Python 官方文档:入门教程 => 点击学习
PEP 3107引入了功能注释的语法,PEP 484 加入了类型检查 标准库 typing 为类型提示指定的运行时提供支持。 示例: def f(a: str, b:int) -> str: ret
PEP 3107引入了功能注释的语法,PEP 484 加入了类型检查
标准库 typing 为类型提示指定的运行时提供支持。
示例:
def f(a: str, b:int) -> str:
return a * b
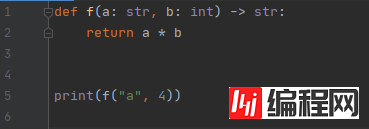
如果实参不是预期的类型:
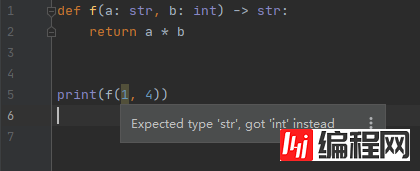
但是,python运行时不强制执行函数和变量类型注释。使用类型检查器,IDE,lint等才能帮助代码进行强制类型检查。
NewType() 是一个辅助函数,用于向类型检查器指示不同的类型,在运行时,它返回一个函数,该函数返回其参数。
import typing
Id = typing.NewType("Id", int)
a = Id(2020)
使用 NewType() 创建的类型会被类型检查器视为它的原始类型的子类。
将回调函数类型标注为 Callable[[Arg1Type, Arg2Type], ReturnType]。
from typing import Callable
def f(a: int) -> str:
return str(a)
def callback(a: int, func: Callable[[int], str]) -> str:
return func(a)
print(callback(1, f))
为容器元素添加预期的类型
from typing import Mapping
a: Mapping[str, str]
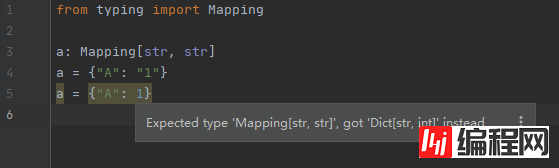
通过 TypeVar 进行参数化来约束一个类型集合:
from typing import TypeVar
T = TypeVar('T') # 可以是任何东西。
A = TypeVar('A', str, bytes) # 必须是 str 或 bytes
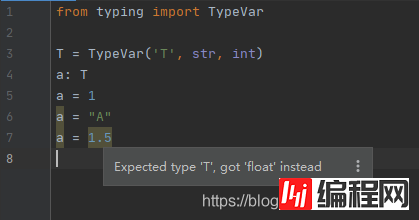
使用 TypeVar 约束一个类型集合,但不允许单个约束
例如:
T = TypeVar('T', str)
这样会抛出一个异常 TypeError: A single constraint is not allowed
AbstractSet = typing.AbstractSet
Any = typing.Any
AnyStr = ~AnyStr
AsyncContextManager = typing.AbstractAsyncContextManager
AsyncGenerator = typing.AsyncGenerator
AsyncIterable = typing.AsyncIterable
AsyncIterator = typing.AsyncIterator
Awaitable = typing.Awaitable
ByteString = typing.ByteString
Callable = typing.Callable
ClassVar = typing.ClassVar
Collection = typing.Collection
Container = typing.Container
ContextManager = typing.AbstractContextManager
Coroutine = typing.Coroutine
Counter = typing.Counter
DefaultDict = typing.DefaultDict
Deque = typing.Deque
Dict = typing.Dict
FrozenSet = typing.FrozenSet
Generator = typing.Generator
Hashable = typing.Hashable
ItemsView = typing.ItemsView
Iterable = typing.Iterable
Iterator = typing.Iterator
KeysView = typing.KeysView
List = typing.List
Mapping = typing.Mapping
MappingView = typing.MappingView
MutableMapping = typing.MutableMapping
MutableSequence = typing.MutableSequence
MutableSet = typing.MutableSet
NoReturn = typing.NoReturn
Optional = typing.Optional
Reversible = typing.Reversible
Sequence = typing.Sequence
Set = typing.Set
Sized = typing.Sized
TYPE_CHECKING = False
Tuple = typing.Tuple
Type = typing.Type
UNIOn = typing.Union
ValuesView = typing.ValuesView
动态语言的灵活性使其在做一些工具,脚本时非常方便,但是同时也给大型项目的开发带来了一些麻烦。
自python3.5开始,PEP484为python引入了类型注解(type hints),虽然在pep3107定义了函数注释(function annotation)的语法,但仍然故意留下了一些未定义的行为.现在已经拥有许多对于静态类型的分析的第三方工具,而pep484引入了一个模块来提供这些工具,同时还规定一些不能使用注释(annoation)的情况
#一个典型的函数注释例子,为参数加上了类型
def greeting(name: str) -> str:
return 'Hello ' + name伴随着python3.6的pep526则更进一步引入了对变量类型的声明,和在以前我们只能在注释中对变量的类型进行说明
# 使用注释来标明变量类型
primes = [] # type:list[int]
