Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
目录前言1.准备2.编写代码3.批量自动识别4.完整代码前言 最近在整理我磁盘上的照片,发现不少猫照,突然觉得若能把这些猫照都挑出来,观察它们的成长轨迹也是一件不错的事情。一张一张
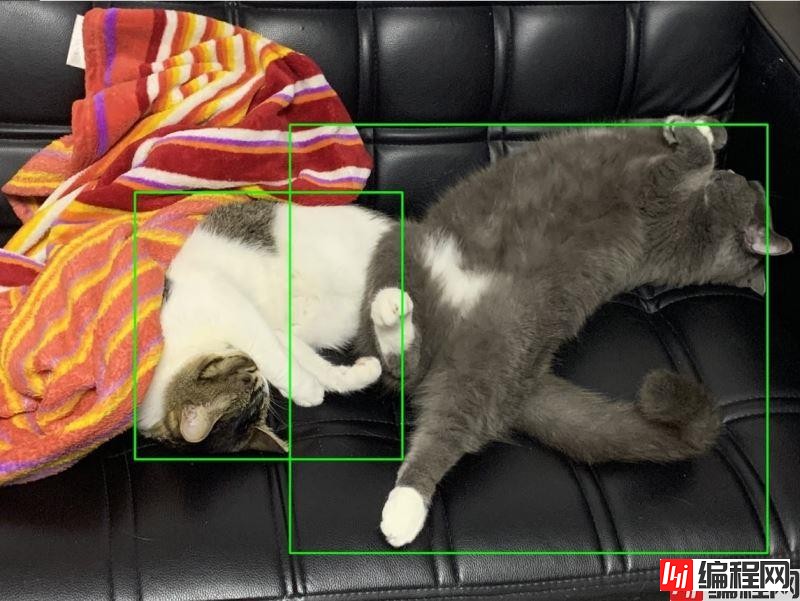
最近在整理我磁盘上的照片,发现不少猫照,突然觉得若能把这些猫照都挑出来,观察它们的成长轨迹也是一件不错的事情。一张一张的找实在是太费劲了,能不能自动化地找出来呢?
目标检测,是许多计算机视觉应用的重中之重,比如说我们上次的实例分割:python 20行代码批量自动抠图,人体关键点提取、人脸识别等。而我们这一次,是要识别猫照。由于时间不多,我们没有时间收集训练集,那么有没有已经训练好的目标检测模型呢?
这时候就要搬出paddlehub了,puddlehub有一个模型叫做YOLOv3,基于 Joseph Redmon和Ali Farhadi提出的单阶段检测器。该检测器与达到同样精度的传统目标检测方法相比,推断速度能达到接近两倍。
YOLOv3将输入图像分成S*S个格子,每个格子预测B个bounding box,每个bounding box预测内容包括: Location(x, y, w, h)、Confidence Score和C个类别的概率,因此我们不仅能够找出猫的照片,还能定位它的位置!甚至能自动数出一张照片里有多少只猫!
开始之前,你要确保Python和pip已经成功安装在电脑上,如果没有,可以访问这篇文章:超详细Python安装指南 进行安装。
(可选1) 如果你用Python的目的是数据分析,可以直接安装Anaconda,它内置了Python和pip.
