Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录字符串字符串常用操作拼接字符串字符串复制计算字符串的长度截取字符串和获取单个字符字符串包含判断常用字符串方法把字符串的第一个字符大写统计字符串出现的次数检查字符串开头检查字符串结

拼接字符串需要使用‘+’运算符可完成对多个字符串的拼接。如
str = "a"+"b"
字符串不允许直接与其他类型的数据拼接,需要将其他类型转换为字符串才可以进行拼接。
使用运算符 * 重复输出字符串
str = "hello world"*2
print(str)# hello worldhello world
不同的字符所占字节数不同,在python中数字、英文、小数点、下划线和空格占一个字节,一个汉字可能会占2~4个字节,取决于采用的编码。汉字在GBK/GB2312编码中占2个字节,在UTF-8/Unicode编码中一般占用3个字节(或4个字节)。Python中默认的编码格式是UTF-8,即一个汉字占3个字节。python中,提供了内置函数len()计算字符串的长度,默认情况下通过len()函数计算字符串的长度时,不区分英文、数字和汉字,所有字符都按照一个字符来计算
str = "hello world"
len = len(str)
print(len)# 11
通过索引 [] 获取字符串中指定位置的字符
str = "hello world"
print(str[0])# h
print(str[1])# e
在 Python 中,使用语法 string[start:end],获取字符串 string 中在 [start, end) 范围的子字符串。注意范围 [start, end) 包含 start,不包含 end。举例如下:
str = "hello world"
print(str[0:3])# hel
print(str[:5]) # hello
print(str[-3:]) # rld
print(str[3:])# lo world
print(str[:])# hello world
通过关键字 in 检查字符串中是否包含指定字符串
pd = "hello" in "hello world" # hello world 是否包含 hello
print(pd) # True
pd = "hello" not in "hello world" # hello world 是否不包含 hello
print(pd) # False
capitalize() 方法把字符串的第一个字符大写,示例如下:
text = 'abc'
text = text.capitalize()
print(text) # Abc
count() 方法用于检索指定字符串中在另一个字符串中出现的次数,如果检索的字符串不存在,则返回0,否则返回出现的次数。
text = 'abc abc'
count = text.count('abc') # 2
print(count)
startswith() 方法用于检索字符串是否以指定的子字符串开头,如果是则返回True,否则返回False。
text = 'abc'
pd = text.startswith('ab')
print(pd)
endswith() 方法用于检索字符串是否以指定的子字符串结尾,如果是则返回True,否则返回False
text = 'abc'
pd = text.endswith('bc')
print(pd)
lower() 方法用于将字符串中的大写字母转换为小写字符,如果字符串中没有需要转换的字符,则将原字符串返回。
text = 'ABC'
lower = text.lower()
print(lower) # abc
upper() 方法用于将字符串中的大写字母转换为小写字符,如果字符串中没有需要转换的字符,则将原字符串返回。
str1 = "asdfg"
print(str1.upper())
swapcase() 方法用于对字符串的大小写字母进行转换,即将大写字母转换为小写字母,小写字母会转换为大写字母。
str1 = 'avvvv'
print(str1.swapcase())
istitle() 方法检测字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母是否为大写,且其他字母为小写。如果字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母是否为大写,且其他字母为小写则返回 True,否则返回 False.
str = "This is string example....wow!!!";
print str.istitle();
title() 方法返回"标题化"的字符串,就是说所有单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均为小写
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
print(str.title())# This Is String Example....Wow!!!
text = ' abcdaaa '
print(text.strip()) # 删除开始和结尾的空格
print(text.lstrip()) # 删除左边的空格
print(text.rstrip()) # 删除右边的空格
合并字符串与拼接字符串不同,它可以将多个字符串采用固定的分隔符连接在一起。合并字符串可以使用字符串对象的join() 方法实现
text = 'abc'
print(text.join("def")) 分割字符串是把字符串分割为列表,通过split() 函数可以实现字符串分割,也就是把一个字符串按照指定的分隔符切分为列表。
text = 'hello,a,v,c'
print(text.split(',')) # ['hello', 'a', 'v', 'c']
splitlines() 按照行(‘\r’, ‘\r\n’, \n’)分隔,返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表,如果参数 keepends 为 False,不包含换行符,如果为 True,则保留换行符。
str1 = 'ab c\n1111\nde fg\rkl\r\n'
print(str1.splitlines()) # ['ab c', '1111', 'de fg', 'kl']
isnumeric() 方法检测字符串是否只由数字组成。如果字符串中只包含数字字符,则返回 True,否则返回 False
str = "2009"
print( str.isnumeric()) # True
isspace() 方法检测字符串是否只由空格组成。 如果字符串中只包含空格,则返回 True,否则返回 False.
str = " ";
print str.isspace();
zfill() 方法返回指定长度的字符串,不够的长度的原字符串前面填充0。
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
print(str.zfill(40)) # 00000000this is string example....wow!!!
ljust() 方法和zfill一样,默认填充空白,我们可以指定填充的内容,填充的方向是右侧
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
print(str.ljust(40,'0')) # this is string example....wow!!!00000000
find() 方法用于检索是否包含指定的子字符串,如果检索的字符串不存在责返回-1,否则返回首次出现该子字符串时的索引
text = 'abcdef'
print(text.find("cd")) # 2
python还提供了rfind() 方法,其作用和find() 方法类似,只是从字符串右边开始检索。
python还提供了index() 方法同find() 方法类似,也是用于检索是否包含指定的子字符串。只不过是用index() 方法时,当指定的字符串不存在时则会抛出异常
python还提供了rindex() 方法其作用同index() 方法类似,只是从字符串右边开始检索。
replace() 方法把字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串),如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
参数
old – 将被替换的子字符串。
new – 新字符串,用于替换old子字符串。
max – 可选字符串, 替换不超过 max 次 (默认最大)
str = "this is string example....wow!!! this is really string"
print(str.replace("is", "was"))
格式化字符串是指先制定一个模板,在这个模板中预留几个空位,然后在根据需要填上相对应的内容。这些空位需要通过指定的符号标记(也称为占位符),而这些符号还不会显示出来。
python中提供了如下两种方法格式化字符串:
使用’%’ 操作符
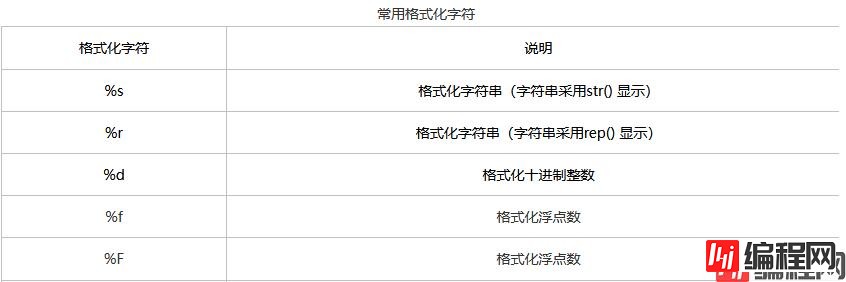
text = 'hello %s' % 'java'
print(text) # hello java
text = 'hello %s %s' % ('java', 'python')
print(text) # hello python world
使用字符串对象的fORMat() 方法
在创建模板时需要使用’{}‘和’:’ ,指定占位符,例如:

Python 3.x 默认采用 UTF-8 编码格式,有效地解决了中文乱码的问题。但是有些时候数据是第三方获取的,那么我们就不能保证编码就是UTF-8的所以我们就需要进行编码转换了
编码
encode() 方法用于将 str 类型转换成 bytes 类型,这个过程也称为“编码”。str.encode([encoding="utf-8"][,errors="strict"])
注意:格式中用 [] 括起来的参数为可选参数,也就是说,在使用此方法时,可以使用 [] 中的参数,也可以不使用。该方法各个参数的含义如表 所示。

注意:使用 encode() 方法对原字符串进行编码,不会直接修改原字符串,如果想修改原字符串,需要重新赋值。
str = "中文网"
encode = str.encode('utf-8') # 返回的类型为bytes
print(encode) # b'\xe4\xb8\xad\xe6\x96\x87\xe7\xbd\x91'
解码
和 encode() 方法正好相反,decode() 方法用于将 bytes 类型的二进制数据转换为 str 类型,这个过程也称为“解码”。bytes.decode([encoding="utf-8"][,errors="strict"])该方法中各参数的含义如表所示。

str = "中文网"
encode = str.encode('utf-8')
decode = encode.decode('utf-8')
print(decode) # 中文网--结束END--
本文标题: Python入门之字符串操作详解
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/120290.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0