captain = ... #type:str
class Starship:
stats = {} #type:Dict[str,int]
primes:List[int] = []
captain:str #Note: no initial value
class Starship:
stats: ClassVar[Dict[str,int]] = {}
typing模块已经被加入标准库的provisional basis中,新的特性可能会增加,如果开发者认为有必要,api也可能会发生改变,即不保证向后兼容性
我们已经在简介中介绍过类型注解,那么除了默认类型的int、str用于类型注解的类型有哪些呢?
typing库便是一个帮助我们实现类型注解的库
类型别名(type alias)
在下面这个例子中,Vector和List[float]可以视为同义词
from typing import List
Vector = List[float]
def scale(Scalar: float, vector: Vector)->Vector:
return [scalar*num for num in vector]
new_vector = scale(2.0, [1.0, -4.2, 5.4])
类型别名有助于简化一些复杂的类型声明
from typing import Dict, Tuple, List
ConnectionOptions = Dict[str, str]
Address = Tuple[str, int]
Server = Tuple[Address, ConnectionOptions]
def broadcast_message(message: str, servers: List[Server]) -> None:
...
# The static type checker will treat the previous type signature as
# being exactly equivalent to this one.
def broadcast_message(
message: str,
servers: List[Tuple[Tuple[str, int], Dict[str, str]]]) -> None:
pass
新类型(New Type)
使用NewType来辅助函数创造不同的类型
fORM typing import NewType
UserId = NewType("UserId", int)
some_id = UserId(524313)
静态类型检查器将将新类型视为原始类型的子类。这对于帮助捕获逻辑错误非常有用
def get_user_name(user_id: UserId) -> str:
pass
# typechecks
user_a = get_user_name(UserId(42351))
# does not typecheck; an int is not a UserId
user_b = get_user_name(-1)
你仍然可以使用int类型变量的所有操作来使用UserId类型的变量,但结果返回的都是都是int类型。例如
# output仍然是int类型而不是UserId类型
output = UserId(23413) + UserId(54341)虽然这无法阻止你使用int类型代替UserId类型,但可以避免你滥用UserId类型
注意,这些检查仅仅被静态检查器强制检查,在运行时Derived = NewType('Derived',base)将派生出一个函数直接返回你传的任何参数,这意味着Derived(some_value)并不会创建任何新类或者创建任何消耗大于普通函数调用消耗的函数
确切地说,这个表达式 some_value is Derived(some_value) 在运行时总是对的。
这也意味着不可能创建派生的子类型,因为它在运行时是一个标识函数,而不是一个实际类型:
from typing import NewType
UserId = NewType('UserId', int)
# Fails at runtime and does not typecheck
class AdminUserId(UserId): pass
然而,它可以创建一个新的类型基于衍生的NewType
from typing import NewType
UserId = NewType('UserId', int)
ProUserId = NewType('ProUserId', UserId)
然后对于ProUserId的类型检查会如预料般工作
Note:回想一下,使用类型别名声明的两个类型是完全一样的,令Doing = Original将会使静态类型检查时把Alias等同于Original,这个结论能够帮助你简化复杂的类型声明
与Alias不同,NewType声明了另一个的子类,令Derived = NewType('Derived', Original)将会使静态类型检查把Derived看做Original的子类,这意味着类型Original不能用于类型Derived,这有助于使用最小的消耗来防止逻辑错误。
回调(callable)
回调函数可以使用类似Callable[[Arg1Type, Arg2Type],ReturnType]的类型注释
例如
from typing import Callable
def feeder(get_next_item: Callable[[], str]) -> None:
# Body
def async_query(on_success: Callable[[int], None],
on_error: Callable[[int, Exception], None]) -> None:
# Body
可以通过对类型提示中的参数列表替换一个文本省略号来声明一个可调用的返回类型,而不指定调用参数,例如 Callable[..., ReturnType]
泛型(Generics)
因为容器中的元素的类型信息由于泛型不同通过一般方式静态推断,因此抽象类被用来拓展表示容器中的元素
from typing import Mapping, Sequence
def notify_by_email(employees: Sequence[Employee],
overrides: Mapping[str, str]) -> None: ...