(可选2) 此外,推荐大家用vscode编辑器,它有许多的优点
为了实现识别猫的功能,我们需要安装 paddlepaddle, 进入他们的官方网站就有详细的指引
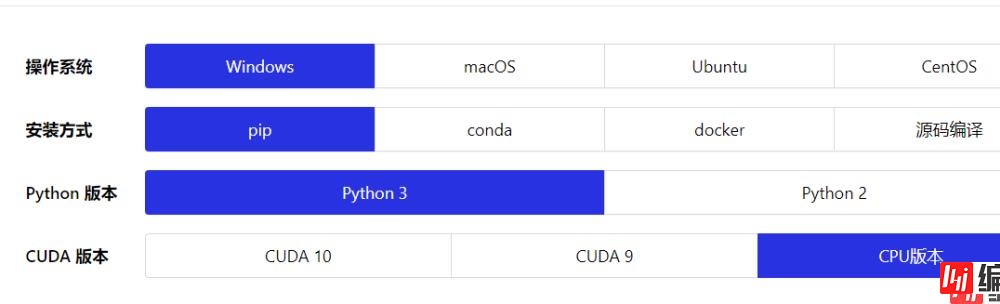
根据你自己的情况选择这些选项,最后一个CUDA版本,由于本实验不需要训练数据,也不需要太大的计算量,所以直接选择CPU版本即可。选择完毕,下方会出现安装指引,不得不说,Paddlepaddle 这些方面做的还是比较贴心的。
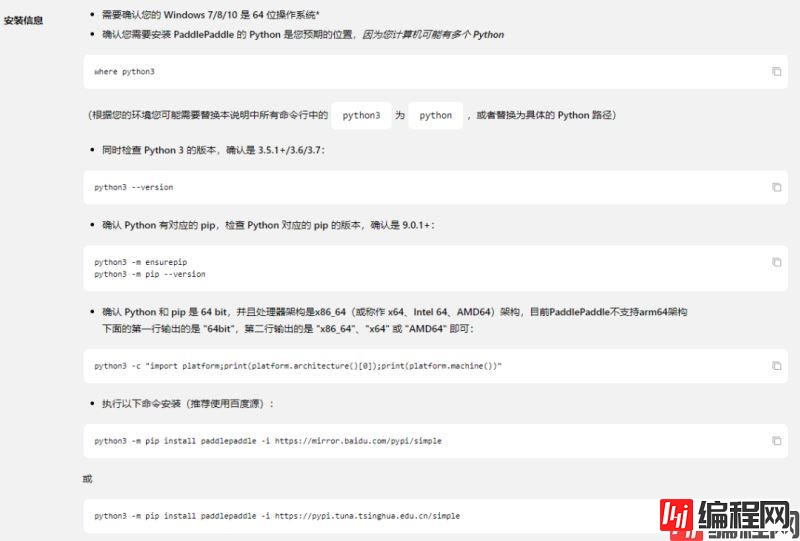
要注意,如果你的python3环境变量里的程序名称是Python,记得将python3 xxx 语句改为Python xxx 如下进行安装:
python -m pip install paddlepaddle -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
你还需要安装paddlehub:
pip install -i Https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple paddlehub
我们先试试单图片识别,找到猫猫:
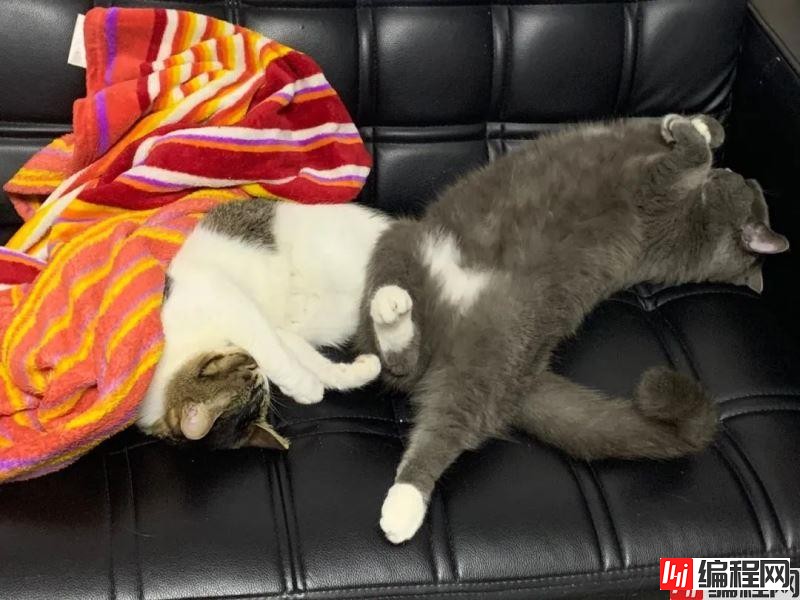

新建predict.py文件,存放猫照在当前文件夹的imgs文件夹下,命名为c1.jpg. 输入以下代码:
import paddlehub as hub
# 加载模型
yolov3 = hub.Module(name="yolov3_darknet53_coco2017")
# 图片位置
test_img_path = "imgs/c1.jpg"
# 输入图片
input_dict = {"image": [test_img_path]}
# 输出结果
results = yolov3.object_detection(data=input_dict)
for result in results:
print(result['path'])
print(result['data'])在终端/CMD输入以下命令运行文件:
python predict.py
# [{'left': 684.79376, 'right': 2024.4724, 'top': 961.53644, 'bottom': 2299.855, 'label': 'cat', 'confidence': 0.94765514}, {'left': 1461.0829, 'right': 3853.3633, 'top': 621.53064, 'bottom': 2769.5376, 'label': 'cat', 'confidence': 0.8093604}]可以看到,识别到了两只猫,其中第一只猫顶部位置为961,右部位置为2024,左部位置为684,底部位置为2299。根据这个位置,编写代码,用于框出相应位置的猫:
def paint_rect(input_img: str, output_path: str,
labels: list, position: list):
"""
画出矩形
:param input_img: 输入图片
:param output_path: 输出图片
:param labels: 标签
:param positions: 坐标
公众号:Python实用宝典
"""
img = cv2.imread(input_img)
for position in positions:
print(position)
# 画矩形框, 输入参数分别为图像、左上角坐标、右下角坐标、颜色数组、粗细
cv2.rectangle(
img, (position['left'], position['top']),
(position['right'], position['bottom']),
(0, 255, 0), thickness=10
)
if 'cat' in labels:
# 若是猫,则存到另一个地方
shutil.move(input_img, output_path + os.sep + input_img.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(output_path + os.sep + 'rect_%s' % input_img.split('/')[-1], img)效果如下:
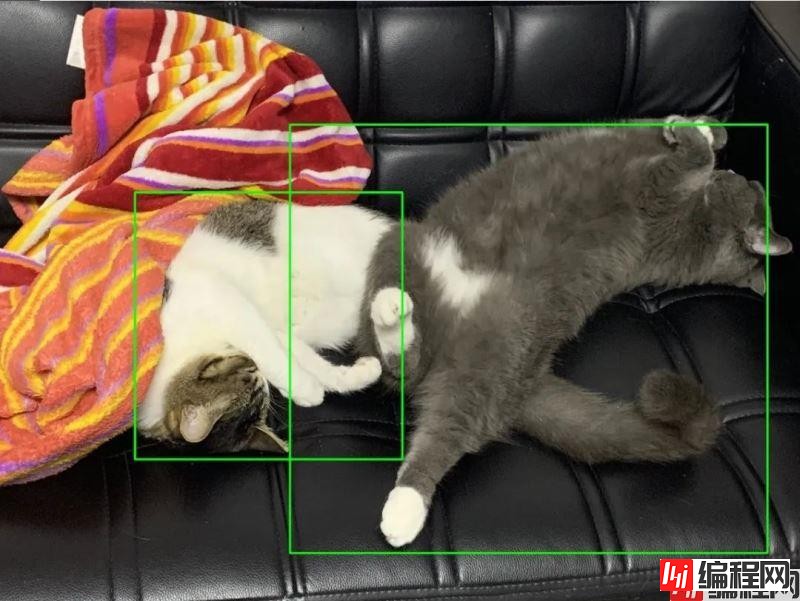
这样,我们就有思路进行自动识别了,首先获得该文件夹下所有的图片,其次,将这些图片都放入分类器中进行分类,最后,再根据分类的标签将其提取出来移动到其他地方。
获得该文件夹下所有图片:
def get_all_path(dirpath, *suffix):
"""
获得所有路径
@param dirpath: 目录
@param *suffix: 后缀
公众号:Python实用宝典
"""
path_array = []
for r, ds, fs in os.walk(dirpath):
for fn in fs:
if os.path.splitext(fn)[1] in suffix:
fname = os.path.join(r, fn)
path_array.append(fname)
return path_array
# 获得所有jpg和png图片
image_paths = get_all_path(source_path, '.jpg', '.JPG', 'png', 'PNG')放入分类器中分类:
# 加载模型
yolov3 = hub.Module(name="yolov3_darknet53_coco2017")
# 输入图片
input_dict = {"image": image_paths}
# 输出结果
results = yolov3.object_detection(data=input_dict, labels=['cat'])根据标签画框并移动:
def paint_rect(input_img: str, output_path: str,
labels: list, position: list):
"""
画出矩形
:param input_img: 输入图片
:param output_path: 输出图片
:param labels: 标签
:param positions: 坐标
公众号:Python实用宝典
"""
img = cv2.imread(input_img)
for position in positions:
# 画矩形框, 输入参数分别为图像、左上角坐标、右下角坐标、颜色数组、粗细
cv2.rectangle(
img, (position['left'], position['top']),
(position['right'], position['bottom']),
(0, 255, 0), thickness=10
)
if 'cat' in labels:
# 若是猫,则存到另一个地方
shutil.move(input_img, output_path + os.sep + input_img.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(output_path + os.sep + 'rect_%s' % input_img.split('/')[-1], img)
results = yolov3.object_detection(data=input_dict, labels=['cat'])
for result in results:
path = result['path']
labels = []
positions = []
for target in result['data']:
labels.append(target.get('label', ''))
positions.append({
'left': target.get('left', -1),
'top': target.get('top', -1),
'right': target.get('right', -1),
'bottom': target.get('bottom', -1)
})
paint_rect(path, target_path, labels, positions)import paddlehub as hub
import cv2
import os
