篇关于Mysql表增删改查的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql表增删改查内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: MySQL表的增删改查基础教程
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/123024.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-10-23
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
2024-10-22
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0