可以通过typing中的TypeVar将泛型参数化
from typing import Sequence, TypeVar
T = TypeVar('T') # 申明类型变量
def first(l: Sequence[T]) -> T: # Generic function
return l[0]
用户定义泛型类型
from typing import TypeVar, Generic
from logging import Logger
T = TypeVar('T')
class LoggedVar(Generic[T]):
def __init__(self, value: T, name: str, logger: Logger) -> None:
self.name = name
self.logger = logger
self.value = value
def set(self, new: T) -> None:
self.log('Set ' + repr(self.value))
self.value = new
def get(self) -> T:
self.log('Get ' + repr(self.value))
return self.value
def log(self, message: str) -> None:
self.logger.info('%s: %s', self.name, message)
定义了Generic[T]作为LoggedVar的基类,同时T也作为了方法中的参数。
通过Generic基类使用元类(metaclass)定义__getitem__()使得LoggedVar[t]是有效类型
from typing import Iterable
def zero_all_vars(vars: Iterable[LoggedVar[int]]) -> None:
for var in vars:
var.set(0)
泛型可以是任意类型的变量,但也可以被约束
from typing import TypeVar, Generic
...
T = TypeVar('T')
S = TypeVar('S', int, str)
class StrangePair(Generic[T, S]):
...
每个类型变量的参数必须是不同的
下面是非法的
from typing import TypeVar, Generic
...
T = TypeVar('T')
class Pair(Generic[T, T]): # INVALID
...
你可以使用Generic实现多继承
from typing import TypeVar, Generic, Sized
T = TypeVar('T')
class LinkedList(Sized, Generic[T]):
...
当继承泛型类时,一些类型变量可以被固定
from typing import TypeVar, Mapping
T = TypeVar('T')
class MyDict(Mapping[str, T]):
...
使用泛型类而不指定类型参数则假定每个位置都是Any,。在下面的例子中,myiterable不是泛型但隐式继承Iterable [Any]
from typing import Iterable
class MyIterable(Iterable): # Same as Iterable[Any]
还支持用户定义的泛型类型别名。实例:
from typing import TypeVar, Iterable, Tuple, Union
S = TypeVar('S')
Response = Union[Iterable[S], int]
# Return type here is same as Union[Iterable[str], int]
def response(query: str) -> Response[str]:
...
T = TypeVar('T', int, float, complex)
Vec = Iterable[Tuple[T, T]]
def inproduct(v: Vec[T]) -> T: # Same as Iterable[Tuple[T, T]]
return sum(x*y for x, y in v)
Generic的元类是abc.ABCMeta的子类,泛型类可以是包含抽象方法或属性的ABC类(A generic class can be an ABC by including abstract methods or properties)
同时泛型类也可以含有ABC类的方法而没有元类冲突。
Any
一种特殊的类型是。静态类型检查器将将每个类型视为与任何类型和任何类型兼容,与每个类型兼容。
from typing import Any
a = None # type: Any
a = [] # OK
a = 2 # OK
s = '' # type: str
s = a # OK
def foo(item: Any) -> int:
# Typechecks; 'item' could be any type,
# and that type might have a 'bar' method
item.bar()
...
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持编程网。
--结束END--
本文标题: Python标准库之typing的用法(类型标注)
本文链接: https://lsjlt.com/news/10825.html(转载时请注明来源链接)
有问题或投稿请发送至: 邮箱/279061341@qq.com QQ/279061341
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-03-01
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
2024-02-29
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
回答
0