import shutil
def get_all_path(dirpath, *suffix):
"""
获得所有路径
@param dirpath: 目录
@param *suffix: 后缀
"""
path_array = []
for r, ds, fs in os.walk(dirpath):
for fn in fs:
if os.path.splitext(fn)[1] in suffix:
fname = os.path.join(r, fn)
path_array.append(fname)
return path_array
def paint_rect(input_img: str, output_path: str,
labels: list, position: list):
"""
画出矩形
:param input_img: 输入图片
:param output_path: 输出图片
:param labels: 标签
:param positions: 坐标
"""
img = cv2.imread(input_img)
for position in positions:
# 画矩形框, 输入参数分别为图像、左上角坐标、右下角坐标、颜色数组、粗细
cv2.rectangle(
img, (position['left'], position['top']),
(position['right'], position['bottom']),
(0, 255, 0), thickness=10
)
if 'cat' in labels:
# 若是猫,则存到另一个地方
shutil.move(input_img, output_path + os.sep + input_img.split('/')[-1])
cv2.imwrite(output_path + os.sep + 'rect_%s' % input_img.split('/')[-1], img)
if __name__ == '__main__':
source_path = './imgs/'
target_path = './target/'
# 获得所有jpg和png图片
image_paths = get_all_path(source_path, '.jpg', '.JPG', 'png', 'PNG')
# 加载模型
yolov3 = hub.Module(name="yolov3_darknet53_coco2017")
# 输入图片
input_dict = {"image": image_paths}
# 输出结果
results = yolov3.object_detection(data=input_dict, labels=['cat'])
for result in results:
path = result['path']
labels = []
positions = []
print(path)
for target in result['data']:
labels.append(target.get('label', ''))
positions.append({
'left': target.get('left', -1),
'top': target.get('top', -1),
'right': target.get('right', -1),
'bottom': target.get('bottom', -1)
})
paint_rect(path, target_path, labels, positions)到此这篇关于基于Python实现一键找出磁盘里所有猫照的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python找出磁盘猫照内容请搜索编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持编程网!
--结束END--
本文标题: 基于Python实现一键找出磁盘里所有猫照
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/117840.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0